|
Metonic
The Metonic cycle or enneadecaeteris (from grc, ἐννεακαιδεκαετηρίς, from ἐννεακαίδεκα, "nineteen") is a period of almost exactly 19 years after which the lunar phases recur at the same time of the year. The recurrence is not perfect, and by precise observation the Metonic cycle defined as 235 synodic months is just 2 hours, 4 minutes and 58 seconds longer than 19 tropical years. Meton of Athens, in the 5th century BC, judged the cycle to be a whole number of days, 6,940. Using these whole numbers facilitates the construction of a lunisolar calendar. A tropical year is longer than 12 lunar months and shorter than 13 of them. The arithmetic identity 12×12 + 7×13 = 235 shows that a combination of 12 "short" years (12 months) and 7 "long" years (13 months) will be almost exactly equal to 19 solar years. Application in traditional calendars In the Babylonian and Hebrew lunisolar calendars, the years 3, 6, 8, 11, 14, 17, and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikythera Mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games which was similar to an Olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games. This artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. On 17 May 1902, it was identified as containing a gear by archaeologist Valerios Stais. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size , was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is approximately in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. In 2008, a team led by Mike Edmunds and Tony Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computus
As a moveable feast, the date of Easter is determined in each year through a calculation known as (). Easter is celebrated on the first Sunday after the Paschal full moon, which is the first full moon on or after 21 March (a fixed approximation of the March equinox). Determining this date in advance requires a correlation between the lunar months and the solar year, while also accounting for the month, date, and weekday of the Julian or Gregorian calendar. The complexity of the algorithm arises because of the desire to associate the date of Easter with the date of the Jewish feast of Passover which, Christians believe, is when Jesus was crucified. It was originally feasible for the entire Christian Church to receive the date of Easter each year through an annual announcement by the Pope. By the early third century, however, communications in the Roman Empire had deteriorated to the point that the church put great value in a system that would allow the clergy to determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
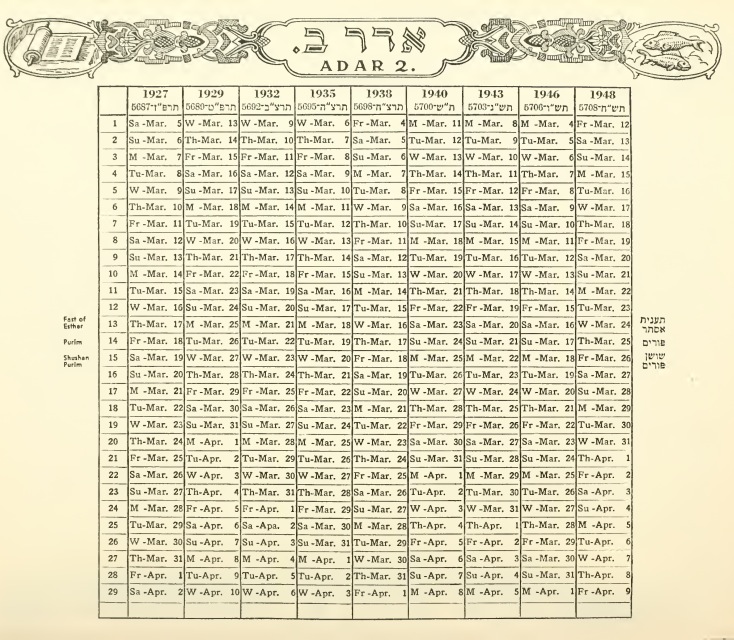
Hebrew Calendar
The Hebrew calendar ( he, הַלּוּחַ הָעִבְרִי, translit=HaLuah HaIvri), also called the Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today for Jewish religious observance, and as an official calendar of the state of Israel. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate Torah reading, public reading of Weekly Torah portion, Torah portions, ''yahrzeits'' (dates to commemorate the death of a relative), and daily Psalm readings, among many ceremonial uses. In Israel, it is used for religious purposes, provides a time frame for agriculture, and is an official calendar for civil holidays, alongside the Gregorian calendar. The present Hebrew calendar is the result of a process of development, including a Babylonian calendar, Babylonian influence. Until the Tannaitic period (approximately 10–220 Common Era, CE), the calendar employed a new lunar phase, crescent moon, with an Intercalation (timekeeping), additional month normally added every two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolius Of Laodicea
Anatolius of Laodicea (early 3rd century – July 3, 283), also known as Anatolios of Alexandria, became Bishop of Laodicea on the Mediterranean coast of Roman Syria in AD 268. He was not only one of the foremost scholars of his day in the physical sciences as well as in Aristotelean philosophy but also a great computist. Anatolius is considered a saint by both the Eastern Orthodox and the Roman Catholic Church. His feast day, like the one of his namesake Saint Anatolius of Constantinople, is celebrated on July 3. Life Anatolius was born and raised in Alexandria, Egypt, during the early 3rd century. Prior to becoming one of the great lights of the Church, Anatolius enjoyed considerable prestige at Alexandria. According to Eusebius of Caesarea, he was credited with a rich knowledge of arithmetic, geometry, physics, rhetoric, dialectic, and astronomy. Also according to Eusebius, Anatolius was deemed worthy to maintain the school of the Aristotelian succession in Alexandria. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meton Of Athens
Meton of Athens ( el, Μέτων ὁ Ἀθηναῖος; ''gen''.: Μέτωνος) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, geometer, and engineer who lived in Athens in the 5th century BC. He is best known for calculations involving the eponymous 19-year Metonic cycle, which he introduced in 432 BC into the lunisolar Attic calendar. Euphronios says that Colonus was Meton's deme. Work The Metonic calendar incorporates knowledge that 19 solar years and 235 lunar months are very nearly of the same duration. Consequently, a given day of a lunar month will often occur on the same day of the solar year as it did 19 years previously. Meton's observations were made in collaboration with Euctemon, about whom nothing else is known. The Greek astronomer Callippus expanded on the work of Meton, proposing what is now called the Callippic cycle. A Callippic cycle runs for 76 years, or four Metonic cycles. Callippus refined the lunisolar calendar, deducting one day from the fourth Metonic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunisolar Calendar
A lunisolar calendar is a calendar in many cultures, combining lunar calendars and solar calendars. The date of Lunisolar calendars therefore indicates both the Moon phase and the time of the solar year, that is the position of the Sun in the Earth's sky. If the sidereal year (such as in a sidereal solar calendar) is used instead of the solar year, then the calendar will predict the constellation near which the full moon may occur. As with all calendars which divide the year into months there is an additional requirement that the year have a whole number of months. In this case ordinary years consist of twelve months but every second or third year is an embolismic year, which adds a thirteenth intercalary, embolismic, or leap month. Their months are based on the regular cycle of the Moon's phases. So lunisolar calendars are lunar calendars with – in contrast to them – additional intercalation rules being used to bring them into a rough agreement with the solar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysius Exiguus
Dionysius Exiguus (Latin for "Dionysius the Humble", Greek: Διονύσιος; – ) was a 6th-century Eastern Roman monk born in Scythia Minor. He was a member of a community of Scythian monks concentrated in Tomis (present day Constanța, Romania), the major city of Scythia Minor. Dionysius is best known as the inventor of Anno Domini (AD) dating, which is used to number the years of both the Gregorian calendar and the (Christianised) Julian calendar. Almost all churches adopted his '' computus'' for the dates of Easter. From around the year 500 until his death, Dionysius lived in Rome. He translated 401 Church canons from Greek into Latin, including the Apostolic Canons and the decrees of the First Council of Nicaea, First Council of Constantinople, Council of Chalcedon, and Council of Sardica, and a collection of the decretals of the popes from Siricius to Anastasius II. These ''Collectiones canonum Dionysianae'' had great authority in the West, and they continu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callippus
Callippus (; grc, Κάλλιππος; c. 370 BC – c. 300 BC) was a Greek astronomer and mathematician. Biography Callippus was born at Cyzicus, and studied under Eudoxus of Cnidus at the Academy of Plato. He also worked with Aristotle at the Lyceum, which means that he was active in Athens prior to Aristotle's death in 322 BC. He observed the movements of the planets and attempted to use Eudoxus' scheme of connected spheres to account for their movements. However, he found that 27 spheres was insufficient to account for the planetary movements, and so he added seven more for a total of 34. According to the description in Aristotle's ''Metaphysics'' (XII.8), he added two spheres for the Sun, two for the Moon, and one each for Mercury, Venus, and Mars. Callippus made careful measurements of the lengths of the seasons, finding them (starting with the spring equinox) to be 94 days, 92 days, 89 days, and 90 days. This variation in the seasons implies a variation in the speed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Calendar
A Runic calendar (also Rune staff or Runic Almanac) is a perpetual calendar, variants of which were used in Northern Europe until the 19th century. A typical runic calendar consisted of several horizontal lines of symbols, one above the other. Special days like solstices, equinoxes, and celebrations (including Christian holidays and feasts) were marked with additional lines of symbols. Runic calendars were written on parchment or carved onto staves of wood, bone, or horn. The oldest one known, and the only one from the Middle Ages, is a staff from Nyköping, Sweden, believed to date from the 13th century. Most of the several thousand which survive are wooden calendars dating from the 16th and the 17th centuries. During the 18th century, Runic calendars had a renaissance, and calendars dating from around 1800 were made in the form of brass tobacco boxes. The calendar is based on the 19 year-long Metonic cycle, correlating the Sun and the Moon, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callippic Cycle
The Callippic cycle (or Calippic) is a particular approximate common multiple of the tropical year and the synodic month, proposed by Callippus in 330 BC. It is a period of 76 years, as an improvement of the 19-year Metonic cycle. Description A century before Callippus, Meton had described a cycle in which 19 years equals 235 lunations. If we assume a year is about days, 19 years total about 6,940 days, which exceeds 235 lunations by almost a third of a day, and 19 tropical years by four tenths of a day. It implicitly gave the solar year a duration of = 365 + = 365 + + days = 365 d 6 h 18 min 56 s. Callippus accepted the 19-year cycle, but held that the duration of the year was more closely days (= 365 d 6 h), so he multiplied the 19-year cycle by 4 to obtain an integer number of days, and then omitted 1 day from the last 19-year cycle. Thus, he computed a cycle of 76 years that consists of 940 lunations and 27,759 days, which has been named the ''Callippic'' cycle after hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom of Northumbria of the Angles (contemporarily Monkwearmouth–Jarrow Abbey in Tyne and Wear, England). Born on lands belonging to the twin monastery of Monkwearmouth–Jarrow in present-day Tyne and Wear, Bede was sent to Monkwearmouth at the age of seven and later joined Abbot Ceolfrith at Jarrow. Both of them survived a plague that struck in 686 and killed a majority of the population there. While Bede spent most of his life in the monastery, he travelled to several abbeys and monasteries across the British Isles, even visiting the archbishop of York and King Ceolwulf of Northumbria. He was an author, teacher ( Alcuin was a student of one of his pupils), and scholar, and his most famous work, '' Ecclesiastical History of the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian Calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematics, Greek mathematicians and Ancient Greek astronomy, astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandria. The calendar became the predominant calendar in the Roman Empire and subsequently most of the Western world for more than 1,600 years until 1582, when Pope Gregory XIII promulgated #Replacement by the Gregorian calendar, a minor modification to reduce the average length of the year from 365.25 days to 365.2425 days and thus corrected the Julian calendar's drift against the Tropical year, solar year. adoption of the Gregorian calendar, Worldwide adoption of this revised calendar, which became known as the Gregorian calendar, took place over the subsequent centuries, first in Catholic Church, Catholic countries and subsequently in Protestantism, Protestant countries of the Western Christianity, West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

_(cropped).jpg)