|
Mitch Bouyer
Mitch Boyer (sometimes spelled 'Bowyer', 'Buoyer', 'Bouyer' or 'Buazer', or in Creole, 'Boye') (c. 1837 – June 25, 1876) was an interpreter and guide in the Old West following the American Civil War. General John Gibbon called him "next to Jim Bridger, the best guide in the country". He was killed at the Battle of the Little Bighorn. Family background He was born Michel Boyer in c. 1837. His father, Jean-Baptiste Boyer,Camp gives 'Vital', probably a confusion with Vital Beauvais, whose surname is similarly pronounced in French was a French Canadian who was employed by the American Fur Company, trading with Sioux in the area that would later become Wyoming. Mitch's mother was a Santee Sioux. His father was killed by Native Americans while trapping, about 1863. Mitch's Sioux name was Kar-pash. He had three full sisters: Marie, Anne, and Thérèse, who seem to have been triplets born in 1840. He also had at least two half-brothers: John Boyer (c. 1845-1871), who was hanged at F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
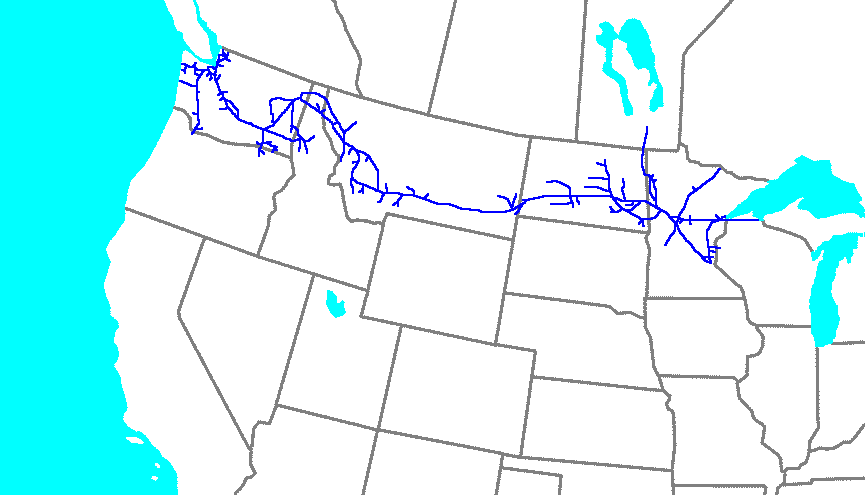
Northern Pacific Railroad
The Northern Pacific Railway was an important American transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the Western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest between 1864 and 1970. It was approved and chartered by the 38th United States Congress, 38th Congress of the United States in the national / federal capital of Washington, D.C., during the last years of the American Civil War (1861-1865), and received nearly of adjacent Land grant, land grants, which it used to raise additional money in Europe (especially in President Henry Villard's home country of the new German Empire), for construction funding. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific Ocean, just south of the United States-Canada border when Ulysses S. Grant, drove in the final "golden spike" completing the line in western Montana Territory (future Montana, State of Montana in 1889), on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Swan
White Swan (18501904), or Mee-nah-tsee-us in the Crow language, was one of six Crow Scouts for George Armstrong Custer's 7th Cavalry Regiment during the 1876 campaign against the Sioux and Northern Cheyenne. At the Battle of the Little Bighorn in the Crow Indian Reservation, White Swan went with Major Reno's detachment, and fought alongside the soldiers at the south end of the village. Of the six Crow scouts at the Battle of the Little Bighorn, White Swan stands out because he aggressively sought combat with multiple Sioux and Cheyenne warriors, and he was the only Crow Scout to be wounded in action, suffering severe wounds to his hand/wrist and leg/foot. After being disabled by his wounds, he was taken to Reno's hill entrenchments by Half Yellow Face, the pipe-bearer (leader) of the Crow scouts, which no doubt saved his life. On the 27th, after the battle, Half Yellow Face made a special horse travois for White Swan and moved him down the Little Horn valley to the ''Far West'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Leforge
Thomas H. Leforge (July 9, 1850 – March 28, 1931) was an American writer who was the author of ''Memoirs of a White Crow Indian'', his highly detailed account of living among the Crow Nation, Crow Indian nation during the mid-to-late 19th century, first published in March 1928 by The Century Company at the hand of Thomas Bailey Marquis, Thomas B. Marquis, and republished by the University of Nebraska Press. Early years Born in Portsmouth, Ohio, on July 9, 1850, he moved with his family to Missouri, then to Kansas, before they finally left in 1864 for Virginia City, Montana, in search of gold. His family set out in prairie wagons with experienced guides on the Jim Bridger, Bridger Trail variant of the Bozeman Trail. The white Indian Leforge joined the Montana militia in 1867 in the Bozeman, Montana, and Livingston, Montana, areas, acquiring both military experience and acquaintance with Native Americans tribes and ways (including raiding parties) by Piegan Blackfeet, his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piebald
A piebald or pied animal is one that has a pattern of unpigmented spots (white) on a pigmented background of hair, feathers or scales. Thus a piebald black and white dog is a black dog with white spots. The animal's skin under the white background is not pigmented. Location of the unpigmented spots is dependent on the migration of melanoblasts (primordial pigment cells) from the neural crest to paired bilateral locations in the skin of the early embryo. The resulting pattern appears symmetrical only if melanoblasts migrate to both locations of a pair and proliferate to the same degree in both locations. The appearance of symmetry can be obliterated if the proliferation of the melanocytes (pigment cells) within the developing spots is so great that the sizes of the spots increase to the point that some of the spots merge, leaving only small areas of the white background among the spots and at the tips of the extremities. Animals with this pattern may include birds, cats, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate. In the human, the skull comprises two prominent parts: the neurocranium and the facial skeleton, which evolved from the first pharyngeal arch. The skull forms the frontmost portion of the axial skeleton and is a product of cephalization and vesicular enlargement of the brain, with several special senses structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and, in fish, specialized tactile organs such as barbels near the mouth. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones and ossicles, which is made up of a number of fused flat and irregular bones. The cranial bones are joined at firm fibrous junctions called sutures and contains many foramina, fossae, processes, and sinuses. In zoology, the openings in the skull are called fenestrae, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008 0909Battlefield0026
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. Etymology English ''eight'', from Old English '', æhta'', Proto-Germanic ''*ahto'' is a direct continuation of Proto-Indo-European '' *oḱtṓ(w)-'', and as such cognate with Greek and Latin , both of which stems are reflected by the English prefix oct(o)-, as in the ordinal adjective ''octaval'' or ''octavary'', the distributive adjective is ''octonary''. The adjective ''octuple'' (Latin ) may also be used as a noun, meaning "a set of eight items"; the diminutive ''octuplet'' is mostly used to refer to eight siblings delivered in one birth. The Semitic numeral is based on a root ''*θmn-'', whence Akkadian ''smn-'', Arabic ''ṯmn-'', Hebrew ''šmn-'' etc. The Chinese numeral, written (Mandarin: ''bā''; Cantonese: ''baat''), is from Old Chinese ''*priāt-'', ultimately from Sino-Tibetan ''b-r-gyat'' or ''b-g-ryat'' which also yielded Tibetan '' brgyat''. It has been argued that, as the cardinal num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Little Big Horn
The Battle of the Little Bighorn, known to the Lakota and other Plains Indians as the Battle of the Greasy Grass, and commonly referred to as Custer's Last Stand, was an armed engagement between combined forces of the Lakota Sioux, Northern Cheyenne, and Arapaho tribes and the 7th Cavalry Regiment of the United States Army. It took place on June 25–26, 1876, along the Little Bighorn River in the Crow Indian Reservation in southeastern Montana Territory. The battle, which resulted in the defeat of U.S. forces, was the most significant action of the Great Sioux War of 1876. Most battles in the Great Sioux War, including the Battle of the Little Bighorn, were on lands those natives had taken from other tribes since 1851. The Lakotas were there without consent from the local Crow tribe, which had a treaty on the area. Already in 1873, Crow chief Blackfoot had called for U.S. military actions against the native intruders. The steady Lakota incursions into treaty areas belonging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of up to one thousand soldiers. A battalion is commanded by a lieutenant colonel and subdivided into several Company (military unit), companies, each typically commanded by a Major (rank), major or a Captain (armed forces), captain. The typical battalion is built from three operational companies, one weapons company and one headquarters company. In some countries, battalions are exclusively infantry, while in others battalions are unit-level organizations. The word ''battalion'' has its origins in the Late Latin word ''battalion'', which is derived from ''battalia'', meaning "battle" or "combat." The term was used to describe a large group of soldiers ready for battle. Over time, its meaning evolved in military terminology. The word "battalion" came into the English language in the 16th century from the French language, French , meaning "battle squadron" (similar to the Italian language, Italian meaning the same thing) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
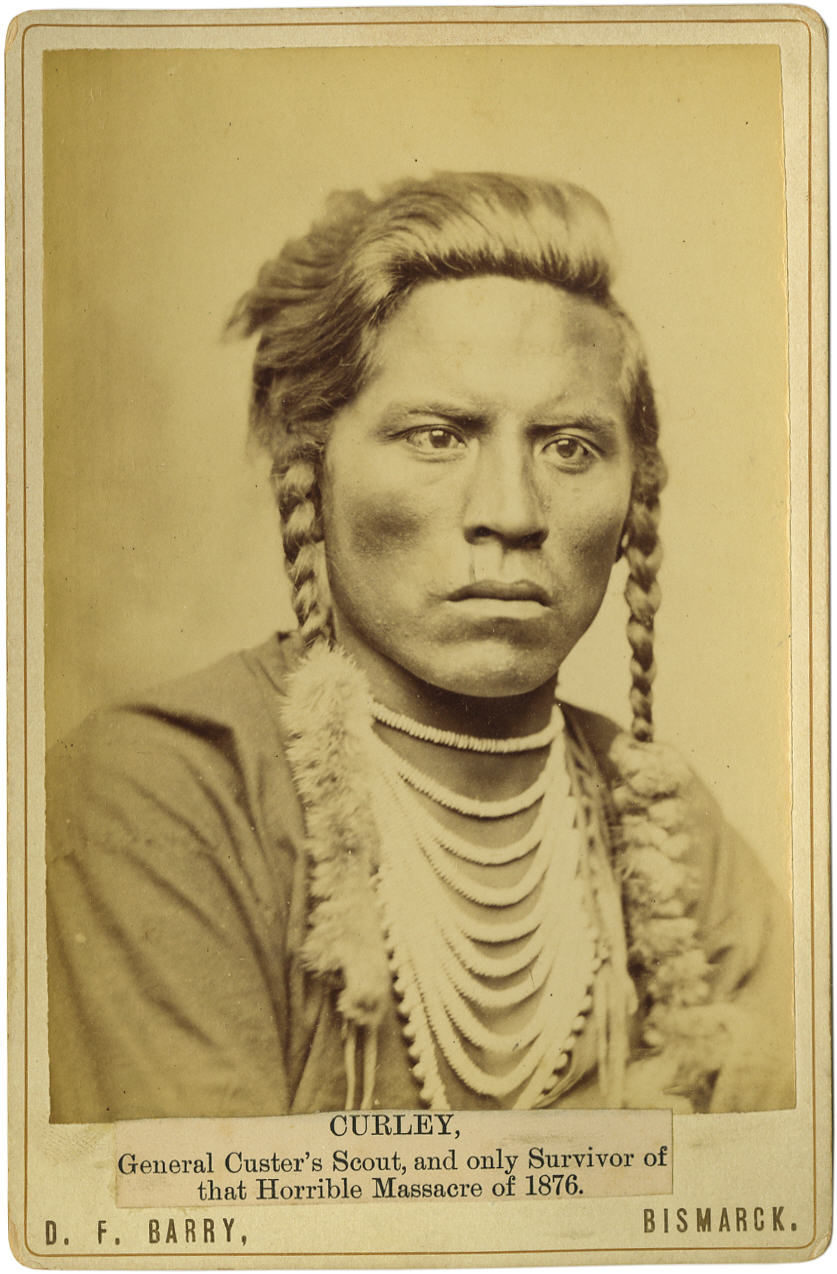
Curly (scout)
Ashishishe ( – 1923), known as Curly (or Curley) and Bull Half White, was a Crow scout in the United States Army during the Sioux Wars, best known for having been the last member of Lt. Colonel George Armstrong Custer's battalion to depart Custer's detachment before its annihilation at the Battle of the Little Bighorn. He did not participate in Custer's final fight, but may have watched from a distance, and was the first to report the defeat of the 7th Cavalry Regiment. Afterward a legend grew that he had been an active participant and managed to escape, leading to conflicting accounts of Curly's involvement in the historical record. Life Ashishishe was born in approximately 1856 in Montana Territory, the son of Strong Bear (Inside the Mouth) and Strikes By the Side of the Water. His name, variously rendered as ''Ashishishe'', ''Shishi'esh'', etc., has been said to literally mean "the crow",Kessel and Wooster, p. 105. however, this may be a misunderstanding as the Crow word for " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arikara
The Arikara ( ), also known as Sahnish, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011) Arikaree, Ree, or Hundi, are a tribe of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans in North Dakota and South Dakota. Today, they are enrolled with the Mandan and the Hidatsa as the federally recognized tribe known as the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation. Synonymy The Arikara's name is believed to mean "horns", in reference to the ancient custom of wearing two upright bones in their hair. The name also could mean "elk people" or "corn eaters".Language The Arikara language is a member of the Caddoan languages, Caddoan language family. Arikara is close to the Pawnee language, but they are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. As of 2 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana Column
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fourth-largest state by area, but the List of U.S. states and territories by population, eighth-least populous state and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, third-least densely populated state. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Helena, Montana, Helena, while the List of municipalities in Montana, most populous city is Billings, Montana, Billings. The western half of the state contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |