|
Microcachrys Tetragona Coniferous Heath
''Microcachrys tetragona'', known as creeping pine or creeping strawberry pine, is a species of dioecious conifer belonging to the podocarp family (Podocarpaceae).Christopher N. Page. 1990. "Podocarpaceae" pages 332-346. In: Klaus Kubitzki (general editor); Karl U. Kramer and Peter S. Green (volume editors) ''The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants'' volume I. Springer-Verlag: Berlin;Heidelberg, Germany. It is the sole species of the genus ''Microcachrys''.James E. Eckenwalder. 2009. ''Conifers of the World''. Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA. . The plant is endemic to western Tasmania, where it is a low shrub growing to 1 m tall at high altitudes. Its leaves are scale-like, arranged (unusually for the Podocarpaceae) in opposite decussate pairs, superficially resembling those of the unrelated '' Diselma archeri'' (Cupressaceae). It shares the common name Creeping pine with several other plants. Females produce tiny, red, edible berries in summer. Fossil record and paleoend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Dalton Hooker
Sir Joseph Dalton Hooker (30 June 1817 – 10 December 1911) was a British botanist and explorer in the 19th century. He was a founder of geographical botany and Charles Darwin's closest friend. For 20 years he served as director of the Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew, succeeding his father, William Jackson Hooker, and was awarded the highest honours of British science. Biography Early years Hooker was born in Halesworth, Suffolk, England. He was the second son of Maria Sarah Turner, eldest daughter of the banker Dawson Turner and sister-in-law of Francis Palgrave, and the famous botanist Sir William Jackson Hooker, Regius Professor of Botany, Glasgow, Regius Professor of Botany. From the age of seven, Hooker attended his father's lectures at the University of Glasgow, taking an early interest in plant geography, plant distribution and the voyages of explorers like Captain James Cook. He was educated at the High School of Glasgow, Glasgow High School and went on to study med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contrasted with the scientific name for the same organism, which is often based in Latin. A common name is sometimes frequently used, but that is not always the case. In chemistry, IUPAC defines a common name as one that, although it unambiguously defines a chemical, does not follow the current systematic naming convention, such as acetone, systematically 2-propanone, while a vernacular name describes one used in a lab, trade or industry that does not unambiguously describe a single chemical, such as copper sulfate, which may refer to either copper(I) sulfate or copper(II) sulfate. Sometimes common names are created by authorities on one particular subject, in an attempt to make it possible for members of the general public (including s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Conifer Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Flora Of Tasmania
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioecious Plants
Dioecy ( ; ; adj. dioecious, ) is a characteristic of certain species that have distinct unisexual individuals, each producing either male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproduction is biparental reproduction. Dioecy has costs, since only the female part of the population directly produces offspring. It is one method for excluding self-fertilization and promoting allogamy (outcrossing), and thus tends to reduce the expression of recessive deleterious mutations present in a population. Plants have several other methods of preventing self-fertilization including, for example, dichogamy, herkogamy, and self-incompatibility. In zoology In zoology, dioecy means that an animal is either male or female, in which case the synonym gonochory is more often used. Most animal species are gonochoric, almost all vertebrate species are gonochoric, and all bird and mammal species are gonochoric. Dioecy may also describe colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zealandia, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia, and the Indian subcontinent. Gondwana was formed by the Accretion (geology), accretion of several cratons (large stable blocks of the Earth's crust), beginning with the East African Orogeny, the collision of India and Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar with East Africa, and culminating in with the overlapping Brasiliano orogeny, Brasiliano and Kuunga orogeny, Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Paleozoic Era, covering an area of some , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. It fused with Laurasia during the Carboniferous to form Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
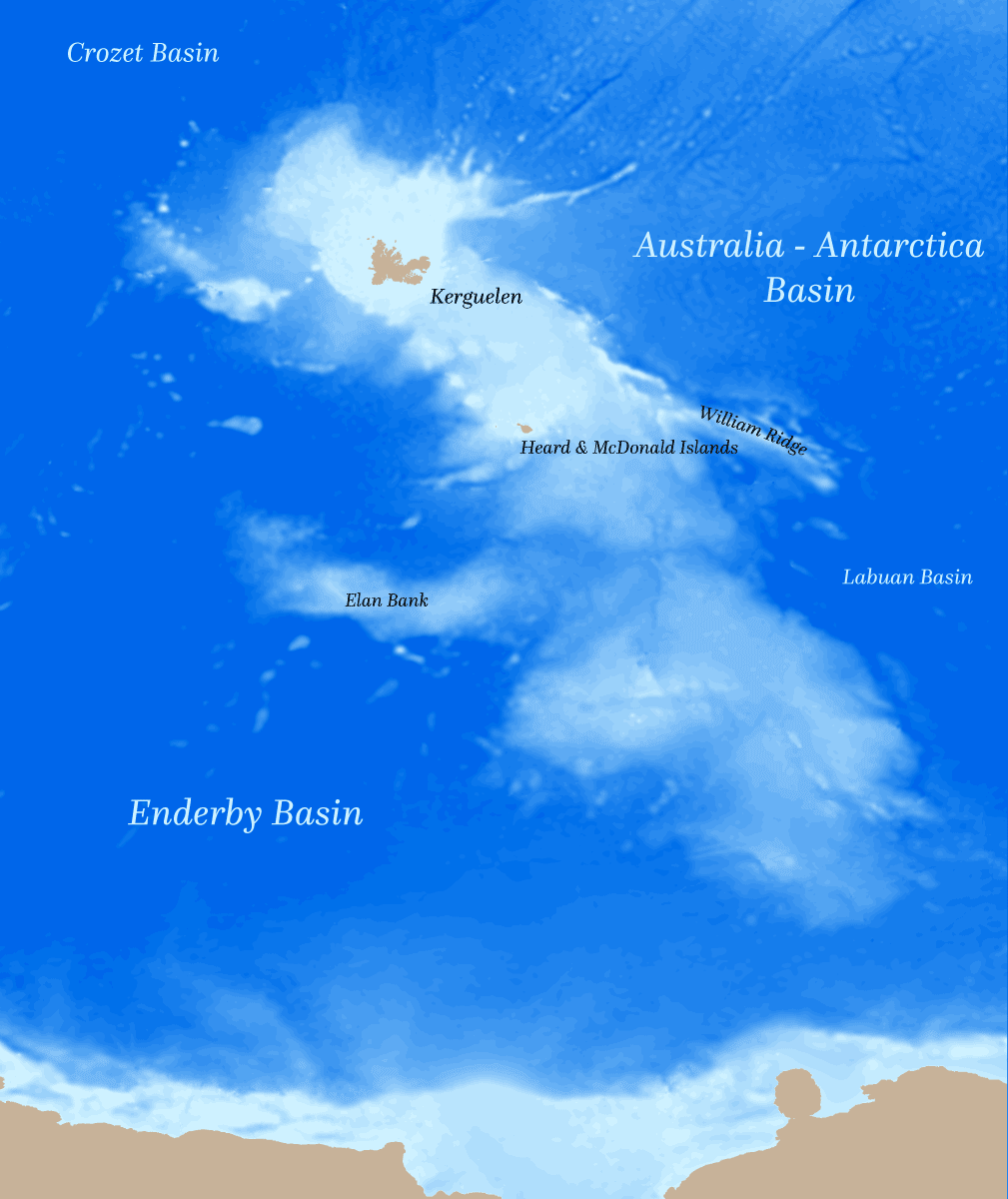
Heard Island And McDonald Islands
The Territory of Heard Island and McDonald Islands (HIMI) is an Australian States and territories of Australia, external territory comprising a volcanic group of mostly barren Antarctic islands, about two-thirds of the way from Madagascar to Antarctica. The group's overall land area is and it has of coastline. Discovered in the mid-19th century, the islands lie on the Kerguelen Plateau in the Indian Ocean and have been an Australian territory since 1947. Heard Island and McDonald Islands contain Australia's only two active volcanoes. The summit of one, Mawson Peak, is higher than any mountain in all other Australian states, territories or land claim, claimed territories, except Dome Argus, Mount McClintock and Mount Menzies in the Australian Antarctic Territory. This Antarctic territory is a land claim unrecognised by most other countries, meaning that Mawson Peak is the highest mountain with undisputed Australian Westphalian sovereignty, sovereignty. The islands are among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerguelen Plateau
The Kerguelen Plateau (, ), also known as the Kerguelen–Heard Plateau, is an oceanic plateau and large igneous province (LIP) located on the Antarctic Plate, in the southern Indian Ocean. It is about to the southwest of Australia and is nearly three times the size of California. The plateau extends for more than in a northwest–southeast direction and lies in deep water. The plateau was produced by the Kerguelen hotspot, starting with or following the breakup of Gondwana about 130 million years ago. A small portion of the plateau breaks sea level, forming the Kerguelen Islands (a overseas territory (France), French overseas territory) plus the Heard Island and McDonald Islands, Heard and McDonald Islands (an states and territories of Australia, Australian external territory). Intermittent volcanism continues on the Heard and McDonald Islands. Geographical extent Symmetrically across the Indian Ocean ridge and due west of Australia is the Broken Ridge underwater volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johanna Alida Coetzee
Johanna Alida Coetzee (1921 - 2007) (also known as Joey Coetzee) was a researcher in the field of Palynology at the University of the Free State and a pioneer in the analysis of fossil pollen. Her DSc thesis received worldwide recognition and praise from the eminent glacial geologist Richard Foster Flint and helped recognise the significance of temperature changes in controlling shifts in global and local vegetation zones. Education and career Coetzee was born in 1921 in Johannesburg and was educated at the Jeppe High School for Girls. She completed a master's degree in Botany at the University of the Witwatersrand. She performed some postgraduate work at the University of the Witwatersrand and the University of Natal before moving to the University of the Free State where she was appointed as an assistant botanist in the Department of Botany in 1946. Coetzee made several overseas journeys where she studied with various experts in the field of botany, including a three-month p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoendemism
Paleoendemism along with neoendemism is a possible subcategory of endemism. Paleoendemism refers to species that were formerly widespread but are now restricted to a smaller area. Neoendemism refers to species that have recently arisen, such as through divergence and reproductive isolation or through hybridization and polyploidy in plants. Etymology The first part of the word, paleo, comes from the Greek word ''palaiós, meaning "ancient".'' The second part of the word, ''endemism'' is from Neo-Latin ''endēmicus'', from Greek ενδήμος, ''endēmos'', "native". ''Endēmos'' is formed of ''en'' meaning "in", and ''dēmos'' meaning "the people". Causes Changes in climate are thought to be the driving force in creating paleoendemic species, generally due to habitat loss. Regions where the climate has remained relatively stable form refugia which are more likely to be endemic hotspots today. This applies to both neoendemism and paleoendemism. However, paleoendemism differs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |