|
Militia Of The Faith Of Jesus Christ
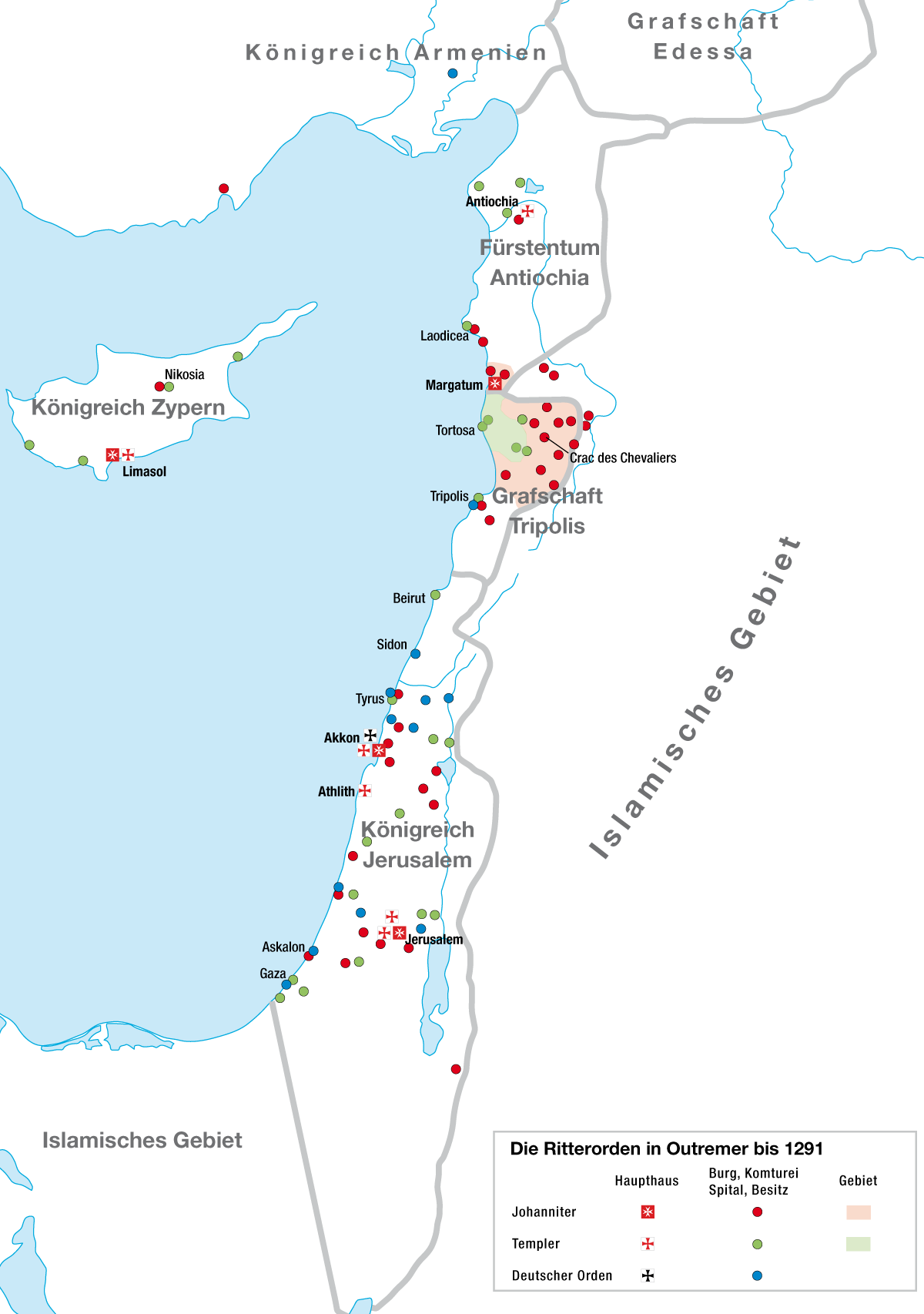
The Militia or Order of the (Holy) Faith of Jesus Christ () was an ephemeral Military order (society), military order founded in Languedoc in or shortly before 1221. It owed its origins probably to Folquet de Marselha, the Bishop of Toulouse; Simon de Montfort, 5th Earl of Leicester, leader of the Albigensian Crusade; and possibly to Saint Dominic, Dominic of Caleruega, the founder of the Friars Preachers. Foundation In June 1221 it appears to have been approved by Pope Honorius III, who gave it permission to observe the ordinances of the Knights Templar, Order of the Temple of Solomon. In July the Pope appears to have transferred all authority over the foundation of the order (and therefore its survival) to the papal legate Conrad of Urach.Forey (1989), 6. The specific purpose of the founding was "to promise aid and succour to Amaury de Montfort (died 1241), Amaury de Montfort and his heirs, for the defence of his person and domains"Sismondi, 161. and as Inquisition, inquisitors f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order (society)
A military order () is a Christianity, Christian religious society of Knight, knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of the Holy Sepulchre (Catholic), Order of the Holy Sepulchre, the Order of Santiago, Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Order, Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades - in the Holy Land, the Baltic states, Baltics, and the Iberian Peninsula, Iberian peninsula; their members being initially dedicated to the protection of Christians , Christian pilgrims, and eventually to the defence of the Crusader states and the conquest of non-Christian or even non-Western Christianity , Catholic lands. They are the predecessors of Order of chivalry, chivalric orders. Most members of military orders were Laity, laymen who took religious vows, such as of Evangelical counsels, poverty, chastity, and obedience, according to Monasticism, monastic ideals. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catharism
Catharism ( ; from the , "the pure ones") was a Christian quasi- dualist and pseudo-Gnostic movement which thrived in Southern Europe, particularly in northern Italy and southern France, between the 12th and 14th centuries. Denounced as a heretical sect by the Catholic Church, its followers were attacked first by the Albigensian Crusade and later by the Medieval Inquisition, which eradicated the sect by 1350. Around 1 million were slaughtered, hanged, or burnt at the stake. Followers were known as Cathars or Albigensians, after the French city Albi where the movement first took hold, but referred to themselves as Good Christians. They famously believed that there were not one, but two Godsthe good God of Heaven and the evil god of this age (). According to tradition, Cathars believed that the good God was the God of the New Testament faith and creator of the spiritual realm. Many Cathars identified the evil god as Satan, the master of the physical world. The Cathars believe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymund Of Capua
Raymond of Capua, (ca. 1303 – 5 October 1399) was a leading member of the Dominican Order and served as its Master General from 1380 until his death. First as Prior Provincial of Lombardy and then as Master General of the Order, Raymond undertook the restoration of Dominican religious life. For his success in this endeavor, he is referred to as its "second founder". Raymond worked also for the return of the papacy to Rome and for a solution to the Western schism. The important mystic and author, Catherine of Siena, accepted him as a spiritual director because of his burning passion for the Church and for the revival of religious life. He was beatified by the Catholic Church in 1899. Life He was born "Raymond della Vigna" about 1330 in Capua (then part of the Kingdom of Naples), a member of a prominent family of that city, and was a descendant of Pietro della Vigna (a figure mentioned in Dante's ''Divine Comedy''). In 1350, while a student of law at the University of Bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicenza
Vicenza ( , ; or , archaically ) is a city in northeastern Italy. It is in the Veneto region, at the northern base of the Monte Berico, where it straddles the Bacchiglione, River Bacchiglione. Vicenza is approximately west of Venice and east of Milan. Vicenza is a thriving and cosmopolitan city, with a rich history and culture, and many museums, art galleries, piazzas, villas, churches and elegant Renaissance ''Palazzo, palazzi''. With the Palladian villas of the Veneto in the surrounding area, and his renowned Teatro Olimpico ("Olympic Theater"), the "city of Palladio" has been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994. Vicenza had an estimated population of 115,927 and a metropolitan area of 270,000 in 2008. Vicenza is the third-largest Italian industrial centre as measured by the value of its exports, and is one of the country's wealthiest cities, in large part due to its textile and steel industries, which employ tens of thousands of people. Additionally, abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartholomew Of Braganca
Bartholomew of Breganze (c. 1200 – 1 July 1271) was an Italian Dominican friar and bishop. Life Bartholomew of Breganze was born in the city of Vicenza to the noble family of Da Breganze (from Breganze). He studied at Padua, receiving there the habit of the recently founded Order from the hands of St. Dominic himself, at about the age of twenty. Following his ordination as a priest, he quickly came to serve in various positions of leadership in the new Order. According to Friar Leander, author of his earliest biography, he was made Master of the Sacred Palace in 1235, during the pontificate of Pope Gregory IX—but there is no mention of this event in his Last Testament, where Bartholomew listed the important offices he had held. During this period, he founded a military order of knights whose purpose was to establish civil order throughout Italy. He was appointed to the See of Nemonicum in Cyprus in 1248 (what city this was is not known now). While Louis IX of France was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habit (monk)
A religious habit is a distinctive set of clothing worn by members of a religious order. Traditionally, some plain garb recognizable as a religious habit has also been worn by those leading the religious eremitic and anchoritic life, although in their case without conformity to a particular uniform style. Uniformity and distinctiveness by order often evolved and changed over time. Interpretation of terms for clothes in religious rules could change over centuries. Furthermore, every time new communities gained importance in a cultural area the need for visual separation increased for new as well as old communities. Thus, modern habits are rooted in historic forms, but do not necessarily resemble them in cut, color, material, detail or use. In Christian monastic orders of the Catholic, Lutheran and Anglican Churches, the habit often consists of a tunic covered by a scapular and cowl, with a hood for monks or friars and a veil for nuns; in apostolic orders it may be a distinctiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan Of Saxony
Jordan of Saxony, OP (referred to in Latin as Jordanis, also known as de Alamania; c. 1190 – 1237), was a German Catholic priest and one of the first leaders of the Dominican Order. His feast day is February 13. Life Jordan belonged to the noble German family of the Counts of Eberstein. He was born in the Castle of Borrenstrick, in the diocese of Paderborn. He began his studies in his native land, and was sent to complete them at the University of Paris."Blessed Jordan of Saxony, OP", The Dominicans, Province of the Most Holy Name of Jesus, February 13, 2012 While a student he met Dominic de Guzman, the founder of the Order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Bull
A papal bull is a type of public decree, letters patent, or charter issued by the pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the leaden Seal (emblem), seal (''bulla (seal), bulla'') traditionally appended to authenticate it. History Papal bulls have been in use at least since the 6th century, but the phrase was not used until around the end of the 13th century, and then only internally for unofficial administrative purposes. However, it had become official by the 15th century, when one of the offices of the Apostolic Chancery was named the "register of bulls" ("''registrum bullarum''"). By the accession of Pope Leo IX in 1048, a clear distinction developed between two classes of bulls of greater and less solemnity. The majority of the "great bulls" now in existence are in the nature of confirmations of property or charters of protection accorded to monasteries and religious institutions. In an era when there was much fabrication of such documents, those who procured bulls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Holy Ghost
The Order of the Holy Ghost (also known as Hospitallers of the Holy Spirit) is a Catholic religious order. It was founded in 1180 in Montpellier by Gui of Montpellier, the son of William VII of Montpellier, for the care of the sick by groups of lay people. Pope Innocent III recognised the order on 23 April 1198. It was originally based in Montpellier and in Rome. A small female remnant survives in Poland. History The order was responsible for running hospitals - known as Hospitals of the Holy Ghost - throughout Europe for centuries. At its prime, they numbered many hundreds. The wealth of its Financial endowment, endowments made it a repeated target for the unscrupulous. The lay Knights of the Holy Ghost formed on analogy to military orders, but without military function, repeatedly attempted to divert the group's assets to their own use. Several popes made efforts to protect the order as a purely religious body, but Pope Pius V in 1619 re-created the Knights and again divert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia Of Jesus Christ
The Militia of Jesus Christ () was a military order in Lombardy during the High Middle Ages. It was founded at Parma by Bartholomew, Bishop of Vicenza, a Dominican, in 1233 and approved by Pope Gregory IX, who gave it a rule in 1234 and placed under the jurisdiction of the Dominicans.Though Lateran IV had prohibited the formulation of new religious rules, Gregory recognised the Militia as an association of laymen completely obedient to their master general and their military life. Its chief purpose was to combat what the Catholic Church viewed as heresy, like Catharism and Waldensianism, and to strengthen the bond between the Roman Church and the local nobility. In imitation of the Order of Santiago, members of the Militia did not take a vow of chastity, nor did they live communally or in poverty.Vincent, 953–54. The membership in turn was divided into two classes: the high-born urban nobility and the bourgeoisie. The urban nature of the militia meant an emphasis on help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Faith And Peace
The Order of the Faith and Peace or Order of the Sword was a military order in Gascony in the mid-13th century. The order was first mentioned by Pope Gregory IX in 1231 in a letter to ''magistro militiae ordinis sancti Jacobi ejusque fratribus tam presentibus quam futuris ad defensionem fidei et pacis in Guasconia constitutis'' ("the master of the military order of Saint James and his brothers present and future constituted for the defence of the faith and of the peace in Gascony").Forey (1989), 7. It was founded by Amanieu I, Archbishop of Auch. Since Amanieu had been appointed to his see in 1226, the date of the foundation must be located in 1226–1231. Gregory had sent a letter to Amanieu in 1227 exhorting him to establish the peace, which may have prompted the founding of an order of knighthood. Amanieu and the order's earliest members travelled to Rome in 1231 and there received confirmation from Gregory. The order had properties mainly west of Toulouse in the dioces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Santiago
The Order of Santiago (; ) is a religious and military order founded in the 12th century. It owes its name to the patron saint of Spain, ''Santiago'' ( St. James the Greater). Its initial objective was to protect the pilgrims on the Way of St. James, to defend Christendom and to remove the Muslim Moors from the Iberian Peninsula with the Reconquista. Entrance was not restricted to nobility of Spain exclusively, and some members have been Catholic Europeans from other parts of Europe. The Order's insignia is particularly recognisable and abundant in Western art. With the culmination of the Reconquista and the death of the Grand Master Alonso de Cárdenas, the Catholic Monarchs incorporated the Order into the Spanish Crown, and the Pope Adrian VI forever united the office of Grand Master of Santiago to the Crown in 1523. The First Republic suppressed the Order in 1873, but it was re-established in the Restoration as a nobiliary institute of honorable character. The Orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |