|
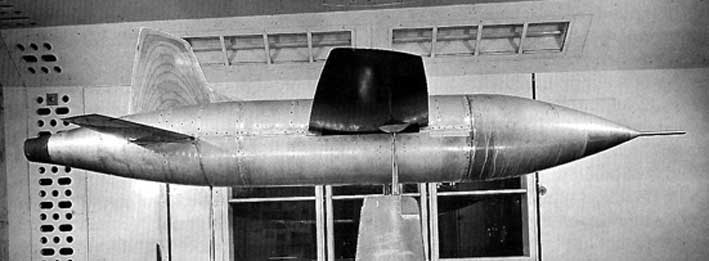
Miles M.52
The Miles M.52 was a turbojet-powered supersonic research aircraft project designed in the United Kingdom in the mid-1940s. In October 1943, Miles Aircraft was issued with a contract to produce the aircraft in accordance with Air Ministry Specification E.24/43. The programme was highly ambitious for its time, aiming to produce an aircraft capable of a speed of at least during level flight, and involved a very high proportion of cutting-edge aerodynamic research and innovative design work. Until 1945 all work on the project was undertaken with a high level of secrecy. In February 1946, the programme was terminated by the new Labour government of Clement Attlee, seemingly due to budgetary reasons as well as the disbelief of some ministry officials regarding the practicality of supersonic aircraft. In September 1946 the existence of the M.52 project was revealed to the general public, leading to criticism of the decision and calls for an official explanation of why the project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is an affinity group for contributors with shared goals within the Wikimedia movement. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sibling projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Gas Turbine Establishment
The National Gas Turbine Establishment (NGTE Pyestock) in Farnborough, part of the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE), was the prime site in the UK for the design and development of gas turbine and jet engines. For over 50 years, Pyestock was at the forefront of gas turbine development. The NGTE came into existence during the mid-1940s, its principal predecessors were Power Jets, a formerly private company headed by Frank Whittle, the inventor of the jet engine, and the RAE turbine development team; the design teams of both entities were incorporated, initially being led by Whittle and Hayne Constant. Upon its creation, it was nationalised and ran as a state-owned entity. A major function of the NGTE was to function as a testing and development centre, both for experimental developments and to support commercial engine companies. It was decided to base the turbine development site at Pyestock, a former golf course in a secluded wooded spot between Farnborough and Fleet; the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force and civil aviation that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State for Air. Organisations before the Air Ministry The Air Committee On 13 April 1912, less than two weeks after the creation of the Royal Flying Corps (which initially consisted of both a naval and a military wing), an Air Committee was established to act as an intermediary between the Admiralty and the War Office in matters relating to aviation. The new Air Committee was composed of representatives of the two war ministries, and although it could make recommendations, it lacked executive authority. The recommendations of the Air Committee had to be ratified by the Admiralty Board and the Imperial General Staff and, in consequence, the Committee was not particularly effective. The increasing separation of army and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Me 262
The Messerschmitt Me 262, nicknamed (German for "Swallow") in fighter versions, or ("Storm Bird") in fighter-bomber versions, is a fighter aircraft and fighter-bomber that was designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt. It was the world's first operational jet-powered fighter aircraft and one of two jet fighter aircraft types to see air-to-air combat in World War Two, the other being the Heinkel He 162. The design of what would become the Me 262 started in April 1939, before World War II. It made its maiden flight on 18 April 1941 with a piston engine, and its first jet-powered flight on 18 July 1942. Progress was delayed by problems with engines, metallurgy Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the ..., and interference from Luftwaffe chie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Me 163
The Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet is a rocket-powered interceptor aircraft primarily designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt. It is the only operational rocket-powered fighter aircraft in history as well as the first piloted aircraft of any type to exceed in level flight. Development of what would become the Me 163 can be traced back to 1937 and the work of the German aeronautical engineer Alexander Lippisch and the '' Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug'' (DFS). Initially an experimental programme that drew upon traditional glider designs while integrating various new innovations such as the rocket engine, the development ran into organisational issues until Lippisch and his team were transferred to Messerschmitt in January 1939. Plans for a propeller-powered intermediary aircraft were quickly dropped in favour of proceeding directly to rocket propulsion. On 1 September 1941, the prototype performed its maiden flight, quickly demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engine
A rocket engine is a reaction engine, producing thrust in accordance with Newton's third law by ejecting reaction mass rearward, usually a high-speed Jet (fluid), jet of high-temperature gas produced by the combustion of rocket propellants stored inside the rocket. However, non-combusting forms such as cold gas thrusters and nuclear thermal rockets also exist. Rocket vehicles carry their own oxidiser, unlike most combustion engines, so rocket engines can be used in a vacuum, and they can achieve great speed, beyond escape velocity. Vehicles commonly propelled by rocket engines include missiles, Rocket-assisted projectile, artillery shells, ballistic missiles and rockets of any size, from tiny Rocket (firework), fireworks to Rocket (weapon), man-sized weapons to huge Space vehicle, spaceships. Compared to other types of jet engine, rocket engines are the lightest and have the highest thrust, but are the least propellant-efficient (they have the lowest specific impulse). The ideal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swept Wing
A swept wing is a wing angled either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than perpendicular to the fuselage. Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investigated in Germany as early as 1935 by Albert Betz and Adolph Busemann, finding application just before the end of the Second World War. It has the effect of delaying the shock waves and accompanying aerodynamic drag rise caused by fluid compressibility near the speed of sound, improving performance. Swept wings are therefore almost always used on jet aircraft designed to fly at these speeds. The term "swept wing" is normally used to mean "swept back", but variants include forward sweep, variable sweep wings and oblique wings in which one side sweeps forward and the other back. The delta wing is also aerodynamically a form of swept wing. Reasons for sweep There are three main reasons for sweeping a wing: 1. to arrange the center of gravity o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Hooker
Sir Stanley George Hooker, CBE, FRS, DPhil, BSc, FRAeS, MIMechE, FAAAS (30 September 1907 – 24 May 1984), was an English mathematician and jet engine engineer. He was employed first at Rolls-Royce where he worked on the earliest designs such as the Welland and Derwent, and later at Bristol Aero Engines where he helped bring the troubled Proteus turboprop and the Olympus turbojet to market. He then designed the famous Pegasus vectored thrust turbofan used in the Hawker Siddeley Harrier. Early life Stanley George Hooker was born at Sheerness, the son of a farm labourer who had earlier been a licensed victualler, and educated at Borden Grammar School. He won a scholarship for Imperial College London to study mathematics, and in particular, hydrodynamics. He became more interested in aerodynamics, won the Busk studentship in aeronautics in 1928 and moved to Brasenose College, Oxford where he received his DPhil in this area in 1935. Rolls-Royce In late 1937, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Busemann
Adolf Busemann (20 April 1901 – 3 November 1986) was a German aerospace engineer and influential Nazi-era pioneer in aerodynamics, specialising in supersonic airflows. He introduced the concept of swept wings and, after emigrating in 1947 to the United States under Operation Paperclip, invented the shockwave-free supersonic Busemann biplane. Education and early life Born in Lübeck, Germany, Busemann attended the Technical University of Braunschweig, receiving his Ph.D. in engineering in 1924. Career and research The next year he was given the position of aeronautical research scientist at the Max-Planck Institute where he joined the famed team led by Ludwig Prandtl, including Theodore von Kármán, Max Munk and Jakob Ackeret. In 1930 he was promoted to professor at University of Göttingen. He held various positions within the German scientific community during this period, and during the war he was the director of the Braunschweig Laboratory, a famous research establishm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion) and (the study of water and other liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moment (physics), moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipeline transport, pipelines, weather forecasting, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space, understanding large scale Geophysical fluid dynamics, geophysical flows involving oceans/atmosphere and Nuclear weapon design, modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressibility
In thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, the compressibility (also known as the coefficient of compressibility or, if the temperature is held constant, the isothermal compressibility) is a measure of the instantaneous relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure (or mean stress) change. In its simple form, the compressibility \kappa (denoted in some fields) may be expressed as :\beta =-\frac\frac, where is volume and is pressure. The choice to define compressibility as the negative of the fraction makes compressibility positive in the (usual) case that an increase in pressure induces a reduction in volume. The reciprocal of compressibility at fixed temperature is called the isothermal bulk modulus. Definition The specification above is incomplete, because for any object or system the magnitude of the compressibility depends strongly on whether the process is isentropic or isothermal. Accordingly, isothermal compressibility is defined: :\beta_T=-\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |