|
Moaning Cavern
Moaning Caverns is a solutional cave located in the Calaveras County, California, near Vallecito, California in the heart of the state's Gold Country. It is developed in marble of the Calaveras Formation. It was discovered in modern times by gold miners in 1851, but it has long been known as an interesting geological feature by prehistoric peoples. It gets its name from the moaning sound that echoed out of the cave luring people to the entrance, however expansion of the opening to allow access for the public disrupted the sounds. The portion of the cave developed for tourists consists of a spacious vertical shaft 165 feet tall, which is descended by a combination of stairs and a unique spiral staircase built in the early 1900s. It is open to the public for walking tours and spelunking. Including the off-trail areas, the cave reaches a depth of 410 feet (124 m). Human remains Moaning Caverns is also an archaeological site. According to archaeologist Phil C. Orr, these human d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moaning Cave
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relating to nonphonemic properties only. Paralanguage may be expressed consciously or unconsciously. The study of paralanguage is known as paralinguistics and was invented by George L. Trager in the 1950s, while he was working at the Foreign Service Institute of the U.S. Department of State. His colleagues at the time included Henry Lee Smith, Charles F. Hockett (working with him on using descriptive linguistics as a model for paralanguage), Edward T. Hall developing proxemics, and Ray Birdwhistell developing kinesics. Trager published his conclusions in 1958, 1960 and 1961. His work has served as a basis for all later research, especially those investigating the relationship between paralanguage and culture (since paralanguage is learned, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington Springs Man
The Arlington Springs man is a set of Late Pleistocene human remains discovered in 1959 on Santa Rosa Island, one of the Channel Islands located off the coast of Southern California. The Arlington Springs archeological site is protected within northern Channel Islands National Park, and in Santa Barbara County. History Archaeology In 1959–1960, two femora were excavated by Phil C. Orr, curator of anthropology and paleontology at the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History, at Arlington Springs on Santa Rosa Island. Orr believed the remains were those of a 10,000-year-old man and dubbed them the "Arlington Springs Man". The Arlington Springs Man was later re-examined in 1989 by Orr's successors at the museum, Dr. John R. Johnson and Don Morris. The two came to the initial assessment that the Arlington Springs Man was actually the "Arlington Springs Woman". Radiocarbon dating determined that the remains dated to 13,000 years BP, making the remains potentially the oldest-kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Show Caves In The United States
Show or The Show may refer to: Competition, event, or artistic production * Agricultural show, associated with agriculture and animal husbandry * Animal show, a judged event in the hobby of animal fancy ** Cat show ** Dog show ** Horse show ** Specialty show, a dog show which reviews a single breed *Show, an artistic production, such as: ** Concert ** Radio show ** Talk show ** Television show ** Theatre production * Trade fair or trade show Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''The Show'' (1922 film), starring Oliver Hardy * ''The Show'' (1927 film), directed by Tod Browning * ''The Show'' (1995 film), a hip hop documentary * ''The Show'' (2017 film), an American satirical drama * ''The Show'' (2020 film), a British mystery film Album * ''Show'' (The Cure album), 1993 * ''Show'' (The Jesus Lizard album), 1994 * ''The Show'' (album), a 2008 album by eMC Songs * "The Show" (Doug E. Fresh song) * "The Show" (Girls Aloud song) * "The Show" (Lenka song) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone Caves
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Calaveras County, California
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of California
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as '' speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statue Of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty (''Liberty Enlightening the World''; French: ''La Liberté éclairant le monde'') is a colossal neoclassical sculpture on Liberty Island in New York Harbor in New York City, in the United States. The copper statue, a gift from the people of France, was designed by French sculptor Frédéric Auguste Bartholdi and its metal framework was built by Gustave Eiffel. The statue was dedicated on October 28, 1886. The statue is a figure of Libertas, a robed Roman liberty goddess. She holds a torch above her head with her right hand, and in her left hand carries a '' tabula ansata'' inscribed JULY IV MDCCLXXVI (July 4, 1776 in Roman numerals), the date of the U.S. Declaration of Independence. A broken shackle and chain lie at her feet as she walks forward, commemorating the recent national abolition of slavery. After its dedication, the statue became an icon of freedom and of the United States, seen as a symbol of welcome to immigrants arriving by sea. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
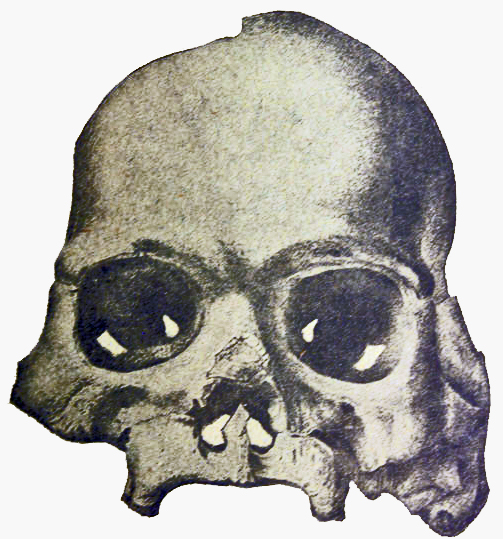
Calaveras Skull
The Calaveras Skull (also known as The Pliocene Skull) was a human skull found by miners in Calaveras County, California, which was purported to prove that humans were in North America as early as the Pliocene, and used to support the idea the humans, mastodons, and mammoths had coexisted. It was later revealed to be a hoax, although it is now known that humans, mastodons, and mammoths had indeed coexisted, but much more recently (the Pleistocene). Coincidentally, is the Spanish word for "skulls". History On February 25, 1866, miners claimed to have found a human skull in a mine, beneath a layer of lava, below the surface of the earth. The skull made it into the hands of Josiah Whitney, then the State Geologist of California as well as a Professor of Geology at Harvard University. A year before the skull came to his attention, Whitney published the belief that humans, mastodons, and mammoths coexisted; the skull served as proof of his convictions. After careful study, he offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
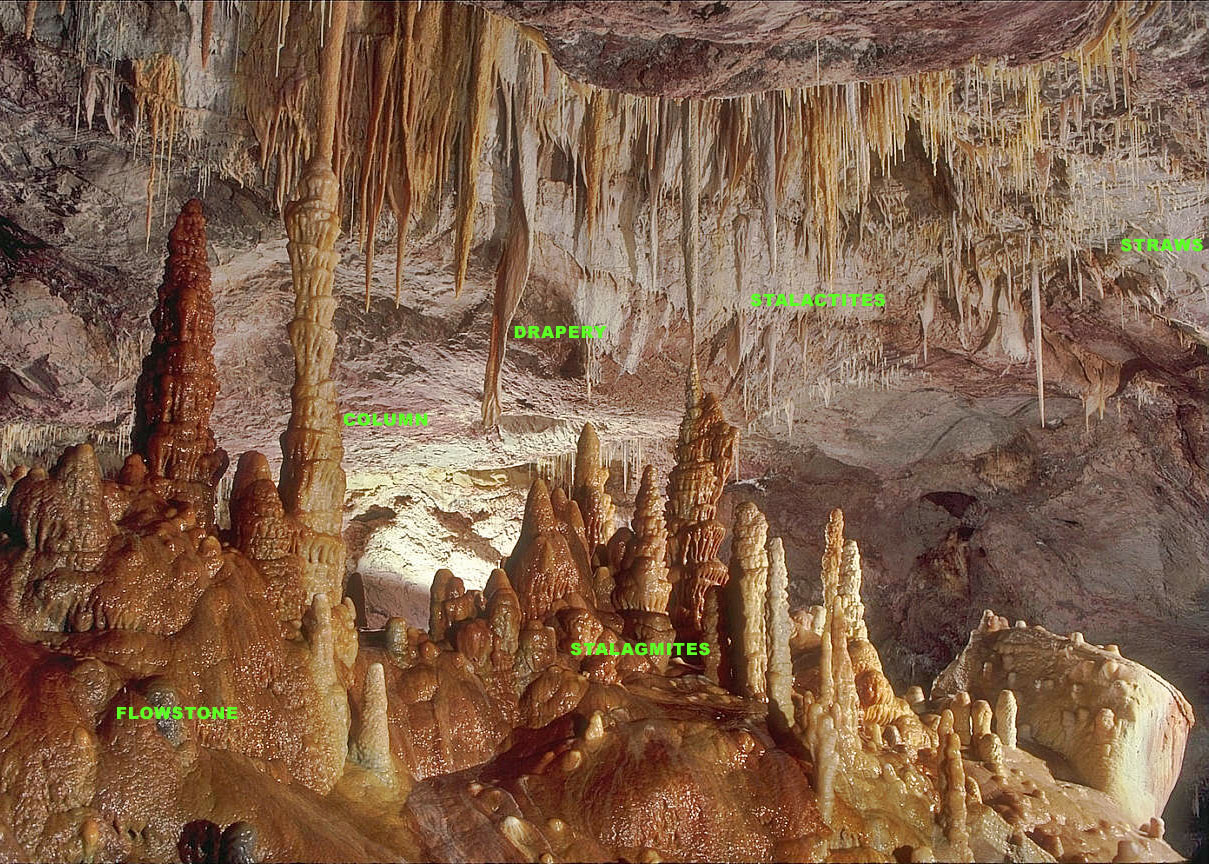
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals ( calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solutional Cave
A solutional cave, solution cave, or karst cave is a cave usually formed in the soluble rock limestone. It is the most frequently occurring type of cave. It can also form in other rocks, including chalk, dolomite, marble, salt beds, and gypsum. Process Bedrock is dissolved by natural acid in groundwater that seeps through bedding-planes, faults, joints and so on. Over geological epochs these openings expand as the walls are dissolved to become caves or cave systems. The portions of a solutional cave that are below the water table or the local level of the groundwater will be flooded. Limestone caves The largest and most abundant solutional caves are located in limestone. Limestone caves are often adorned with calcium carbonate formations produced through slow precipitation. These include flowstones, stalactites, stalagmites, helictites, soda straws, calcite rafts and columns. These secondary mineral deposits in caves are called ''speleothems''. Carbonic acid disso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caving
Caving – also known as spelunking in the United States and Canada and potholing in the United Kingdom and Ireland – is the recreational pastime of exploring wild cave systems (as distinguished from show caves). In contrast, speleology is the scientific study of caves and the cave environment.Caving in New Zealand (from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, Accessed 2012-11.) The challenges involved in caving vary according to the cave being visited; in addition to the total absence of light beyond the entrance, negotiating pitches, squeezes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calaveras Formation
''Calavera'' (Spanish for ''skull'') or its plural ''calaveras'', may refer to: Culture * Calaveras, any of various skull-shaped things associated with the * Literary Calavera, traditional Mexican composition in verse Places * Calaveras River, in the Central Valley of California, USA * Calaveras Creek (California), USA * Calaveras County, California, USA * Rancho Calaveras, California, USA * Calaveras Dome, California, USA; a granite dome * Cerro de la Calavera ( en, Mount Calavera), Carlsbad, California, USA * Calaveras Unified School District, Calaveras County, California, USA * Calaveras Fault, a geological fault in the San Francisco Bay Area, California, USA * Calaveras Valley, California, USA * La Calavera Historical Neighborhood, Smeltertown, Texas, USA * Calaveras, Texas, USA; a small town near San Antonio * Calaveras Creek, Texas, USA * Calaveras Lake (Texas), USA * Isla Calavera, an island in the Gulf of California Facilities and structures * Calaveras Power Statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)