|
Mevastatin
Mevastatin (compactin, ML-236B) is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class. It was isolated from the mold '' Penicillium citrinum'' by Akira Endo in the 1970s, and he identified it as a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, i.e., a statin. Mevastatin might be considered the first statin drug; clinical trials on mevastatin were performed in the late 1970s in Japan, but it was never marketed. The first statin drug available to the general public was lovastatin. Mevastatin has since been derivatized to the compound pravastatin, which is a pharmaceutical used in the lowering of cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular disease. ''In vitro'', it has antiproliferative properties. A British group isolated the same compound from ''Penicillium brevicompactum'', named it ''compactin'', and published their results in 1976. The British group mentions antifungal properties with no mention of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition. High doses inhibit growth and proliferation of melanoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevastatin Structure
Mevastatin (compactin, ML-236B) is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class. It was isolated from the mold ''Penicillium citrinum'' by Akira Endo (biochemist), Akira Endo in the 1970s, and he identified it as a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, i.e., a statin. Mevastatin might be considered the first statin drug; clinical trials on mevastatin were performed in the late 1970s in Japan, but it was never marketed. The first statin drug available to the general public was lovastatin. Mevastatin has since been derivatized to the compound pravastatin, which is a pharmaceutical used in the lowering of cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular disease. ''In vitro'', it has antiproliferative properties. A British group isolated the same compound from ''Penicillium brevicompactum'', named it ''compactin'', and published their results in 1976. The British group mentions antifungal properties with no mention of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition. High doses inhibit growth and prolifer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
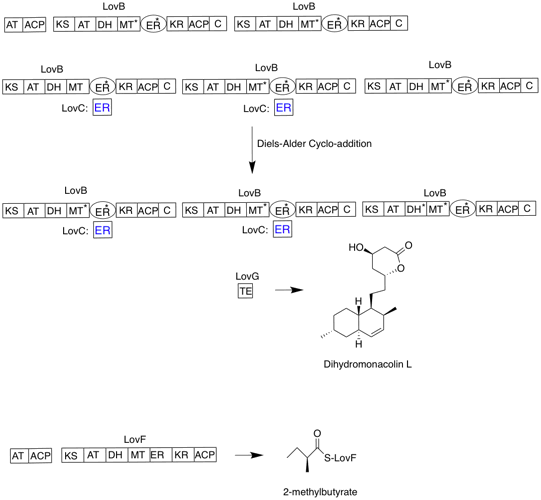
Mevastatin Biosynthesis Corrected
Mevastatin (compactin, ML-236B) is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class. It was isolated from the mold '' Penicillium citrinum'' by Akira Endo in the 1970s, and he identified it as a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, i.e., a statin. Mevastatin might be considered the first statin drug; clinical trials on mevastatin were performed in the late 1970s in Japan, but it was never marketed. The first statin drug available to the general public was lovastatin. Mevastatin has since been derivatized to the compound pravastatin, which is a pharmaceutical used in the lowering of cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular disease. ''In vitro'', it has antiproliferative properties. A British group isolated the same compound from ''Penicillium brevicompactum'', named it ''compactin'', and published their results in 1976. The British group mentions antifungal properties with no mention of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition. High doses inhibit growth and proliferation of melanoma cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akira Endo (biochemist)
was a Japanese biochemist whose research into the relationship between fungi and cholesterol biosynthesis led to the development of statin drugs, which are some of the best-selling pharmaceuticals in history. Endo received the Japan Prize in 2006,The Science and Technology Foundation of JapanJapan Prize official release, accessed 21 June 2006 the Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award in 2008, the Canada Gairdner International Award in 2017. Biography Endo was born on a farm in Northern Japan and had an interest in fungi already at a young age, being an admirer of Alexander Fleming. He obtained a BA at Tohoku University (Faculty of Agriculture) in Sendai in 1957 and a PhD in biochemistry at the same university in 1966. Endo died of pneumonia on 5 June 2024, at the age of 90. Career From 1957 to 1978 he worked as a research fellow at chemical company Sankyo Co.; initially he worked on fungal enzymes for processing fruit juice. Successful discoveries in this field ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. As lipid-lowering medications, statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol; they are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes, and abnormal blood levels of certain liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage, and very rarely rhabdomyolysis. They act by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of choleste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headache, muscles pains, rash, and trouble sleeping. Serious side effects may include liver problems, muscle breakdown, and kidney failure. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended. It works by decreasing the liver's ability to produce cholesterol by blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 111th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses The primary uses of lovastatin is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statins
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. As lipid-lowering medications, statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol; they are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes, and abnormal blood levels of certain liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage, and very rarely rhabdomyolysis. They act by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-adenosylmethionine Synthetase Enzyme
''S''-Adenosylmethionine synthetase (), also known as methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), is an enzyme that creates ''S''-adenosylmethionine (also known as AdoMet, SAM or SAMe) by reacting methionine (a non-polar amino acid) and ATP (the basic currency of energy). Function AdoMet is a methyl donor for transmethylation. It gives away its methyl group and is also the propylamino donor in polyamine biosynthesis. S-adenosylmethionine synthesis can be considered the rate-limiting step of the methionine cycle. As a methyl donor SAM allows DNA methylation. Once DNA is methylated, it switches the genes off and therefore, S-adenosylmethionine can be considered to control gene expression. SAM is also involved in gene transcription, cell proliferation, and production of secondary metabolites. Hence SAM synthetase is fast becoming a drug target, in particular for the following diseases: depression, dementia, vacuolar myelopathy, liver injury, migraine, osteoarthritis, and as a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium
''Penicillium'' () is a genus of Ascomycota, ascomycetous fungus, fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production. Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Other species are used in cheesemaking. According to the ''Dictionary of the Fungi'' (10th edition, 2008), the widespread genus contains over 300 species. Taxonomy The genus was first described in the scientific literature by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in his 1809 work ; he wrote, , () where means "having tufts of fine hair". Link included three species—''Penicillium candidum, P. candidum'', ''Penicillium expansum, P. expansum'', and ''Penicillium glaucum, P. glaucum''—all of which produced a brush-like conidiophore (asexual spore-producing structure). The common apple rot fungus ''P.&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicinal Molds
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include those treating infection with amoeba, bacteria, fungus, virus, inhibitors of cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis, and psychotropics. Mushroom dietary supplements, commonly made from powdered or extracted fruiting bodies or mycelium, are marketed for various health benefits but lack sufficient scientific evidence for safety or effectiveness, and quality can vary due to inconsistent processing and labeling. History In Ancient Egypt moldy bread was applied to wound infection. '' Inonotus obliquus'' was used in folk medicine tumor treatment in Russia and Northern Europe during the 16th century. Hallucinogenic mushrooms include ''Amanita muscaria'', the fly agaric and "magic mushrooms", which contain psilocybin and psilocin. The ability to identify beneficial prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endothelial NOS
Endothelial NOS (eNOS), also known as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3) or constitutive NOS (cNOS), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NOS3'' gene located in the 7q35-7q36 region of chromosome 7. This enzyme is one of three isoforms that synthesize nitric oxide (NO), a small gaseous and lipophilic molecule that participates in several biological processes. The other isoforms include neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS), which is constitutively expressed in specific neurons of the brain and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), whose expression is typically induced in inflammatory diseases. eNOS is primarily responsible for the generation of NO in the vascular endothelium, a monolayer of flat cells lining the interior surface of blood vessels, at the interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the remainder of the vessel wall. NO produced by eNOS in the vascular endothelium plays crucial roles in regulating vascular tone, cellular proliferation, leukocyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |