|
Midan - Jezmatieh Street
Al-Midan ( ar, حي الميدان) is a neighbourhood and municipality in Damascus, Syria, south of the old walled city and near the modern city centre. In the 2004 census, it had a population of 177,456. Today, the neighbourhood is often considered to be one of the most conservative in Damascus. Etymology The name Midan is derived from Midan Al Hassa ( ar, ميدان الحصى) or the field of gravel. The neighbourhood was located between two sub Barada streams and when it rained heavily, the land gravel deposits filled the streams and consequently, the neighbourhood. History Al-Midan started during the Mamluk rule over Damascus. It took its final form about 400 years ago during the Ottoman empire and has not experienced any major changes since. It is considered the Southern Gate of Damascus and was created as a trading center by the people of Damascus for them to be closer to the people of the Hauran and to improve trade and economic relations between them. During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries Of The World
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq ( ar, ميشيل عفلق, Mīšīl ʿAflaq, , 9 January 1910 – 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociology, sociologist and Arab nationalism, Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its political movement; he is considered by several Ba'athists to be the principal founder of Ba'athist thought. He published various books during his lifetime, the most notable being ''The Battle for One Destiny'' (1958) and ''The Struggle Against Distorting the Movement of Arab Revolution'' (1975). Born into a middle-class family in Damascus, Syria, Aflaq studied at the University of Paris, Sorbonne, where he met his future political companion Salah al-Din al-Bitar. He returned to Syria in 1932, and began his political career in Communism, communist politics. Aflaq became a communist activist, but broke his ties with the communist movement when the Syrian–Lebanese Communist Party supported colonial policies through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Zahra Al-Jadeeda
Al-Zahra al-Jadeeda is a neighbourhood of Damascus, Syria. It lies within the Al-Midan Al-Midan ( ar, حي الميدان) is a neighbourhood and municipality in Damascus, Syria, south of the old walled city and near the modern city centre. In the 2004 census, it had a population of 177,456. Today, the neighbourhood is often ... municipality, east of the Al-Midan neighbourhood. References Neighborhoods of Damascus {{DamascusSY-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadamon, Syria
Tadamon ( ar, التضامن, at-Taḍāmun; also spelled ''Tadamoun'' or ''Tadamun'') is a neighborhood and district of the al-Midan municipality of Damascus, Syria. The neighborhood has been active in the Syrian civil war. History Until the 1960s, the area of Tadamon was largely covered by orchards. However, the area began to be populated by Syrians who had fled the Golan Heights after Israel occupied that region in the 1967 Six Day War. The area also saw an influx of Syrians moving in from the countryside of Damascus. Most of the people who moved to Tadamon built their homes without government permits and the area has since developed as an informal neighborhood where roughly 90% of homes lack formally registered property deeds. During the Syrian Civil War, in 2012, most of Tadamon was overrun by rebels fighting under the banner of the Free Syrian Army (FSA). In 2013, the area was the site of the Tadamon massacre, where 280+ people were executed by Syrian Military Intelligence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrian Arab News Agency
The Syrian Arab News Agency (SANA) ( ar, الوكالة العربية السورية للأنباء (سانا), ) is a Syrian state-controlled news agency, linked to the country's ministry of information. It was established in June 1965. Website SANA launched its website in 1997. Up until November 2012, SANA's website was hosted in Dallas, Texas, by the United States company SoftLayer. Due to sanctions related to the Syrian Civil War, which make this hosting illegal, the SoftLayer company was obliged to terminate its hosting responsibilities with SANA. SANA's English website states that the agency "adopts Syria's national firm stances and its support to the Arab and Islamic causes and principles with the aim of presenting the real civilized image of Syria." Critiques According to a German funded state public news agency '' DW News SANA'' "when it comes to hard politics, the agency has a clear agenda" and "SANA, being a public news agency, has a stake in the conflict to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awameh
Lokma, also known by their Greek name, loukoumades, are pastries made of leavened and deep fried dough balls, soaked in syrup or honey, sometimes coated with cinnamon or other ingredients. The dish was described as early as the 13th century by al-Baghdadi as ''luqmat al-qādi'' (), "judge's morsels". Etymology The Arabic word () (plural ), means ''morsel'', ''mouthful'', or ''bite''. The dish was known as () or "judge's morsels" in 13th century Arabic cookery books, and the word ''luqma'' or ''loqma'' by itself has come to refer to it. The Turkish name for the dish, , is derived from the Arabic, as is the Greek name (). History The recipe for ''Luqmat al-Qadi'', yeast-leavened dough boiled in oil and doused in honey or sugar syrup with rosewater, dates back to at least the early medieval period and the 13th-century Abbasid Caliphate, where it is mentioned in several of the existent cookery books of the time. It is also mentioned in the ''One Thousand and One Nights'', in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basbousa
Basbousa () is a sweet, syrup-soaked semolina cake that originated in Egypt. The semolina batter is baked in a sheet pan, then sweetened with orange flower water, rose water or simple syrup, and typically cut into diamond (lozenge) shapes or squares. The dish has also spread within most areas of the former Ottoman Empire, and is generally featured in Middle Eastern cuisines, Greek cuisine, Azerbaijani cuisine, Ethiopian cuisine, and many others. Names It is found in the cuisines of the Middle East, the Balkans and the North Africa under a variety of names. *Arabic: هريسة ''harīsa'' (meaning mashed or crushed), نمورة ''nammoura'', بسبوسة ''basbūsah'' * * *Greek: ραβανί (''ravani''), ρεβανί (''revani''), σάμαλι (''samali'') * * *Macedonian and * * * Basbousa is the most common name for this dessert in the Middle East but it may be named differently depending on the region; It is often called "hareesa" in the Levant. Note that "harissa" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
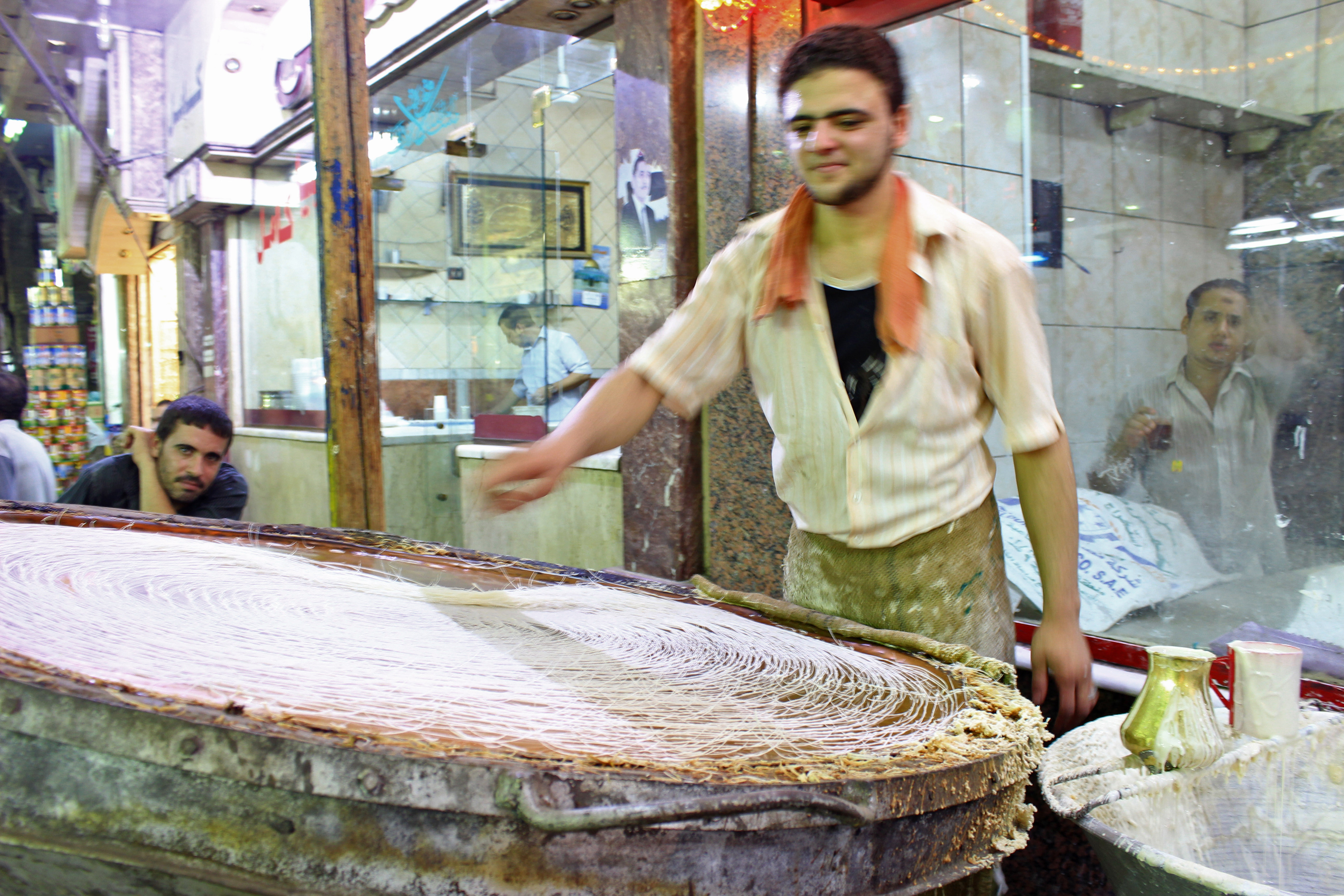
Kanafeh
Knafeh ( ar, كنافة) is a traditional Middle Eastern dessert made with spun pastry called ''kataifi'', soaked in a sweet, sugar-based syrup called attar, and typically layered with cheese, or with other ingredients such as clotted cream, pistachio or nuts, depending on the region. It is popular in the Middle East. Variants are also found in Turkey, Greece, and the Balkans. In Arabic, the name may refer to the string pastry itself, or to the entire dessert dish. In Turkish, the string pastry is known as , and the cheese-based dessert that uses it as . In the Balkans, the shredded dough is similarly known as , and in Greece as , and is the basis of various dishes rolled or layered with it, including dessert pastries with nuts and sweet syrups. One of the most well-known preparations of the dessert is ''knafeh Nabulsiyeh'', which originated in the city of Nablus, and is the most representative Palestinian dessert. uses a white- brine cheese called Nabulsi. It is prepared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barazek
Barazek or barazeq (in Arabic برازق ''barāzeq'') is a Syrian-Palestinian cookie whose main ingredient is sesame (سمسم ''sumsum'') and often also contain pieces of pistachio. It probably originated during Ottoman rule in the Syrian capital, Damascus, particularly in the Al-Midan neighborhood, although today it is so popular that it can be found in most pastry shops throughout the Levantine area (Lebanon, Jordan, Palestine and Syria) and beyond. It is also one of the more traditional Palestinian desserts and it is easy to find stalls selling barazek on the streets of Jerusalem. It is considered one of the most famous Syrian desserts and has a multitude of variants. All include flour, butter, sugar, and sesame; some may also include egg, milk, pistachios, honey, mahleb, yeast, and vanilla, as well as clarified butter ('' samneh'') instead of regular butter. It has a sweet, buttery and nutty flavor, and a crisp and brittle texture. Preparation The following recipe does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baklava
Baklava (, or ; ota, باقلوا ) is a layered pastry dessert made of filo pastry, filled with chopped nuts, and sweetened with syrup or honey. It was one of the most popular sweet pastries of Ottoman cuisine. The pre- Ottoman origin of the dish is unknown, but, in modern times, it is a common dessert of Turkish, Iranian and Arab cuisines, and other countries of the Levant and Maghreb, along with the South Caucasus, Balkans, and Central Asia. Etymology The word ''baklava'' is first attested in English in 1650, a borrowing from ota, باقلاوه . The name baklava is used in many languages with minor phonetic and spelling variations. Historian Paul D. Buell argues that the word "baklava" may come from the Mongolian root ' 'to tie, wrap up, pile up' composed with the Turkic verbal ending ''-v''; baγla- itself in Mongolian is a Turkic loanword. Sevan Nişanyan considers its oldest known forms (pre-1500) to be ''baklağı'' and ''baklağu'', and labels it as being of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Midani Sweet Shop
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, r ..., common examples include Holiday, holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like court dress, lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years—the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is commonly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain Trade
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals and other food grains such as wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other agricultural products. Healthy grain supply and trade is important to many societies, providing a caloric base for most food systems as well as important role in animal feed for animal agriculture. The grain trade is as old as agricultural settlement, identified in many of the early cultures that adopted sedentary farming. Major societal changes have been directly connected to the grain trade, such as the fall of the Roman Empire. From the early modern period onward, grain trade has been an important part of colonial expansion and international power dynamics. The geopolitical dominance of countries like Australia, the United States, Canada and the Soviet Union during the 20th century was connected with their status as grain surpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |