|
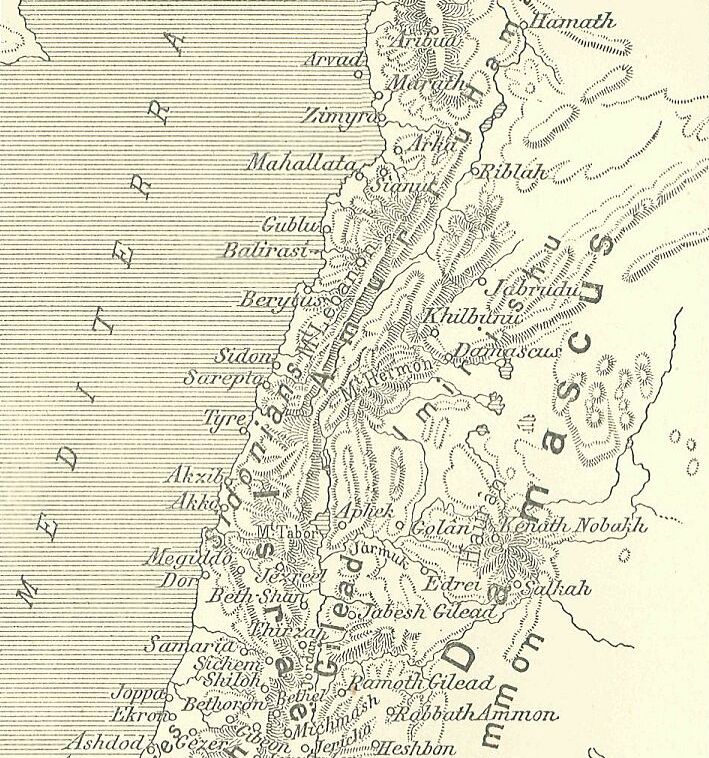
Milkilu
Milki-ilu of Gezer (Milkilu, Milk-ilu, Ili-Milku), was the mayor/ruler of the Land of ''Gazru'' (Gezer) around 1350 BC. He is known as the son-in-law of Tagi of Ginti-Kirmil and cooperating with Labaya of Shechem, during a period of turmoil among the vassals of Egypt. He is accused of being a rebel, employing mercenaries from the Habiru men (lu2-meš ḫa-bi-ri). He is known from several letter in that Amarna Archive. There is one letter from the King of Egypt to Milki-ilu (EA 369), there are five letters from Milki-ilu to the King of Egypt (EA 267-271), and several letters from other mayors mentioning Milki-ilu. He is one of several known mayors of Gezer. Adda-danu and Yapahu were also mayors of '' Gazru''. The Amarna Period was characterized by the heretic king Akhenaten, succeeded by the boy-king Tutankhamen. Canaan consisted of smaller city-states and vassals of Egypt. At the same time, Suppiluliuma I of Hatti attacked Tushratta of Mitanni for control over Syria. Fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labaya
Labaya (Labayu or Lib'ayu) was the ruler of Shechem and warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan during the Amarna Period (c. 1350 BC). He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters (abbreviated "EA", for 'el Amarna'). He is the author of letters Amarna letter EA 252, EA 252–Amarna letter EA 254, 54. Labaya was active over the whole length of Samaria and slightly beyond, as he gave land to Habiru in the vicinity of Šakmu (Shechem) and he and his sons threatened such powerful towns as Jerusalem and Gazru (Gezer) to the south, and Megiddo (place), Megiddo to the north. Career The Amarna letters give an incomplete look at Labaya's career. In the first of Labaya's letters thus far discovered (EA 252), he defends himself to the Pharaoh against complaints of other city rulers about him, for example, the complaint that he has hired mercenaries from among the Habiru. Labaya further admitted to having invaded Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yapahu
Yapahu was a mayor/ruler of the city/city-state of ''Gazru'' (modern Gezer) of the 1350 BC, 1350-1335 BC Amarna letters Text corpus, correspondence. Two other mayors of Gazru during the Amarna letters period, were Adda-danu and Milkilu. Yapahu is the author of five Amarna letters to the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, Egypt, EA 297-300, and EA 378, (EA (el Amarna), EA for 'el Amarna'). 2 examples of Yapahu's letters EA 297, title: "The sweet breath of the king" :"Say to the king-(i.e. pharaoh), my lord, my god, my Sun: Message of ''Yapahu'', your servant, the dirt at your feet, I Prostration formula, fall at the feet of the king, my lord, my god, my Sun, 7 times and 7 times. Whatsoever the king, my lord, has said to me, I have listened to with the greatest care. Moreover, I have become like a (bronze)–pot: ''sí-ri'' given in pledge, because of the Suteans. I have, however, just heard the sweet breath of the king. It has come forth to me, and my heart is very content." -EA 297, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adda-danu
Adda-danu was the 'mayor' of the city/city-state of Gazru-(modern Gezer, Israel) of the Amarna letters period, 1350-1335 BC. 'Adda' is the name of the Northwest Semitic god Hadad, and Adda-danu translates as: ''"Hadad (is the) Judge"''. Adda-danu is one of the three mayors who ruled Gazru in the 20–year Amarna letters correspondence, the others being Milkilu, and Yapahu. Adda-danu is the author of one letter, EA 292, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). The letter is entitled: ''"Like a pot held in pledge"''. It is of note that some of the 382 Amarna letters contain phrases, quotes, or parables and the title refers to, ''The Pot of a Debt''. Amarna letter--no. 292 Adda-danu's letter to pharaoh Akhenaten Title: ''"Like a pot held in pledge"'' :Say to the king-(pharaoh), my lord, ygo my Sun: Message of ''Adda-danu'', your servant, the dirt at your feet. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord, my god, my Sun, 7 times and 7 times. I looked this way, and looked that way, and there was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pítati
The Pitati (Egyptian: , Cuneiform: ) were a contingent of Nubian archers of ancient Egypt that were often requested and dispatched to support Egyptian vassals in Canaan. They are recorded in the correspondence of the 1350 BC Amarna letters, and were often requested to defend against the Habiru, also rogue vassal-kings and foreign troops of neighboring kingdoms (for example, Hatti), who were on the attack. The vassal cities and "city-states" were constantly requesting the services (protection) of the Pharaoh's armies, by means of this "archer-army" force, basically garrison forces. A request for lodging, and preparations of food, drink, straw, and other supplies required,Moran, William L., 1992. ''The Amarna Letters,'' p. 352-353. ''EA 325'': Title: (from, Man of the City: Yidya): ''Preparations completed, (2)'', "...indeed prepared absolutely everything—food, strong drink, oxen, 'sheep and goats', grain, straw, absolutely everything that the king, my lord, commanded." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagi Of Ginti
Tagi was the ruler/mayor of ancient Ginti–(Gintikirmil), of the 14th century BC Amarna letters. Tagi's name is a Hurrian hypocoristicon for the word ''beautiful''. Tagi was the father-in-law of Milkilu, mayor of ancient Gazru-(modern Gezer), (one of three mayors). Tagi was the author of 3 short, but complete Amarna letters, EA 264-66, (EA for 'el Amarna'), and Tagi is also referenced in two other letters. The authored letters are written to the pharaoh of Egypt. The 3 letters of Tagi EA 264: ''"The ubiquitous king"''-(Caravans) :To the king, m lord: Message of ''Tagi'', you servant. I fall at the feet of the king, my lord, 7 times and 7 times. As I am the servant of the king, I tried to assemble a caravan, with my brother in charge, but he barely escaped being killed. He is unable to send my caravan to the king, my lord. Ask your commissioner if my brother did not barely escape being killed. Moreover, as far as we are concerned, it is to you that my eyes (are directed). S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 1950–1880 BC and are depicted on cylinder seals from Central Anatolia Region, Central Anatolia in Kültepe dated to c. 1900 BC. The critical invention that allowed the construction of light, horse-drawn chariots was the spoked wheel. The chariot was a fast, light, open, two-wheeled conveyance drawn by two or more Equidae, equids (usually horses) that were hitched side by side, and was little more than a floor with a waist-high guard at the front and sides. It was initially used for ancient warfare during the Bronze Age, Bronze and Iron Age, Iron Ages, but after its military capabilities had been superseded by Light cavalry, light and Heavy cavalry, heavy cavalries, chariots continued to be used for travel and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shekel
A shekel or sheqel (; , , plural , ) is an ancient Mesopotamian coin, usually of silver. A shekel was first a unit of weight—very roughly 11 grams (0.35 ozt)—and became currency in ancient Tyre, Carthage and Hasmonean Judea. Name The word is based on the triliteral Proto-Semitic root , cognate to the Akkadian or , a unit of weight equivalent to the Sumerian . Use of the word was first attested in under the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad, and later in in the Code of Hammurabi. The Hebrew reflex of the root is found in the Hebrew words for "to weigh" (), "weight" () and "consideration" (). It is cognate to the Aramaic root and the Arabic root ( ث ق ل, in words such as "weight", "heavy" or , a unit of weight). The famous writing on the wall in the Book of Daniel includes a cryptic use of the word in Aramaic: "". Shekel came into the English language via the Hebrew Bible, where it is first used in Genesis 23. The term "shekel" has been used for a unit of we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. His oracle in Siwa Oasis, located in Western Egypt near the Libyan Desert, remained the only oracle of Amun throughout. With the 11th Dynasty ( BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. Initially possibly one of eight deities in the Hermapolite creation myth, his worship expanded. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). On his own, he was also thought to be the king of the gods. Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th–11th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper And Lower Egypt
In History of ancient Egypt, Egyptian history, the Upper and Lower Egypt period (also known as The Two Lands) was the final stage of prehistoric Egypt and directly preceded the Early Dynastic Period (Egypt), unification of the realm. The conception of Egypt as the Two Lands was an example of the dualism in ancient Egyptian culture and frequently appeared in texts and imagery, including in the titles of Egyptian pharaohs. The Egyptian title ''wikt:zmꜣ#Egyptian, zmꜣ-wikt:tꜣwj#Egyptian, tꜣwj'' (Egyptological pronunciation ''sema-tawy'') is usually translated as "Uniter of the Two Lands" and was depicted as a human trachea entwined with the papyrus and lily plant. The trachea stood for unification, while the papyrus and lily plant represent Lower and Upper Egypt. Standard titles of the pharaoh included the prenomen (Ancient Egypt), prenomen, quite literally "Of the Cyperaceae, Sedge and Bee" (wikt:nswt-bjtj, nswt-bjtj, the symbols of Upper and Lower Egypt) and "lord of the Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also includes the persimmon tree. A few ''Diospyros'' species, such as macassar and mun ebony, are dense enough to sink in water. Ebony is finely textured and has a mirror finish when polished, making it valuable as an ornamental wood. It is often cited as one of the most expensive woods in the world. Etymology The word ''ebony'' comes from the Ancient Egyptian ', through the Ancient Greek ('), into Latin () and Middle English. Species Species of ebony include '' Diospyros ebenum'' (Ceylon ebony), native to southern India and Sri Lanka; '' D. crassiflora'' (Gabon ebony), native to western Africa; '' D. humilis'' (Queensland ebony), native to Queensland, the Northern Territory, New Guinea and Timor; and '' D. celebica'' (Sulawesi ebony), native to Indonesia and prized for its luxuriant, multi-colored wood grain. Mauritius ebony, '' D. tessellaria'', was largely exploited by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic chemistry, organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, Jet (gemstone), jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or Lustre (mineralogy), luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semiprecious stone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker; the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used interchangeably. Both carnelian and sard are varieties of the silica mineral chalcedony colored by impurities of iron oxide. The color can vary greatly, ranging from pale orange to an intense almost-black coloration. Significant localities include Yanacodo (Peru); Ratnapura (Sri Lanka); and Thailand. It has been found in Indonesia, Brazil, India, Iran, Russia (Siberia), and Germany. In the United States, the official State Gem of Maryland is also a variety of carnelian called Patuxent River stone. History upright=1.1, Polish engraved_gem.html" ;"title="signet ring in light-orange carnelian engraved gem">intaglio showing Korwin coat of arms The red variety of chalcedony has been known to be used as beads since the Early Neolithic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |