|
Microducts
Microducts are small ducts used for the installation of fibre optic cables. They have a typical size ranging from 3 to 16 mm and are installed as bundles within larger ducts. Description Microducts are typically small-diameter, flexible, or semi-flexible ducts designed to provide clean, continuous, low-friction paths for placing optical cables that have relatively low pulling tension limits. As stated in industry requirements document Telcordiabr>GR-3155 Telcordia. ''Generic Requirements for Microducts for Fiber Optic Cables,'' microduct products are expected to: * Be compatible with existing construction designs and building configurations for both riser- and plenum-rated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Jetting
Cable jetting is a technique to install cables in ducts. It is commonly used to install cables with optical fibers in underground polyethylene ducts and is an alternative to ''pulling''. Pulling Traditionally, fibre optic cables were pulled through cable ducts in the same way as other cables, via a winch line. Every time the fibre passes a bend or undulation in the duct, the pulling force is multiplied by a friction-dependent factor (which can be reduced by using lubricant). This means that the higher the local pulling force is, the more friction the cable will experience while being pulled against the internal duct wall. This "capstan effect" leads to an exponential force build-up with pull distance, producing generally high pulling forces. Jetting Cable jetting is the process of blowing a cable through a duct while simultaneously pushing the cable into the duct. Compressed air is injected at the duct inlet and flows through the duct and along the cable at high speed. (Preferabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protective Duct With Bundle
Protection is any measure taken to guard a thing against damage caused by outside forces. Protection can be provided to physical objects, including organisms, to systems, and to intangible things like civil and political rights. Although the mechanisms for providing protection vary widely, the basic meaning of the term remains the same. This is illustrated by an explanation found in a manual on electrical wiring: Some kind of protection is a characteristic of all life, as living things have evolved at least some protective mechanisms to counter damaging environmental phenomena, such as ultraviolet light. Biological membranes such as bark on trees and skin on animals offer protection from various threats, with skin playing a key role in protecting organisms against pathogens and excessive water loss. Additional structures like scales and hair offer further protection from the elements and from predators, with some animals having features such as spines or camouflage servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
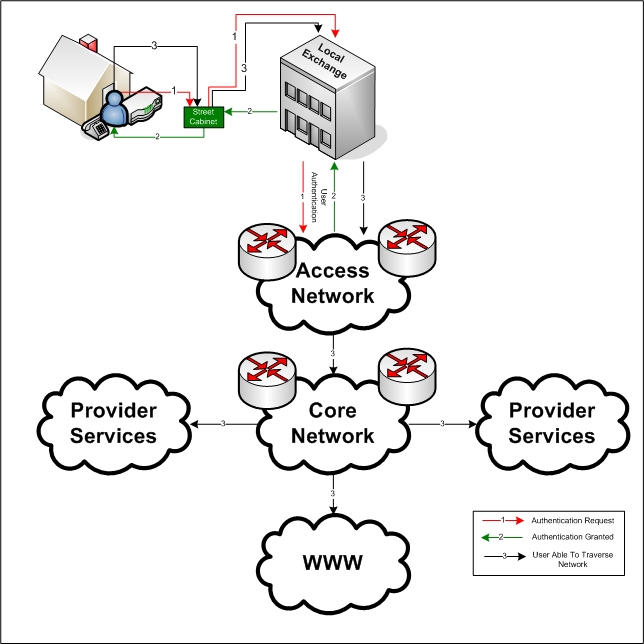
Telephone Exchange
telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a telecommunications system used in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It interconnects telephone subscriber lines or virtual circuits of digital systems to establish telephone calls between subscribers. In historical perspective, telecommunication terms have been used with different semantics over time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. Often, a ''central office'' is defined as a building used to house the inside plant equipment of potentially several telephone exchanges, each serving a certain geographical area. Such an area has also been referred to as the exchange or exchange area. In North America, a central office location may also be identified as a ''wire center'', designating a facility to which a telephone is connected and obtains dial tone. For business and billing purposes, telecommunication carriers def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurescom
Eurescom is a private organisation for managing European research and development projects in telecommunications. Eurescom is based in Heidelberg, Germany, and currently has 16 network operators as members performing collaborative research and development. History In 1991, the European Institute for Research and Strategic Studies in Telecommunications GmbH (Eurescom) was founded by European telecommunications network operators as an organisation for coordinating collaborative research and development programmes. In mid-1990, 26 European network operators signed a Memorandum of Understanding as a basis for establishing the institute as a centre for collaborative research and development in Heidelberg, Germany. Since 1991, Eurescom produced several hundred European telecommunications technology project results. Eurescom made, for example, contributions to the introduction of interoperable European ISDN, the design of network management systems, specifications in the Internet domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundle Jetting
Bundle or Bundling may refer to: * Bundling (packaging), the process of using straps to bundle up items Biology * Bundle of His, a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction * Bundle of Kent, an extra conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles in the heart * Hair bundle, a group of cellular processes resembling hair, characteristic of a hair cell Computing * Bundle (OS X), a type of directory in NEXTSTEP and OS X * Bundle (software distribution), a package containing a software and everything it needs to operate * Bundle adjustment, a photogrammetry/computer vision technique Economics * Bundled payment, a method for reimbursing health care providers * Product bundling, a marketing strategy that involves offering several products for sale as one combined product Mathematics and engineering * Bundle (mathematics), a generalization of a fiber bundle dropping the condition of a local product structure * Bundle conductor (power engineering) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications network which connects subscribers to their immediate service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality of the records which describe the network. In 2006, accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outside Plant
In telecommunication, the term outside plant has the following meanings: *In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure (such as conduit, cabinets, tower or poles), and any associated hardware (such as repeaters) located between a demarcation point in a switching facility and a demarcation point in another switching center or customer premises. *In the United States, the DOD defines outside plant as the communications equipment located between a main distribution frame (MDF) and a user end instrument. The CATV industry divides its fixed assets between head end or inside plant, and outside plant. The electrical power industry also uses the term outside plant to refer to electric power distribution systems. Context Network connections between devices such as computers, printers, and phones require a physical infrastructure to carry and process signals. Typically, this infrastructure will consist of: * C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre Optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber and find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at higher bandwidths (data transfer rates) than electrical cables. Fibers are used instead of metal wires because signals travel along them with less loss; in addition, fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, a problem from which metal wires suffer. Fibers are also used for illumination and imaging, and are often wrapped in bundles so they may be used to carry light into, or images out of confined spaces, as in the case of a fiberscope. Specially designed fibers are also used for a variety of other applications, some of them being fiber optic sensors and fiber lasers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FTTH
Fiber to the ''x'' (FTTX; also spelled "fibre") or fiber in the loop is a generic term for any broadband network architecture using optical fiber to provide all or part of the local loop used for last mile telecommunications. As fiber optic cables are able to carry much more data than copper cables, especially over long distances, copper telephone networks built in the 20th century are being replaced by fiber. FTTX is a generalization for several configurations of fiber deployment, arranged into two groups: FTTP/FTTH/FTTB (Fiber laid all the way to the premises/home/building) and FTTC/N (fiber laid to the cabinet/node, with copper wires completing the connection). Residential areas already served by balanced pair distribution plant call for a trade-off between cost and capacity. The closer the fiber head, the higher the cost of construction and the higher the channel capacity. In places not served by metallic facilities, little cost is saved by not running fiber to the home. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)