|
Mikołaj Kunicki
Mikołaj Kunicki (1914 – 2001) was a Polish soldier, who also served in the German auxiliary units (Kompanieführer in Schutzmannschaft 104), and later became commander of the Polish-Soviet Rally Brigade Partisan (in the rank of captain). Biography In 1939, he participated in the September campaign. He fought to defend Warsaw. In 1939, he escaped from German captivity and returned to his family home. In 1942, he was called to serve in Schutzmannschaft, in Kobryn. From March to November 1942, he was in training at the German military school in Kobrin (sabotage-diversion). He graduated from the field of Feldwebel. From January 1943, the company commander in the , which liquidated, among others UPA branches near Wysocka. After the attack of Ukrainian militias on Polish villages and then the refusal of the German command to retaliate against the Ukrainians, he and his company (150 soldiers) deserted. In March 1943, he made contact with the Soviet partisans, and then joined them, kil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collaboration In German-occupied Poland
During the German occupation of Poland, citizens of all its major ethnic groups collaborated with the Germans. Estimates of the number of collaborators vary. Collaboration in Poland was less institutionalized than in some other countries and has been described as marginal, a point of pride with the Polish people. During and after the war, the Polish government in exile (a member of the Allied coalition that fought Nazi Germany) and the Polish resistance movement punished collaborators and sentenced thousands of them to death. Background Following the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in March 1939, Hitler sought to establish Poland as a client state, proposing a multilateral territorial exchange and an extension of the German–Polish non-aggression pact. The Polish government, fearing subjugation to Nazi Germany, instead chose to form an alliance with Britain (and later with France). In response, Germany withdrew from the non-aggression pact and shortly before invading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
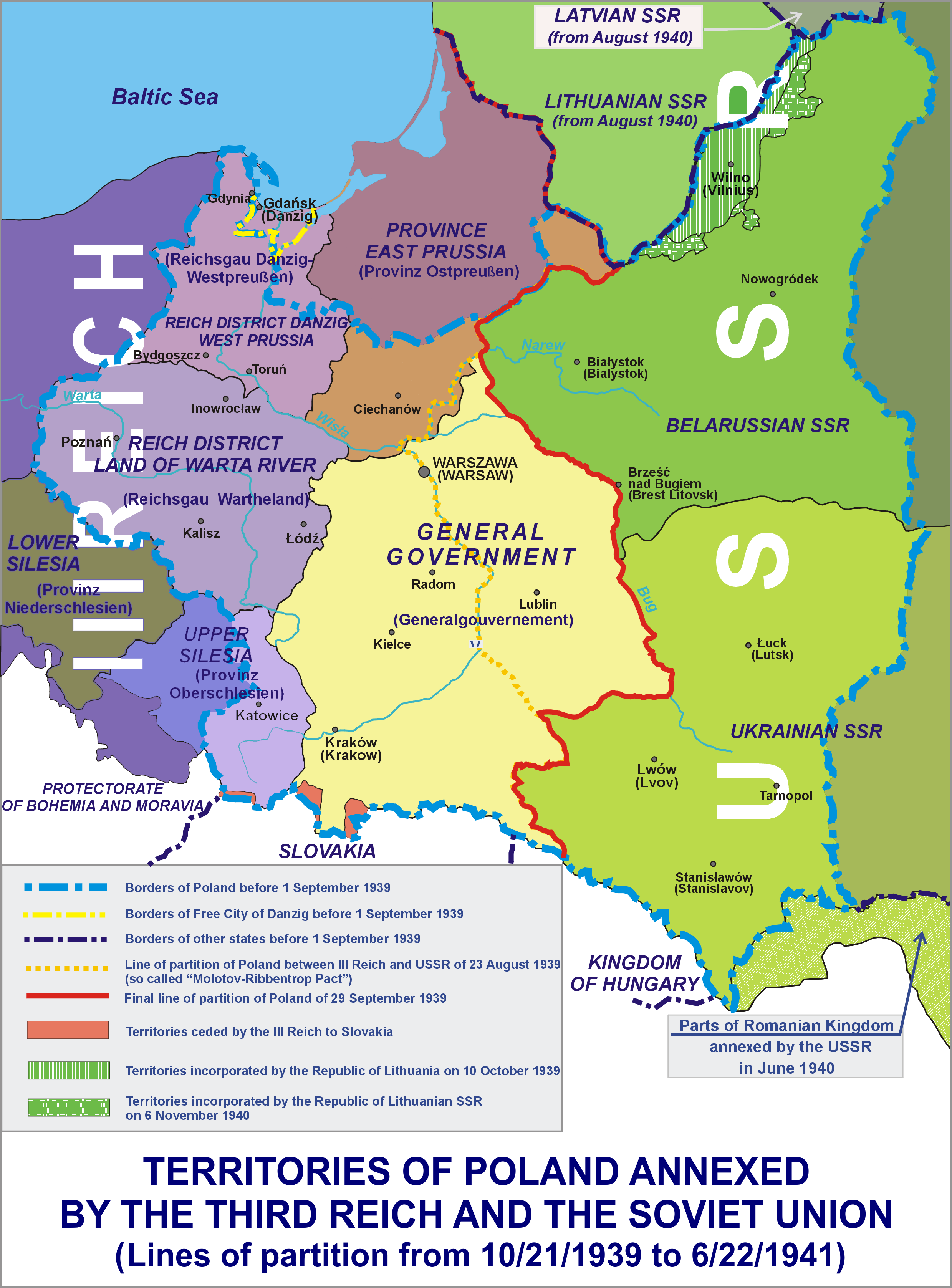
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic, and the Soviet Union, which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviet invasion of Poland, Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The aim of the invasion was to disestablish Poland as a sovereign country, with its citizens destined for The Holocaust, extermination. German and Field Army Bernolák, Slovak forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzmannschaft
The ''Schutzmannschaft'', or Auxiliary Police ( "protection team"; plural: ''Schutzmannschaften'', abbreviated as ''Schuma'') was the collaborationist auxiliary police of native policemen serving in those areas of the Soviet Union and the Baltic states occupied by Nazi Germany during World War II. Heinrich Himmler, head of the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS), established the ''Schutzmannschaft'' on 25 July 1941, and subordinated it to the Order Police (''Ordnungspolizei''; Orpo). By the end of 1941, some 45,000 men served in ''Schutzmannschaft'' units, about half of them in the battalions. During 1942, ''Schutzmannschaften'' expanded to an estimated 300,000 men, with battalions accounting for about a third, or less than one half of the local force. Everywhere, local police far outnumbered the equivalent German personnel several times; in most places, the ratio of Germans to natives was about 1-to-10. The auxiliary police battalions (''Schutzmannschaft-Bataillone'') were created to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The American Historical Review
''The American Historical Review'' is a quarterly academic history journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Historical Association, for which it is an official publication. It targets readers interested in all periods and facets of history and has often been described as the premier journal of American history in the world. In the 2011 ''Journal Citation Reports'', the ''AHR'' had the highest impact factor among all history journals. The journal publishes four issues per year, in March, June, September, and December with research articles, reviews, and other items. The acceptance rate for research article submissions is 8-10%. The journal publishes approximately 650 reviews per year. History Founded in 1895, ''The American Historical Review'' was a joint effort between the history departments at Cornell University and at Harvard University, modeled on '' The English Historical Review'' and the French '' Revue historique'', "for the promotion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Partisans
Soviet partisans were members of Resistance during World War II, resistance movements that fought a Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against Axis powers, Axis forces during World War II in the Soviet Union, the previously Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union, Soviet-occupied territories of interwar Poland in 1941–45 and eastern Finland. The activity emerged after Nazi Germany's Operation Barbarossa was launched from mid-1941 on. It was Central Headquarters of the Partisan Movement, coordinated and controlled by the Soviet government and modeled on that of the Red Army. The partisans made a significant contribution to the war by countering German plans to exploit occupied Soviet territories economically, gave considerable help to the Red Army by conducting systematic attacks against Germany's rear communication network, disseminated political rhetoric among the local population by publishing newspapers and leaflets, and succeeded in creating and maintaining feelings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily Begma
Vasili, Vasily, Vasilii or Vasiliy (Russian: Василий) is a Russian masculine given name of Greek origin and corresponds to ''Basil''. It may refer to: *Vasily I of Moscow Grand Prince from 1389–1425 *Vasily II of Moscow Grand Prince from 1425–1462 *Vasili III of Russia Grand Prince from 1505–1533 *Vasili IV of Russia Tsar from 1606–1610 *Basil Fool for Christ (1469–1557), also known as Saint Basil, or Vasily Blazhenny *Vasily Alekseyev (1942–2011), Soviet weightlifter *Vasily Arkhipov (1926–1998), Soviet Naval officer in the Cuban Missile Crisis *Vasily Boldyrev (1875–1933), Russian general *Vasily Chapayev (1887–1969), Russian Army commander *Vasily Chuikov (1900–1982), Soviet marshal *Vasily Degtyaryov (1880–1949), Russian weapons designer and Major General *Vasily Dzhugashvili (1921–1962), Stalin's son *Vasili Golovachov (born 1948), Russian science fiction author *Vasily Grossman (1905–1964), Soviet writer and journalist *Vasily Ignatenko (1961 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |