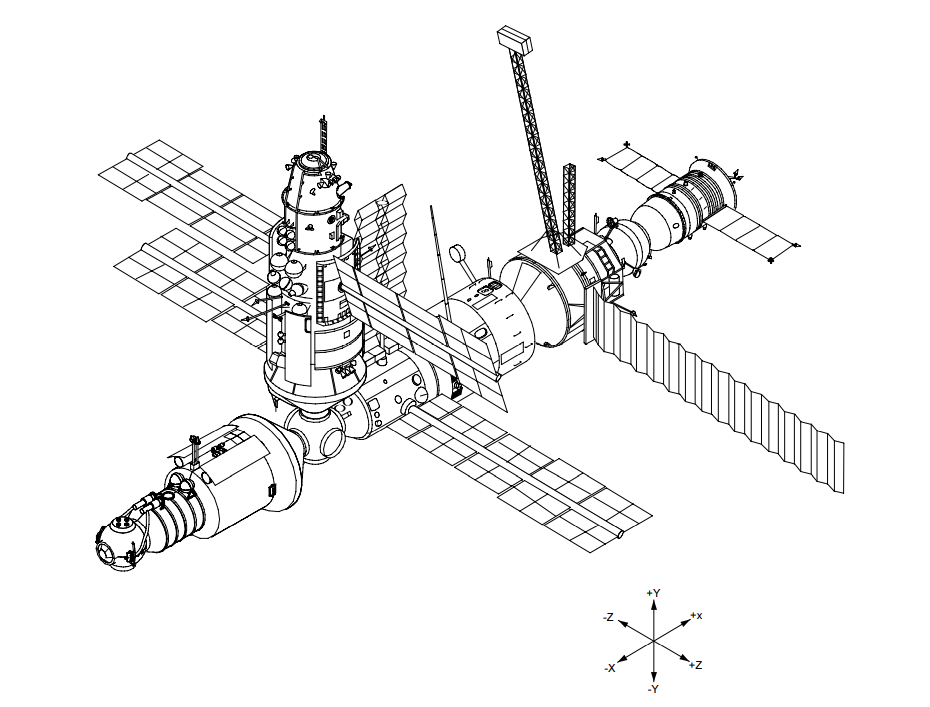
|
Mir EO-18
Soyuz TM-21 was a crewed Soyuz spaceflight to ''Mir''. The mission launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket, at 06:11:34 UTC on 14 March 1995. The flight marked the first time thirteen humans were flying in space simultaneously, with three aboard the Soyuz, three aboard ''Mir'' and seven aboard Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', flying STS-67. The spacecraft carried expedition EO-18 to the space station. This included the first American astronaut to launch on a Soyuz spacecraft and board ''Mir'', Norman Thagard, for the American Thagard Increment aboard the station, which was the first Increment of the Shuttle-Mir program. The three crew members it launched were relieved by Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' during STS-71, when they were replaced by expedition EO-19. The crew returned to earth aboard Soyuz TM-21 on 11 September 1995. Crew Mir Principal Expedition 18 The major objectives of the Mir 18 mission were to conduct joint U.S.-Russian medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Agency
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency,, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (). which was established on 25 February 1992 and restructured in 1999 and 2004 as the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (), established on 25 May 1999. and the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), (Роскосмос), ''Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)''. respectively. In 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was merged with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, a government corporation, to re-nationalize the space industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome is a spaceport operated by Russia within Kazakhstan. Located in the Kazakh city of Baikonur, it is the largest operational space launch facility in terms of area. All Russian Human spaceflight, crewed spaceflights are launched from Baikonur. Situated in the Kazakh Steppe, some above sea level, it is to the east of the Aral Sea and north of the Syr Darya. It is close to Töretam, a station on the Trans-Aral Railway. Russia, as the official successor state to the Soviet Union, has retained control over the facility since 1991; it originally assumed this role through the post-Soviet Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), but ratified an agreement with Kazakhstan in 2005 that allowed it to lease the spaceport until 2050. It is jointly managed by Roscosmos and the Russian Aerospace Forces. In 1955, the Ministry of Defense (Soviet Union), Soviet Ministry of Defense issued a decree and founded the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It was originally built as the chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Viktorenko
Aleksandr Stepanovich Viktorenko (; 29 March 1947 – 9 August 2023) was a Soviet and Russian cosmonaut. Viktorenko was selected as a cosmonaut on 23 March 1978 and retired on 30 May 1997. He was commander of Soyuz TM-3, Soyuz TM-8, Soyuz TM-14, and Soyuz TM-20. He spent a total of 489 days in space. The Russian tradition of Russian Orthodox priests blessing cosmonauts on launch day was initiated by Viktorenko when he requested one for the launch of Soyuz TM-20 in 1994. Aleksandr Viktorenko died on 9 August 2023, at the age of 76. He was buried at the Federal Military Memorial Cemetery on 12 August. Honours and awards * Hero of the Soviet Union * Order of Merit for the Fatherland, 3rd class (10 April 1995) for their courage and heroism displayed during prolonged space flight on the orbital scientific research complex ''Mir'' * Order of Friendship of Peoples (11 August 1992) for the successful implementation of long-duration space flight on the orbital station ''Mir'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RKA Mission Control Center
The RKA Mission Control CenterRKA (): Russian space agency (, ). (), also known by its acronym TsUP () or by its radio callsign Mission Control Moscow, is the mission control center of Roscosmos. It is located in Korolyov, Moscow Oblast, on Pionerskaya Street near the S.P. Korolev Rocket and Space Corporation Energia plant. It contains an active control room for the International Space Station. It also houses a memorial control room for the Mir space station where the last few orbits of Mir before it burned up in the atmosphere are shown on the display screens. TsUP provides practical flight control for spacecraft of several different classes: crewed orbital complexes, spaceships, space probes and civilian, and scientific satellite A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viktor Chernomyrdin
Viktor Stepanovich Chernomyrdin (, ; 9 April 19383 November 2010) was a Soviet and Russian politician and businessman. He was the Minister of Gas Industry of the Soviet Union (13 February 1985 – 17 July 1989), after which he became first chairman of Gazprom energy company and the second-longest-serving Prime Minister of Russia (1992–1998) based on consecutive years. He was a key figure in Russian politics in the 1990s and a participant in the transition from a Planned economy, planned to a Market economy, market economy. From 2001 to 2009, he was Russia's ambassador to Ukraine. After that, he was designated as a presidential adviser. Chernomyrdin was known in Russia and List of countries where Russian is an official language, Russian-speaking countries for his language style, which contained numerous malapropisms and Syntax, syntactic errors. Many of his sayings became aphorisms and idioms in the Russian language, two examples being the expression "We wanted the best, but it t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Koptev
Yuri Nikolayevich Koptev (, March 13, 1940) is a former General Director of the Russian Space Agency (now known as Roscosmos), serving in that role from 1992 to 2004. He was replaced in 2004 by Anatoly Perminov, a former commander of the Russian Space Forces. He has the federal state civilian service rank of 1st class Active State Councillor of the Russian Federation. Beginning in 1965, he worked as an engineer at NPO Lavochkin. Koptev is a Winner of the Golden Space Medal FAI (2000), a State Councillor of the Russian Federation, 1st class and was awarded the Order "For Merit to the Fatherland", 2nd and 3rd classes. Education * 1957-1960 — Cadet of the Riga Civil Aviation Engineers Institute. * 1960-1965 — A student of the Bauman Moscow State Technical University, graduated with a degree in mechanical engineering. International sanctions On June 28, 2022, in connection with the ongoing Russian aggression in Ukraine, he was included in the US sanctions list as a person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roscosmos
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a State corporation (Russia), state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space science, space flights, List of space agencies, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency,, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (). which was established on 25 February 1992 and restructured in 1999 and 2004 as the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (), established on 25 May 1999. and the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), (Роскосмос), ''Federalnoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo (Roskosmos)''. respectively. In 2015, the Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) was merged with the United Rocket and Space Corporation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress M-26
Progress M-26 () was a Russian unmanned Progress cargo spacecraft, which was launched in February 1995 to resupply the Mir space station. Launch Progress M-26 launched on 15 February 1995 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It used a Soyuz-U rocket. Docking Progress M-26 docked with the aft port of the Kvant-1 module of Mir on 17 February 1995 at 18:21:34 UTC, and was undocked on 15 March 1995 at 02:26:38 UTC. Decay It remained in orbit until 15 March 1995, when it was deorbited. The deorbit burn occurred at 05:28 UTC and the mission ended at 06:15 UTC. See also * 1995 in spaceflight * List of Progress missions * List of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir This is a list of uncrewed spaceflights to Mir. Components of the space station are indicated in green. *A. - Time from docking until debris impact in the Pacific Ocean at approximately 05:59 GMT on 23 March 2001. *B. - From time of launch *C. ... References Progress (spacecraft) missions 1995 in Kazakhstan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-71
As the third mission of the US/Russian Shuttle-Mir Program, STS-71 became the first Space Shuttle to dock with the Russian space station ''Mir''. STS-71 began on June 27, 1995, with the launch of Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' from launchpad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Shuttle delivered a relief crew of two cosmonauts Anatoly Solovyev and Nikolai Budarin to the station and recovered Increment astronaut Norman Thagard. ''Atlantis'' returned to Earth on July 7 with a crew of eight. It was the first of seven straight missions to ''Mir'' flown by ''Atlantis'', and the second Shuttle mission to land with an eight-person crew after STS-61-A in 1985. For the five days the Shuttle was docked to ''Mir'' they were the largest spacecraft in orbit at the time. STS-71 marked the first docking of a Space Shuttle to a space station, the first time a Shuttle crew switched members with the crew of a station, and the 100th crewed space launch by the United States. The mission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Atlantis
Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' (Orbiter Vehicle designation: OV‑104) is a retired Space Shuttle orbiter vehicle which belongs to NASA, the spaceflight and space exploration agency of the United States. ''Atlantis'' was manufactured by the Rockwell International company in Southern California and was delivered to the Kennedy Space Center in Eastern Florida in April 1985. ''Atlantis'' is the fourth operational and the second-to-last Space Shuttle built. Its maiden flight was STS-51-J made from October 3 to 7, 1985. ''Atlantis'' embarked on its 33rd and final mission, also the final mission of a space shuttle, STS-135, on July 8, 2011. STS-134 by Space Shuttle Endeavour, ''Endeavour'' was expected to be the final flight before STS-135 was authorized in October 2010. STS-135 took advantage of the processing for the STS-335 Launch on Need mission that would have been necessary if STS-134's crew became stranded in orbit. ''Atlantis'' landed for the final time at the Kennedy Space Cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |