|
Michel Luc
Michel Luc (7 February 1927 – 18 January 2010) was a French zoologist (nematologist) and one of the founding fathers of the field of plant-nematology. He spent his career with ORSTOM (''Office de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique Outre-Mer''), now IRD (''Institut de recherche pour le développement''). He created the first French nematology laboratory in the ORSTOM research station of Adiopodoumé, near Abidjan (Ivory Coast) in 1955, and a second nematology lab at Dakar Bel-Air (Senegal) in 1969. In 1978, he launched the ''Revue de Nématologie'' (soon renamed ''Fundamental and Applied Nematology'') that fused with ''Nematologica'' in 1999 to become ''Nematology'', currently the leading nematology journal in the field. He was a world-renowned authority on nematode taxonomy. Biography Michel Luc was born on 7 February 1927 in Tunis (Tunisia). From 1945, on, he studied biology in Paris at the Sorbonne, where he attended classes delivered by biologists such as Georges Mangeno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematology
Nematology is the scientific discipline concerned with the study of nematodes, or roundworms. Although nematological investigation dates back to the days of Aristotle or even earlier, nematology as an independent discipline has its recognizable beginnings in the mid to late 19th century.Chen, Z. X., Chen, S. Y., and Dickson, D. W. (2004). "A Century of Plant Nematology", pp. 1–42 in ''Nematology Advances and Perspectives'', Vol 1. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China.Chitwood, B. G., and Chitwood, M. B. (1950). "An Introduction to Nematology", pp. 1–5 in ''Introduction to Nematology''. University Park Press, Baltimore. History: pre-1850 Nematology research, like most fields of science, has its foundations in observations and the recording of these observations. The earliest written account of a nematode "sighting", as it were, may be found in the Pentateuch of the Old Testament in the Bible, in the Fourth Book of Moses called Numbers: "And the Lord sent fiery serpen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the south, and the North Sea to the west. Belgium covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.8 million; its population density of ranks List of countries and dependencies by population density, 22nd in the world and Area and population of European countries, sixth in Europe. The capital and Metropolitan areas in Belgium, largest metropolitan region is City of Brussels, Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy with a complex Federation, federal system structured on regional and linguistic grounds. The country is divided into three highly autonomous Communities, regions and language areas o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematology
Nematology is the scientific discipline concerned with the study of nematodes, or roundworms. Although nematological investigation dates back to the days of Aristotle or even earlier, nematology as an independent discipline has its recognizable beginnings in the mid to late 19th century.Chen, Z. X., Chen, S. Y., and Dickson, D. W. (2004). "A Century of Plant Nematology", pp. 1–42 in ''Nematology Advances and Perspectives'', Vol 1. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China.Chitwood, B. G., and Chitwood, M. B. (1950). "An Introduction to Nematology", pp. 1–5 in ''Introduction to Nematology''. University Park Press, Baltimore. History: pre-1850 Nematology research, like most fields of science, has its foundations in observations and the recording of these observations. The earliest written account of a nematode "sighting", as it were, may be found in the Pentateuch of the Old Testament in the Bible, in the Fourth Book of Moses called Numbers: "And the Lord sent fiery serpen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tylenchida
Tylenchida is an order (biology), order of nematodes. List of families * Superfamily Criconematoidea ** Family Criconematidae ** Family Tylenchulidae * Superfamily Tylenchoidea ** Family Anguinidae ** Family Belonolaimidae ** Family Dolichodoridae ** Family Ecphyadophoridae ** Family Hoplolaimidae ** Family Heteroderidae ** Family Pratylenchidae ** Family Tylenchidae * Superfamily Sphaerularina ** Family Allantonematidae ** Family Fergusobiidae ** Family Iotonchiidae ** Family Parasitylenchidae ** Family Sphaerulariidae References Further reading * Mohammad Rafiq Siddiqui. ''Tylenchida: Parasites of Plants and Insects''. 2nd ed. Wallingford: CABI Publishing, 2000. External links Order Tylenchida Nematode Identification at the University of Florida Entomology and Nematology Department {{Authority control Tylenchida, Nematode orders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the science, scientific study of naming, defining (Circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxon, taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain (biology), domain, kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class (biology), class, order (biology), order, family (biology), family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, having developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiphinema
''Xiphinema'' is a genus of ectoparasitic root nematodes commonly known as dagger nematodes.Whitehead, A.G. 1998. Plant Nematode Control The genus is of economic importance on grape, strawberry, hops and a few other crops. Major species include ''X.americanum, X.diversicaudatum, X.index, X.italiae'' and ''X.pachtaicum''.Evans, K., Trudgill, D.L., Webster, J.M. 1998. Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Temperate Agriculture. They can be easily recognized by their long bodies and stylets which are long enough to reach the vascular tissue of plants.''Xiphinema'' at Nemaplex, Different members of the genus have been shown to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systematics
Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phylogenies have two components: branching order (showing group relationships, graphically represented in cladograms) and branch length (showing amount of evolution). Phylogenetic trees of species and higher taxa are used to study the evolution of traits (e.g., anatomical or molecular characteristics) and the distribution of organisms ( biogeography). Systematics, in other words, is used to understand the evolutionary history of life on Earth. The word systematics is derived from the Latin word of Ancient Greek origin '' systema,'' which means systematic arrangement of organisms. Carl Linnaeus used 'Systema Naturae' as the title of his book. Branches and applications In the study of biological systematics, researchers use the different br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muséum National D'Histoire Naturelle
The French National Museum of Natural History ( ; abbr. MNHN) is the national natural history museum of France and a of higher education part of Sorbonne University. The main museum, with four galleries, is located in Paris, France, within the Jardin des Plantes on the left bank of the River Seine. It was formally founded in 1793, during the French Revolution, but was begun even earlier in 1635 as the royal garden of medicinal plants. The museum now has 14 sites throughout France. Since the 2014 reform, it has been headed by a chairman, assisted by deputy managing directors. The Museum has a staff of approximately 2,350 members, including six hundred researchers. It is a member of the national network of naturalist collections (RECOLNAT). History 17th–18th century File:Jardin du roi 1636.png, The Royal Garden of Medicinal Plants in 1636 File:Buffon statue dsc00979.jpg, Statue of Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in the formal garden File:Buffon, Georges Louis - Leclerc, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals". When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss, in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. This classification remained widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, and even became elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom, kingdom, and then sometimes included within the paraphyletic Protoctista or Protista. By the 1970s, it became usual to require that all taxa be monophyletic (derived from a common ancestor that would also be regarded as protozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helminth
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels. Some parasitic worms, including leeches and monogeneans, are ectoparasites thus, they are not classified as helminths, which are endoparasites. Parasitic worms live in and feed in living hosts. They receive nourishment and protection while disrupting their hosts' ability to absorb nutrients. This can cause weakness and disease in the host, and poses a global health and economic problem. Parasitic worms cannot reproduce entirely within their host's body; they have a life cycle that includes some stages that need to take place outside of the host. Helminths are able to survive in their mammalian hosts for many years due to their ability to manipulate the host's immune respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
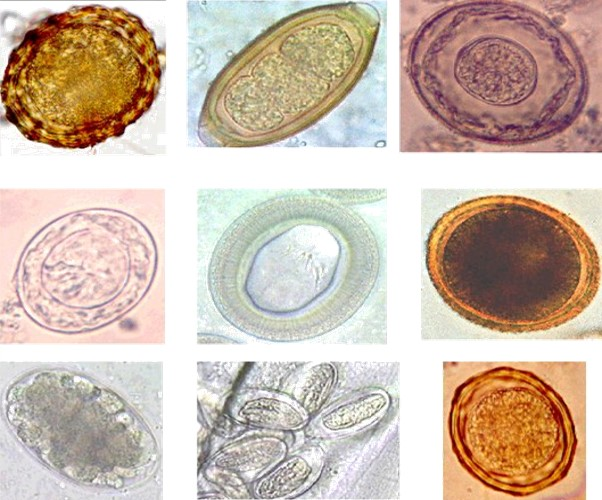
Nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases. They are classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa. Unlike the flatworms, nematodes have a tubular digestive system, with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species are uncertain. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity suggested there are over 25,000. Estimates of the total number of extant species are su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alain Chabaud
Alain Chabaud (13 March 1923 – 11 March 2013) was a French parasitologist, mainly a specialist of nematodes and sporozoa. He was the Director of the Laboratoire de Zoologie (Vers) in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris from 1960 to 1989. He was one of the founders of the Société Française de Parasitologie in 1962 and its president until 1975, and president of the Société zoologique de France in 1967. Taxa named in his honour Chabaud's name is honoured in many parasite taxa described by his colleagues. The most famous species named in the honour of Chabaud is '' Plasmodium chabaudi'' Landau, 1965, a species studied in many laboratories. Several genera of Nematoda were named in the honour of Chabaud, including '' Chabaudacuaria'' Mutafchiev & Kinsella, 2012, '' Chabaudechina'' Smales, 1999, '' Chabaudgolvania'' Freitas, 1958 (also honouring French parasitologist Jean-Yves Golvan). '' Chabaudus chabaudi'' Inglis & Ogden, 1965 has both genus and species names h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |