|
Methylprednisolone
Methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol, Medrol, Solu-Medrol) is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used at high doses during acute flares. Methylprednisolone and its derivatives can be administered orally or parenterally. Regardless of the route of administration, methylprednisolone integrates systemically as exhibited by its effectiveness to quickly reduce inflammation during acute flares. It is associated with many adverse reactions that require tapering off the drug as soon as the disease is under control. Serious side effects include iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome, hypertension, osteoporosis, diabetes, infection, psychosis, and skin atrophy. Chemically, methylprednisolone is a synthetic pregnane steroid hormone derived from hydrocortisone and prednisolone. It belongs to a class of synthetic glucocorticoids and more generally, corticosteroids. It acts as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
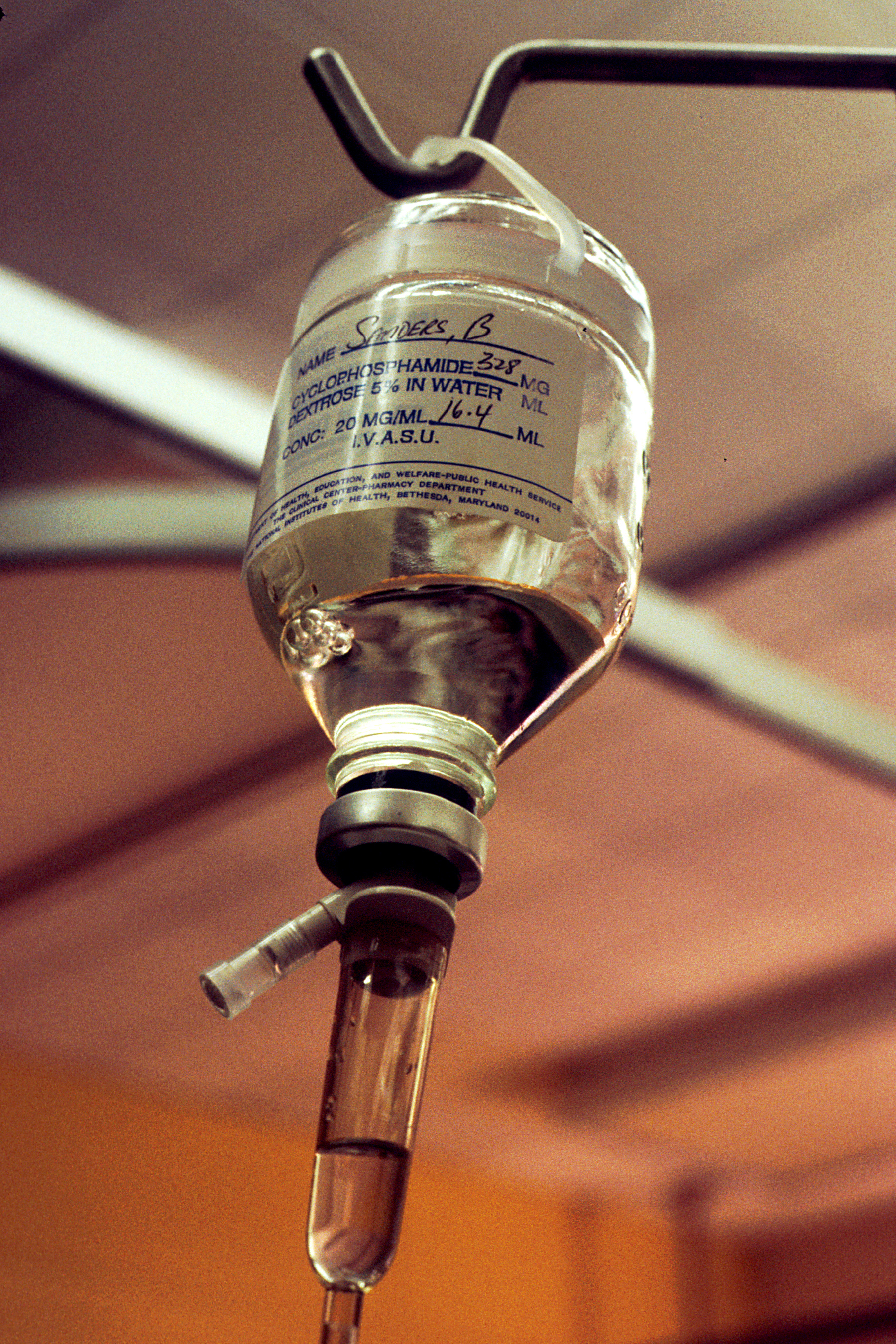
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, ANCA-associated vasculitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was approved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau of "glucose", "cortex", and "steroid" and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an Autoimmunity, overactive immune system, such as Allergy, allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many Side effect, diverse effects such as pleiotropy (drugs), pleiotropy, including Adverse drug reaction, potentially harmful side effects. They also interfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisolone
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid, a steroid hormone used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammation, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, Electrolyte imbalance, electrolyte imbalances and skin conditions. Some of these conditions include adrenocortical insufficiency, hypercalcemia, high blood calcium, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, eye inflammation, asthma, multiple sclerosis, and phimosis. It can be taken Oral administration, by mouth, intravenous, injected into a vein, used Topical medication, topically as a skin cream, or as Ophthalmic drug administration, eye drops. It differs from the similarly named prednisone in having a hydroxy group, hydroxyl at the 11th carbon instead of a ketone. Common side effects with short-term use include nausea, difficulty concentrating, insomnia, increased appetite, and fatigue. More severe side effects include psychiatric problems, which may occur in about 5% of people. Common side effects with long-term use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditions. Atopic dermatitis results in puritis, itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which can thicken over time. Atopic dermatitis affects about 20% of people at some point in their lives. It is more common in younger children. Females are affected slightly more often than males. Many people outgrow the condition. While the condition may occur at any age, it typically starts in childhood, with changing severity over the years. In children under one year of age, the face and limbs and much of the body may be affected. As children get older, the areas on the insides of the knees and folds of the elbows and around the neck are most commonly affected. In adults, the hands and feet are commonly affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum Sickness
Serum sickness in humans is a adverse drug reaction, reaction to proteins in antiserum derived from a non-human animal source, occurring 5–10 days after exposure. Symptoms often include a rash, Arthralgia, joint pain, fever, and lymphadenopathy. It is a type of hypersensitivity, specifically immune complex hypersensitivity (Type III hypersensitivity, type III). The term serum sickness–like reaction (SSLR) is occasionally used to refer to similar illnesses that arise from the introduction of certain non-protein substances, such as penicillin. Serum sickness may be diagnosed based on the symptoms, and using a blood test and a Clinical urine tests, urine test. It may be prevented by not using an antitoxin derived from animal serum, and through prophylactic antihistamines or corticosteroids. It usually resolves naturally, but may be treated with corticosteroids, antihistamines, Analgesic, analgesics, and (in severe cases) prednisone. It was first characterized in 1906. Signs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red or flesh-colored, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and typically do not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks (a condition known as chronic urticaria). The condition frequently recurs. Hives frequently occur following an infection or as a result of an allergic reaction such as to medication, insect bites, or food. Psychological stress, cold temperature, or vibration may also be a trigger. In half of cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include having conditions such as hay fever or asthma. Diagnosis is typically based on appearance. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. Prevention is by avoiding whatever it is that causes the condition. Treatment is typically with antihistamines, with the second generation antihistamines su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. A sudden worsening of asthma symptoms sometimes called an 'asthma attack' or an 'asthma exacerbation' can occur when allergens, pollen, dust, or other particles, are inhaled into the lungs, causing the bronchioles to constrict and produce mucus, which then restricts oxygen flow to the alveoli. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are swelling within the upper skin. Onset is typically over minutes to hours. The underlying mechanism typically involves histamine or bradykinin. The version related to histamine is due to an allergic reaction to agents such as insect bites, foods, or medications. The version related to bradykinin may occur due to an inherited problem known as C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, medications known as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, or a lymphoproliferative disorder. Treatment to protect the airway may include intubation or cricothyroidotomy. Histamine-related angioedema can be treated with antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine. In those with bradykinin-related disease a C1 esterase inhibitor, ecallantide, or icati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and adults, but not recommended in elderly patients), rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow intravenous infusion (injected slowly through an IV line). The most common side effects with intravenous infusions are reactions related to the infusion (such as fever, chills and shivering) while most common serious side effects are infusion reactions, infections and heart-related problems. Similar side effects are seen when it is injected under the skin, with the exception of reactions around the injections site (pain, swelling and rash), which occur more frequently with the skin inject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |