|
Michael Tuts
Philip Michael Tuts is an American high-energy experimental particle physicist, and Professor and Chair of the Columbia University Physics Department. Tuts is a Fellow of the American Physical Society. He holds a seat on the executive committees of the United States LHC Users' Association and the American Physics Society Forum on Physics and Society, and is Divisional Councilor of the Division of Particles and Fields of APS. Tuts earned his Bachelor's in Physics from MIT in 1974, and his MA and PhD from the State University of New York at Stony Brook in 1976 and 1979, respectively. He joined the physics department at Columbia University in the City of New York in 1983 and was appointed Chair in 2014. Tuts is currently a member of the ATLAS experiment team at CERN and formerly served as US ATLAS Operations Program Manager. As operations manager, he led the team of 400 American physicists working on ATLAS during the experiment that led to the discovery of the Higgs boson. Tuts is p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physics
Experimental physics is the category of disciplines and sub-disciplines in the field of physics that are concerned with the observation of physical phenomena and experiments. Methods vary from discipline to discipline, from simple experiments and observations, such as experiments by Galileo Galilei, to more complicated ones, such as the Large Hadron Collider. Overview Experimental physics is a branch of physics that is concerned with data acquisition, data-acquisition methods, and the detailed conceptualization (beyond simple thought experiments) and realization of laboratory experiments. It is often contrasted with theoretical physics, which is more concerned with predicting and explaining the physical behaviour of nature than with acquiring empirical data. Although experimental and theoretical physics are concerned with different aspects of nature, they both share the same goal of understanding it and have a symbiotic relationship. The former provides data about the universe, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
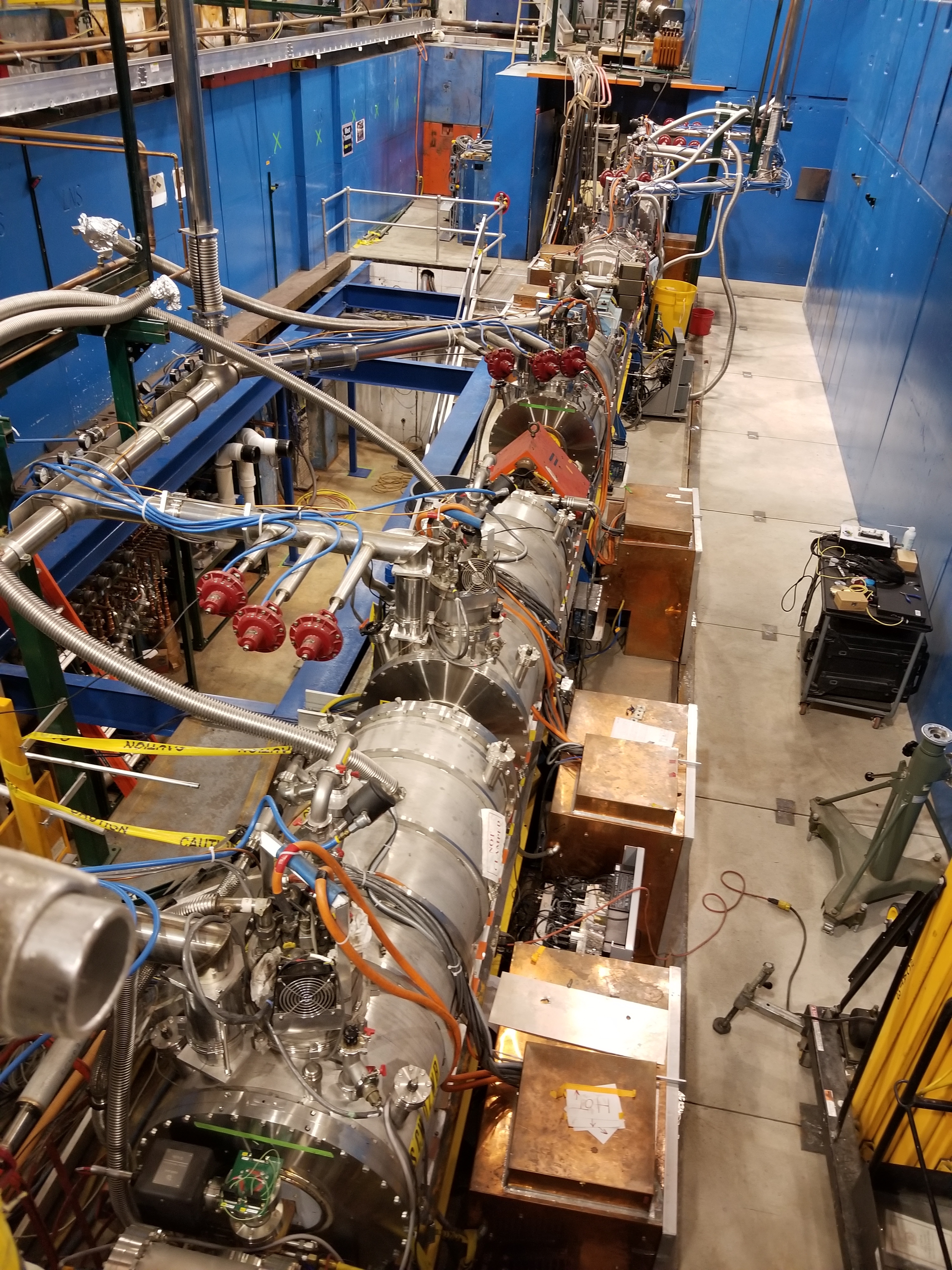
Cornell Electron Storage Ring
The Cornell Electron Storage Ring (CESR, pronounced Julius Caesar, Caesar) is a particle accelerator operated by Cornell University and located 40 feet beneath a football field on their Ithaca, New York, Ithaca campus. The accelerator has contributed to fundamental research in Particle physics, high energy physics and accelerator physics, as well as solid state physics, biology, art history and other fields through its use as a synchrotron light source. For many years, CESR held the world luminosity record for electron-positron collisions. CESR pioneered several new accelerator techniques, including Superconductivity, superconducting radio-frequency cavities and pretzel orbits. Electron Positron Collider CESR was built in the already existing tunnel for the 10 GeV synchrotron and was originally constructed as an electron-positron collider. The project was led by Cornell physicist Maury Tigner who devised a "fiendishly clever" method of filling the ring with positrons gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |