|
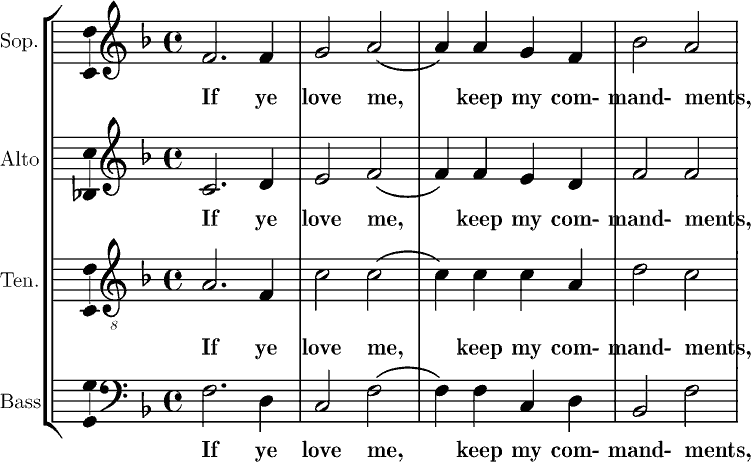
Missa Brevis In C (Brixi)
The in C is a composition by František Xaver Brixi. The missa brevis (short mass) is a setting of the Tridentine Mass for SATB soloists and choir, trumpets, timpani, strings and organ. Manuscripts were held in several monasteries in today's Czech Republic, Austria and Germany. It was published by Dr. J. Butz in 2004. History František Xaver Brixi became ''regens chori'' (choir director) and kapellmeister of Prague's St. Vitus Cathedral in 1759 at age 27 and held the position until his death in 1771. He was a prolific composer of music for the liturgy, who wrote more than 100 masses, vespers and motets, among others. He also composed secular music such as oratorios and incidental music, concertos and symphonies. He composed the Missa brevis in C, a setting of the Latin order of Mass, for SATB soloists and choir, trumpets, timpani, strings and organ. The duration is given as 13 minutes. The mass was often copied, indicating that it was widely distributed. Five extant ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
František Xaver Brixi
František () is a masculine given name of Czech origin. It is a cognate of Francis, Francisco, François, and Franz. People with the name include: * Frank Daniel (František Daniel) (1926–1996), Czech film director, producer, and screenwriter *Frank Musil (František Musil) (born 1964), Czech professional ice hockey player and coach *František Albert (1856–1923), Czech surgeon and writer * František Balvín (born 1915), Czech Olympic cross-country skier * František Bartoš (other), multiple people **František Bartoš (folklorist) (1837–1906), Moravian ethnomusicologist and folklorist ** František Bartoš (motorcycle racer) (born 1926), Czech Grand Prix motorcycle road racer * František Běhounek (1898–1973), Czech scientist, explorer, and writer * František Bělský (1921–2000), Czech sculptor * František Bílek (1872–1941), Czech Art Nouveau and Symbolist sculptor and architect * František Bolček (1920–1968), Slovak professional football player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Mass
Order of Mass is an outline of a Mass celebration, describing how and in what order liturgical texts and rituals are employed to constitute a Mass. The expression Order of Mass is particularly tied to the Roman Rite where the sections under that title in the Roman Missal also contain a set of liturgical texts that recur in most or in all Eucharistic liturgies (the so-called invariable texts, or ''ordinary'' of the Mass), while the rubrics indicate the rituals, and the insertion points of the variable texts known as the proper of the Mass. Having been virtually unchanged for many centuries, the Roman Catholic Order of Mass changed decisively after the Second Vatican Council. Other Christian denominations have comparable descriptions of their liturgical practices for the Eucharist, which are however usually not called Order of Mass. Sections of the Order of Mass The Order of Mass in Western liturgy generally consists of the following sections: 1. Liturgy of the Word # The Prayer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masses (music)
Mass is the quantity of matter in a physical body and a measure of the body's inertia. Mass or Maß may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music *Mass (music), a choral composition that sets liturgical text to music * ''Mass'' (Stravinsky), a composition by Igor Stravinsky * ''Mass'' (Bernstein), a musical theater work by Leonard Bernstein * Mass (English band), a post-punk band * ''Mass'' (Grotus album), 1996 * ''Mass'' (Alastair Galbraith album), 2011 * ''Mass'' (The Gazette album), 2021 * ''The Mass'' (album), by musical project Era Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Mass'' (2004 film), Indian Telugu-language film * ''Mass'' (2021 film), American drama film * ''Mass'' (novel), a 1973 novel by Filipino author F. Sionil José * Mass media, communication channels which can reach huge numbers of people * ''The Masses'', a socialist magazine published in the US from 1911 to 1917 Military * MASS (decoy system), a naval defence system *M26 Modular Accesso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carus-Verlag
Carus-Verlag is a German music publisher founded in 1972 and based in Stuttgart. Carus was founded by choral conductor Günter Graulich and his wife Waltraud with an emphasis on choral repertoire. The catalogue currently includes more than 26,000 works (January 2016). The company produces the standard editions of the complete works of Josef Rheinberger and Max Reger.''Harald Wanger, Rheinberger-Archivar, Organist, Pädagoge'' Harald Wanger, Franz-Georg Rössler, Robert Allgäuer - 2003 p. 48 Carus-Verlag, Musikalische Schätze abseits bekannter Pfade - Harald Wanger und der Carus-Verlag "Für den Carus-Verlag ist die Verbindung zu Harald Wanger und dem Josef Rheinberger-Archiv ein Glücksfall." Record label The company also produces CDs to accompany some of its printed editions. Currently the publishers are working on recordings accompanying the complete editions of Wilhelm Friedemann Bach. Opera rarities include Schubert's '' Sakuntala'' and Johann Rudolf Zumsteeg's ''Die G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantabile
In music, ''cantabile'' , an Italian word, means literally "singable" or "songlike". In instrumental music, it is a particular style of playing designed to imitate the human voice. For 18th-century composers, ''cantabile'' is often synonymous with "cantando" (singing) and indicates a measured tempo and flexible, legato playing. For later composers, particularly in piano music, ''cantabile'' is the drawing out of one particular musical line against the accompaniment (compare counterpoint). Felix Mendelssohn's six books of '' Songs Without Words'' are short lyrical piano pieces with song-like melodies written between 1829 and 1845. A modern example is an instrumental by Harry James & His Orchestra, called "Trumpet Blues and Cantabile". A cantabile movement, or simply a "cantabile", is the first half of a double aria, followed by a cabaletta. The cantabile movement would be slower and more free-form to contrast with the structured and generally faster cabaletta. Louis Spohr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture (music), texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chord (music), chords, homophony. Within the context of the Western musical tradition, the term ''polyphony'' is usually used to refer to music of the late Medieval music, Middle Ages and Renaissance music, Renaissance. Baroque music, Baroque forms such as fugue, which might be called polyphonic, are usually described instead as counterpoint, contrapuntal. Also, as opposed to the ''species'' terminology of counterpoint, polyphony was generally either "pitch-against-pitch" / "point-against-point" or "sustained-pitch" in one part with melismas of varying lengths in another. In all cases the conception was probably what Margaret Bent (1999) calls "dyadic counterpoint", with each part being written generally against one other part, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh out the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottobeuren Abbey
Ottobeuren is a Benedictine abbey, located in Ottobeuren, near Memmingen in the Bavarian Allgäu, Germany. For part of its history Ottobeuren Abbey was one of the 40-odd self-ruling imperial abbeys of the Holy Roman Empire and, as such, was a virtually independent state. At the time of its dissolution in 1802, the imperial abbey covered 266 square kilometers and had about 10,000 subjects. First foundation It was founded in 764 by Blessed Toto, and dedicated to St. Alexander, the martyr. Of its early history little is known beyond the fact that Toto, its first abbot, died about 815 and that Saint Ulrich was its abbot in 972. In the 11th century its discipline was on the decline, until Abbot Adalhalm (1082–94) introduced the Hirsau Reform. The same abbot began a restoration of the decaying buildings, which was completed along with the addition of a convent for noble ladies, by his successor, Abbot Rupert I (1102–45). Under the rule of the latter the newly founded Marienberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kremsmünster Abbey
Kremsmünster Abbey (german: Stift Kremsmünster) is a Benedictine monastery in Kremsmünster in Upper Austria. History The monastery was founded in 777 AD by Tassilo III, Duke of Bavaria. According to the foundation legend, Tassilo founded the monastery on the site where his son, Gunther, had been attacked and killed by a wild boar during a hunting trip. The first colony of monks came from Lower Bavaria, under Fateric, the first abbot. The new foundation received generous endowments from the founder and also from Charlemagne and his successors. The position and reputation of the abbey soon became such that its abbots, in the absence of the bishop of the diocese ( Passau), exercised the episcopal jurisdiction. In the 10th century the abbey was destroyed in a raid by the Hungarians, and its possessions were divided among the Duke of Bavaria and other nobles and the bishops. It was restored, however, and recovered its property, under the emperor Henry II, when Saint Gotthard b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Litoměřice
Litoměřice (; german: Leitmeritz) is a town in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 23,000 inhabitants. The town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument reservation. The town is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Litoměřice. Administrative parts Litoměřice is made up of four town parts: Litoměřice-Město, Pokratice, Předměstí and Za nemocnicí. Geography Litoměřice is located about south of Ústí nad Labem and northwest of Prague. The northwestern half of the municipal territory lies in the Central Bohemian Uplands, the southeastern half lies in the Lower Eger Table, on the edge of the Polabí lowlands. The highest point, located in the northern tip of the territory, is at above sea level. The town is situated on the right (northern) bank of the Elbe River, at its confluence with the Ohře, which flows from the south. History Early history The settlement of Litoměřice has a deep history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutná Hora
Kutná Hora (; medieval Czech: ''Hory Kutné''; german: Kuttenberg) is a town in the Central Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 20,000 inhabitants. The centre of Kutná Hora, including the Sedlec Abbey and its ossuary, was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995 because of its outstanding architecture and its influence on subsequent architectural developments in other Central European city centres. Since 1961, the town centre is also protected by law as an urban monument reservation, the fourth largest in the country. Administrative parts The town is made up of twelve town parts and villages: *Kutná Hora-Vnitřní Město *Hlouška *Kaňk *Karlov *Malín *Neškaredice *Perštejnec *Poličany *Sedlec *Šipší *Vrchlice *Žižkov Geography Kutná Hora is located about east of Prague. It lies on the Vrchlice stream. The eastern part of the municipal territory lies in a flat agricultural landscape of the Central Elbe Table lowland. The western part lies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedlec Abbey
Sedlec Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in Sedlec, part of Kutná Hora in the Czech Republic. Founded in 1142, it was the first Cistercian foundation in Bohemia. Along with the rest of the Kutná Hora town centre, it was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1995, because of its outstanding Baroque architecture. It is well known for housing the Sedlec Ossuary. History Sedlec Abbey was founded in 1142 from Waldsassen Abbey in Sedlec as the first Cistercian monastery in Bohemia. The grounds covered by wood and swamp were granted by Miroslav, House of Wartenberg. (PDF; 273 kB) in den Mittheilungen der k.k. Central-Commission 1856 It flour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |