|
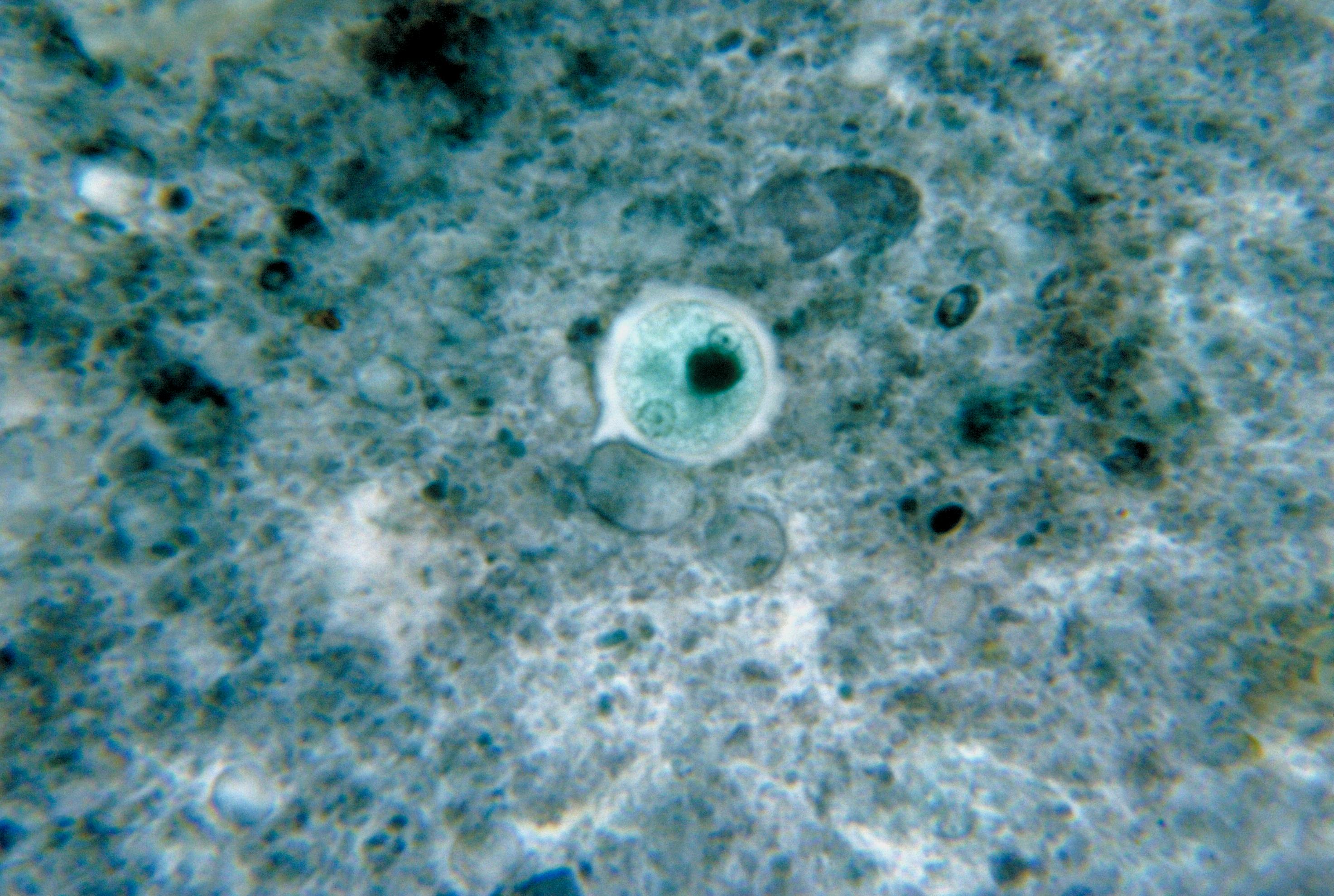
Mixotricha
''Mixotricha paradoxa'' is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species ''Mastotermes darwiniensis''. It is composed of five different organisms: three bacterial ectosymbionts live on its surface for locomotion and at least one endosymbiont lives inside to help digest cellulose in wood to produce acetate for its host(s). ''Mixotricha'' mitochondria degenerated in hydrogenosomes and mitosomes and lost the ability to produce energy aerobically by oxidative phosphorylation. The mitochondria-derived nuclear genes were however conserved. Discovery The name was given by the Australian biologist J.L. Sutherland, who first described ''Mixotricha'' in 1933. The name means "the paradoxical being with mixed-up hairs" because this protist has both cilia and flagella, which was not thought to be possible for protists. Behavior ''Mixotricha'' is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species ''Mastotermes darwin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endosymbiont
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), which live in the root nodules of legumes, single-cell algae inside Coral reef, reef-building corals, and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to insects. Endosymbiosis played key roles in the development of eukaryotes and plants. Roughly 2.2 billion years ago an archaeon absorbed a bacterium through phagocytosis, that eventually became the mitochondria that provide energy to almost all living Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. Approximately 1 billion years ago, some of those cells absorbed cyanobacteria that eventually became chloroplasts, organelles that produce energy from sunlight. Approximately 100 million years ago, a lineage of amoeba in the genus ''Paulinella'' independently engulfed a cyanobacterium that evolved to be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastotermes Darwiniensis
''Mastotermes darwiniensis'', common names giant northern termite and Darwin termite, is a termite species found only in northern Australia. It is the most primitive extant termite species. Contrary to common belief, this species does not form mounds as the nests are subterranean and inconspicuous. Colonies will readily occupy and infest decomposing wood but primarily live in a complex subterranean network of tunnels and galleries which they use to travel to new food sites. Colonies may eventually split and form isolated satellite colonies. Evolutionary significance This species shows uncanny similarities to certain cockroaches, the termites' closest relatives. These similarities include the anal lobe of the wing and the laying of eggs in bunches, rather than singly. It is the only living member of its genus '' Mastotermes'' and its family Mastotermitidae, though numerous fossil taxa are known. The termites were traditionally placed in the Exopterygota, but such an indiscrimina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomonadida
Trichomonadida is an order of anaerobic protists, included with the parabasalids. Members of this order are referred to as trichomonads. Some organisms in this order include: *''Trichomonas vaginalis'', an organism living inside the vagina of humans *'' Dientamoeba fragilis'', parasitic ameboid in humans *''Histomonas meleagridis'', parasite that causes blackhead disease in poultry *'' Mixotricha paradoxa'', a symbiotic organism inside termites, host of endosymbionts Anatomy Species in this order typically have four to six flagella at the cell's apical pole, one of which is recurrent - that is, it runs along a surface wave, giving the aspect of an undulating membrane. Like other parabasalids, they typically have an axostyle, a pelta, a costa, and parabasal bodies. In '' Histomonas'' only one flagellum and a reduced axostyle are found, and in '' Dientamoeba'', both are absent. Behavior Most species are either parasites or other endosymbionts of animals. Trichomonads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophozoite
A trophozoite (G. ''trope'', nourishment + ''zoon'', animal) is the activated, feeding stage in the life cycle of certain protozoa such as malaria-causing ''Plasmodium falciparum'' and those of the ''Giardia'' group. The complementary form of the trophozoite state is the thick-walled microbial cyst, cyst form. They are often different from the cyst stage, which is a protective, dormant form of the protozoa. Trophozoites are often found in the host's body fluids and tissues and in many cases, they are the form of the protozoan that causes disease in the host. In the protozoan, ''Entamoeba histolytica'' it invades the intestinal mucosa of its host, causing dysentery, which aid in the trophozoites traveling to the liver and leading to the production of hepatic abscesses. Life cycle stages ''Plasmodium falciparium'' The causative organism of malaria is a protozoan, ''Plasmodium falciparium'', that is carried by the female Anopheles mosquito, ''Anopheles'' mosquito. Malaria is reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiont
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Fission
Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that takes two arguments * Binary relation, a relation involving two elements * Finger binary, a system for counting in binary numbers on the fingers of human hands Computing * Binary code, the representation of text and data using only the digits 1 and 0 * Bit, or binary digit, the basic unit of information in computers * Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text ** Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute * Binary tree, a computer tree data structure in which each node has at most two children * Binary-coded decimal, a method for encoding for decimal digits in binary sequences Astronomy * Binary star, a star system with two stars in it * Binary pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, that can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Many groups of single-celled, microscopic organisms, or microbes, possess the ability to enter this dormant state. Encystment, the process of cyst formation, can function as a method for dispersal and as a way for an organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. These two functions can be combined when a microbe needs to be able to survive harsh conditions between habitable environments (such as between hosts) in order to disperse. Cysts can also be sites for nuclear reorganization and cell division, and in parasitic species they are often the infectious stage between hosts. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilium
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with two subtypes, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core, called the axoneme, determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |