|
Microphonism
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which is intentionally designed to convert vibrations to electrical signals. Description When electronic equipment was built using vacuum tubes, microphonics were often a serious design problem. The charged elements in the vacuum tubes can mechanically vibrate, changing the distance between the elements, producing charge flows in and out of the tube in a manner identical to a capacitor microphone. A system sufficiently susceptible to microphonics could experience audio feedback, and make noises if jarred or bumped. To minimize these effects, some vacuum tubes were made with thicker internal insulating plates and more supports, and tube-socket assemblies were sometimes shock-mounted by means of small rubber grommets placed in the screw hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubber Grommet
A cable grommet is a tube or ring through which an electrical cable passes. They are usually made of rubber or metal. The grommet is usually inserted in holes in certain materials in order to protect, improve friction or seal cables passing through it, from a possible mechanical or chemical attack. Grommets used as wire managers for furniture A grommet can be used in furniture to protect wires, cables or cords for computer equipment or other electronic equipment in homes or offices. At the same time, they are used decoratively to embellish the furniture and can be bought in a large variety of sizes, colors and finishes. The grommets usually consist of two pieces: A liner that goes into the hole of the furniture and a cap with a hole (often adjustable in size) for the cables to go through. When there is no need to use them they can be blanked either by turning one piece 90° against the other or by inserting an extra plastic piece designed to fit that purpose. Rubber grommets " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Hammer
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in Electronics, electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise (electronics), noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which is intentionally designed to convert vibrations to electrical signals. Description When electronic equipment was built using vacuum tubes, microphonics were often a serious design problem. The charged elements in the vacuum tubes can mechanically vibrate, changing the distance between the elements, producing charge flows in and out of the tube in a manner identical to a capacitor microphone. A system sufficiently susceptible to microphonics could experience audio feedback, and make noises if jarred or bumped. To minimize these effects, some vacuum tubes were made with thicker internal insulating plates and more supports, and tube-socket assemblies were sometimes shock-mounted by means of small rubber g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Capacitor
Film capacitors, plastic film capacitors, film dielectric capacitors, or polymer film capacitors, generically called film caps as well as power film capacitors, are electrical capacitors with an insulating plastic film as the dielectric, sometimes combined with paper as carrier of the electrodes. The dielectric films, depending on the desired dielectric strength, are drawn in a special process to an extremely thin thickness, and are then provided with electrodes. The electrodes of film capacitors may be metallized aluminum or zinc applied directly to the surface of the plastic film, or a separate metallic foil. Two of these conductive layers are wound into a cylinder-shaped winding, usually flattened to reduce mounting space requirements on a printed circuit board, or layered as multiple single layers stacked together, to form a capacitor body. Film capacitors, together with ceramic capacitors and electrolytic capacitors, are the most common capacitor types for use in electronic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In-ear Monitor
An in-ear monitor (IEMs), in-ear, or colloquially earpiece is a listening device placed into the ear. More narrowly, the term in-ear monitor is defined as such a device used by musicians, audio engineers and audiophiles to listen to music or to hear a personal mix of vocals and stage instrumentation for live performance or recording studio mixing, often specifically in order to hear themselves through a sound system in real time. They are also used by television presenters to receive vocal instructions, information and breaking news announcements from a producer that only the presenter hears. They are often custom-fitted to an individual's ears to provide comfort and a high level of noise reduction from ambient surroundings. Their origins as a tool in live music performance can be traced back to the mid-1980s. A stage monitor system is any system that provides a mix of audio sources to a performer on stage. Traditionally, loudspeakers were placed on the stage directed toward th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Player
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as corresponding physical deviations of a helical or spiral groove engraved, etched, incised, or impressed into the surface of a rotating cylinder or disc, called a ''Phonograph record, record''. To recreate the sound, the surface is similarly rotated while a playback #Stylus, stylus traces the groove and is therefore vibrated by it, faintly reproducing the recorded sound. In early acoustic phonographs, the stylus vibrated a Diaphragm (acoustics), diaphragm that produced sound waves coupled to the open air through a flaring Horn loudspeaker, horn, or directly to the listener's ears through stethoscope-type earphones. The phonograph was invented in 1877 by Thomas Edison; its use would rise the following year. Alexander Graham Bell's Volta Laboratory an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Camera Tube
Video camera tubes are devices based on the cathode-ray tube that were used in television cameras to capture television images, prior to the introduction of charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensors in the 1980s. Several different types of tubes were in use from the early 1930s, and as late as the 1990s. In these tubes, an cathode ray, electron beam is scanned across an image of the scene to be broadcast focused on a target. This generated a current that is dependent on the brightness of the image on the target at the scan point. The size of the striking ray is tiny compared to the size of the target, allowing 480–486 horizontal scan lines per image in the NTSC format, 576 lines in PAL, and as many as 1035 lines in Multiple sub-Nyquist sampling encoding, Hi-Vision. Cathode-ray tube Any vacuum tube which operates using a focused beam of electrons, originally called cathode rays, is known as a cathode-ray tube (CRT). These are usually seen as display devices as used in older (i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by Doping (semiconductor), p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chassis
A chassis (, ; plural ''chassis'' from French châssis ) is the load-bearing framework of a manufactured object, which structurally supports the object in its construction and function. An example of a chassis is a vehicle frame, the underpart of a motor vehicle, on which the body is mounted; if the running gear such as wheels and transmission, and sometimes even the driver's seat, are included, then the assembly is described as a rolling chassis. Examples Vehicles In the case of vehicles, the term ''rolling chassis'' means the frame plus the "running gear" like engine, transmission, drive shaft, differential, and suspension. The "rolling chassis" description originated from assembly production when an integrated chassis "rolled on its own tires" just before truck bodies were bolted to the frames near the end of the line. An underbody (sometimes referred to as " coachwork"), which is usually not necessary for the integrity of the structure, is built on the chassis to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
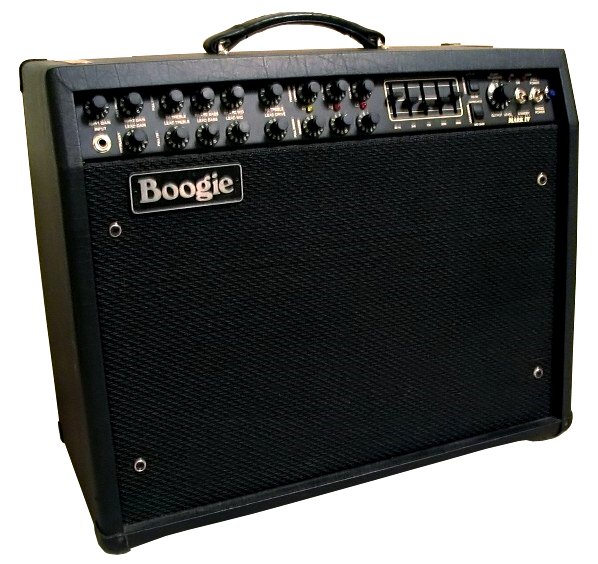
Guitar Amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic amplifier, electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a Pickup (music technology), pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce sound through one or more loudspeakers, which are typically housed in a wooden speaker enclosure, cabinet. A guitar amplifier may be a standalone wood or metal cabinet that contains only the power amplifier (and preamplifier) circuits, requiring the use of a separate speaker cabinet–or it may be a ''combo'' amplifier, which contains both the amplifier and one or more speakers in a wooden cabinet. There is a wide range of sizes and power ratings for guitar amplifiers, from small, lightweight practice amplifiers with a single 6-inch speaker and a 10-watt amp to heavy combo amps with four 10-inch or four 12-inch speakers and a 100-watt amplifier, which are loud enough to use in a nightclub or bar performance. Guitar amplifiers can also modify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric current, current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor. A static electric charge can be created whenever two surfaces contact and/or slide against each other and then separate. The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because they can feel, hear, and even see sparks if the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to an electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shockmore specifically, an electrostatic dischargeis caused by the neutralization of a charge. Causes Materials are made of atoms that are normally electrically neutral because they contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |