|
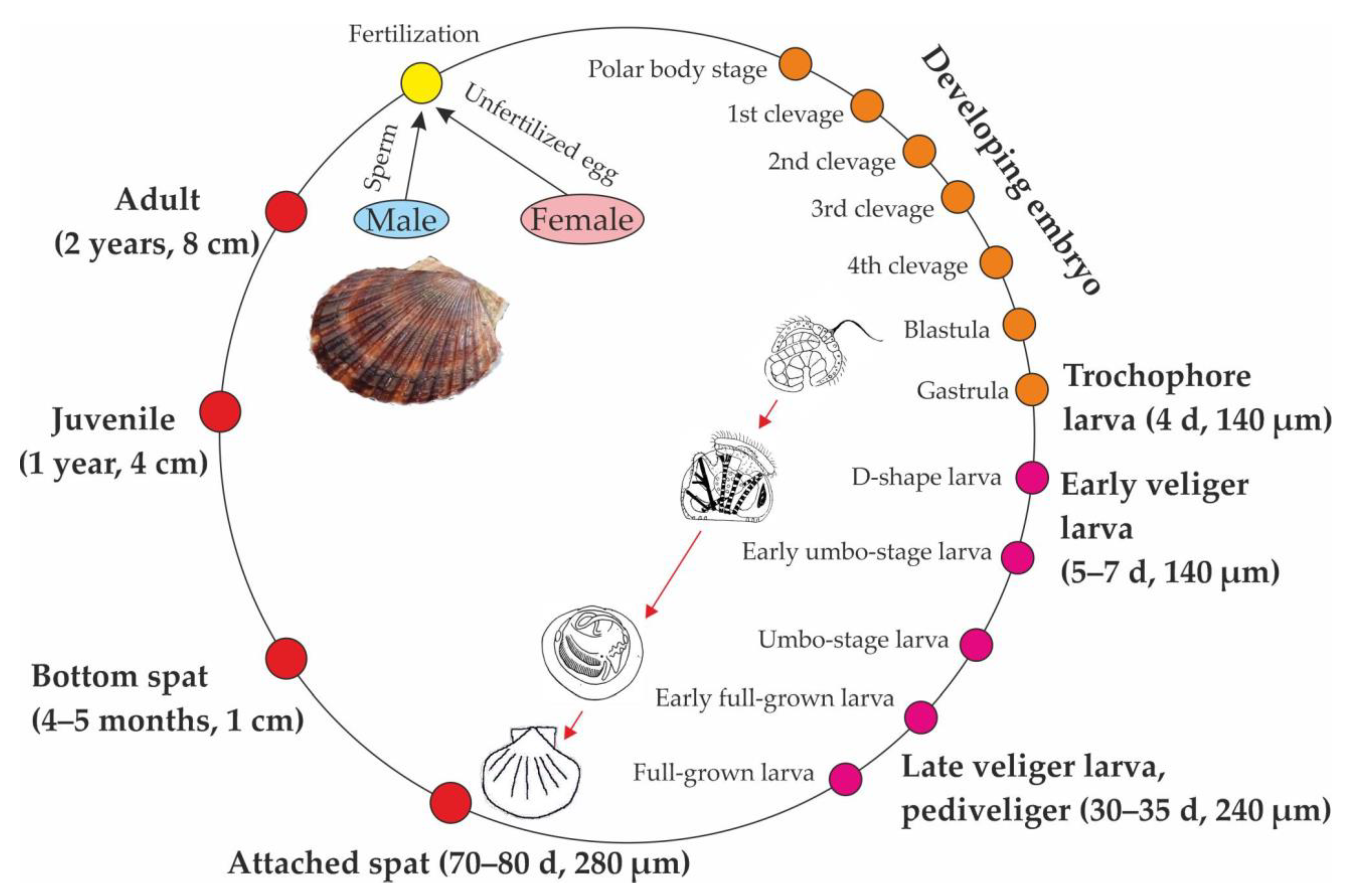
Mizuhopecten Yessoensis
''Mizuhopecten yessoensis'' (Yesso scallop, giant Ezo scallop) is a species of Marine (ocean), marine bivalve mollusc, mollusks in the family (biology), family Pectinidae, the scallops. Its name Yesso/Ezo refers to its being found north of Japan. Its tissues bioaccumulate algal yessotoxins and are studied extensively. Description The Yesso scallop (''Mizuhopecten yessoensis'') is a cold water marine Bivalvia, bivalve species. The valves have a convex center with a smooth exterior shell. On one side it is white and on the other dark brown. Habitat The Yesso scallop is widely distributed along the cold coast of Northern Japan. Scallop cultivation is located in the northern islands of Honshu and Hokkaido, with the Sea of Okhotsk, Saroma Lake and Funka Bay in Hokkaido accounting for more than 80% of the scallop production during the period of 1991 to 2002. Ecology and behavior Temperature plays a key role in the timing of spawning and larvae settlement of the Yesso scallo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yesso Scallop Total Production Thousand Tonnes 1950-2022
is the Japanese term historically used to refer to the people and the lands to the northeast of the Japanese island of Honshu. This included the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido, which changed its name from "Ezo" to "Hokkaidō" in 1869, Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Ezo"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 184. and sometimes included Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands. The word ''Ezo'' means 'the shrimp barbarians' in Japanese. In reference to the people of that region, the same two kanji used to write the word ''Ezo'' can also be read ''Emishi''. The descendants of these people are most likely related to the Ainu people of today. Etymology Japanese sources that include an etymology describe ''Ezo'' as probably originally a borrowing from the Ainu word meaning . The term is first attested in Japanese in a text from 1153 in reference to any of the non-Japanese people living in the northeast of Honshū, and then later in 1485 in reference to the northern islands where these peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south along with the Riau Islands in Indonesia, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor along with the State of Johor in Malaysia to the north. In its early history, Singapore was a maritime emporium known as '' Temasek''; subsequently, it was part of a major constituent part of several successive thalassocratic empires. Its contemporary era began in 1819, when Stamford Raffles established Singapore as an entrepôt trading post of the British Empire. In 1867, Singapore came under the direct control of Britain as part of the Straits Settlements. During World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutsu Bay
is a bay located within Aomori Prefecture, in the northern Tōhoku region of northern Japan. It has an east-west distance of approximately and a north-south distance of approximately at its eastern end, with a total area of approximately . Names ''Mutsu Bay'' is the dominant English term used in English for the body of water; however, it has historically been referred to as the ''Gulf of Mutsu''. The Japanese name for the body of water is . Geography Mutsu Bay is bordered by the Tsugaru Peninsula to the west and the Shimokita Peninsula to the east and north. It has an east-west distance of approximately and a north-south distance of approximately at its eastern end, with a total area of approximately . The outlet of the bay is the wide Tairadate Strait which connects Mutsu Bay to the Tsugaru Strait separating the islands of Honshu and Hokkaido. The bay has an average depth of , with a maximum depth of near its outlet to the Tsugaru Strait. Mutsu Bay includes Aomori Bay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conpoy
Conpoy or dried scallop is a type of Cantonese dried seafood product that is made from the adductor muscle of scallops. The smell of conpoy is marine, pungent, and reminiscent of certain salt-cured meats. Its taste is rich in umami due to its high content of various free amino acids, such as glycine, alanine, and glutamic acid. It is also rich in nucleic acids such as inosinic acid, amino acid byproducts such as taurine, and minerals, such as calcium and zinc. Conpoy is produced by cooking raw scallops and then drying them. Terminology ''Conpoy'' is a loanword from the Cantonese pronunciation of 乾貝 (), which literally means "dried shell(fish)". Usage In Hong Kong, conpoy from two types of scallops are common. Conpoy made from '' Atrina pectinata'' or ' ( 江珧) from mainland China is small and milder in taste. '' Mizuhopecten yessoensis'' or ' ( 扇貝), a sea scallop imported from Japan (''hotategai'', 帆立貝 in Japanese), produces a conpoy that is stronger and ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sushi
is a traditional Japanese dish made with , typically seasoned with sugar and salt, and combined with a variety of , such as seafood, vegetables, or meat: raw seafood is the most common, although some may be cooked. While sushi comes in numerous styles and presentation, the current defining component is the vinegared rice, also known as , or . The modern form of sushi is believed to have been created by Hanaya Yohei, who invented nigiri-zushi, the most commonly recognized type today, in which seafood is placed on hand-pressed vinegared rice. This innovation occurred around 1824 in the Edo period (1603–1867). It was the fast food of the ''chōnin'' class in the Edo period. Sushi is traditionally made with medium-grain white rice, although it can also be prepared with brown rice or short-grain rice. It is commonly prepared with seafood, such as Squid as food, squid, Eel as food, eel, Japanese amberjack, yellowtail, Salmon as food, salmon, Tuna as food, tuna or Crab stick, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sashimi
is a Japanese cuisine, Japanese delicacy consisting of fresh raw fish or Raw meat, meat sliced into thin pieces and often eaten with soy sauce. Origin The word ''sashimi'' means 'pierced body', i.e., "wikt:刺身, 刺身" = ''sashimi'', where wikt:刺, 刺 wikt:し, し = ''sashi'' (pierced, stuck) and wikt:身, 身 = ''mi'' (body, meat). This word dates from the Muromachi period (1336-1573) and there are multiple theories as to its etymology: The term was possibly coined when the word "wikt:切る, 切る" = ''kiru'' (cut), the culinary step, was considered too inauspicious to be used by anyone other than a samurai. This word may derive from the culinary practice of sticking the fish's tail and fin to the slices for the purpose of identifying the fish being eaten. Another possibility for the name is the traditional method of harvesting. "''Sashimi''-grade" fish is caught by individual handline. As soon as the fish is landed, its brain is pierced with a sharp spike, and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Muscles (bivalve)
The adductor muscles are the main muscular system in bivalve mollusks (e.g. in clams, scallops, mussels, oysters, etc.). In many parts of the world, when people eat scallops, the adductor muscles are the only part of the animal which is eaten. Adductor muscles leave noticeable scars or marks on the interior of the shell's valves. Those marks (known as adductor muscle scars) are often used by scientists who are in the process of identifying empty shells to determine their correct taxonomic placement. Bivalve mollusks generally have either one or two adductor muscles. The muscles are strong enough to close the valves of the shell when they contract, and they are what enable the animal to close its valves tightly when necessary, such as when the bivalve is exposed to the air by low water levels, or when it is attacked by a predator. Most bivalve species have two adductor muscles, which are located on the anterior and posterior sides of the body. Some families of bivalves h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissolved Organic Carbon
Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) is the fraction of organic carbon Operational definition, operationally defined as that which can pass through a filter with a pore size typically between 0.22 and 0.7 micrometre, micrometers. The fraction remaining on the filter is called particulate organic carbon (POC). Dissolved organic matter (DOM) is a closely related term often used interchangeably with DOC. While DOC refers specifically to the mass of carbon in the dissolved organic material, DOM refers to the total mass of the dissolved organic matter. So DOM also includes the mass of other elements present in the organic material, such as nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen. DOC is a component of DOM and there is typically about twice as much DOM as DOC. Many statements that can be made about DOC apply equally to DOM, and ''vice versa''. DOC is abundant in Marine ecosystem, marine and Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater systems and is one of the greatest cycled reservoirs of organic matter on Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritus
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Remineralisation, remineralise) it. Such microorganisms may be decomposers, detritivores, or coprophages. In terrestrial ecosystems detritus is present as plant litter and other organic matter that is intermixed with soil, known as soil organic matter. The detritus of aquatic ecosystems is organic substances suspended in the water and accumulated in depositions on the floor of the body of water; when this floor is a seabed, such a deposition is called marine snow. Theory The remains of decaying plants or animals, or their tissue parts, and feces gradually lose their form due to physical processes and the action of decomposers, including grazers, bacteria, and fungi. Decomposition, the process by which organic matter is decomposed, occurs in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |