|
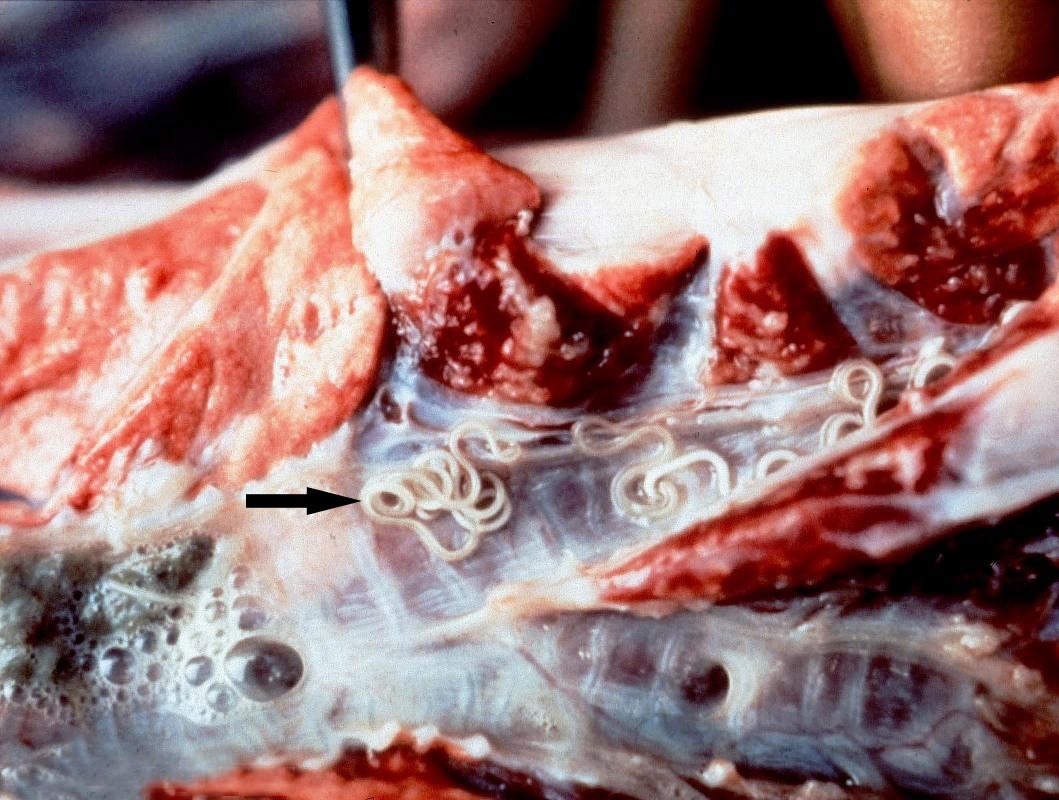
Metastrongylus
''Metastrongylus'' is a genus of nematodes of the family Metastrongylidae, usually found as lungworms in pigs and sometimes causing parasitic bronchitis. It causes a disease called metastrongylosis. Species *'' Metastrongylus elongatus'' (Dujardin, 1845) synonym '' Metastrongylus apri'' (Gmelin, 1780) *'' Metastrongylus pudendotectus'' (Wostokow, 1905) *'' Metastrongylus salmi'' (Gedoelst, 1823) *'' Metastrongylus confusus'' (Jansen, 1964) *'' Metastrongylus asymmetricus'' (Noda, 1973) Life cycle The lifecycle is indirect. The eggs are laid by the adult worm in the bronchi. They are coughed up, swallowed, and passed out via the feces. The eggs are then eaten by earthworms in which they develop through three larval stages over 10 days to become infective. The cycle is completed by the pig eating the earthworm. Infection, therefore, only occurs where pigs have access to earthworms, for example, in outdoor production. The larvae from the earthworm penetrate the intestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastrongylosis
Metastrongylosis is a parasitic disease that affects wild boars and pigs which live outdoors. It is caused by various species of roundworms of the genus ''Metastrongylus''. A handful of cases of metastrongylosis have been reported in humans. ''Metastrongylus'' species have a life cycle which involves earthworms as an intermediate host. Pigs root for earthworms in soil Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ..., and ingest the ''Metastrongylus'' larvae which are infesting the earthworms. The larvae migrate to the lungs, and cause the pig to cough and have difficulty breathing. References External links Swine diseases Helminthiases Veterinary helminthology {{Veterinary-med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastrongylidae
The Metastrongylidae are a family of nematodes. Genera in the family Metastrongylidae include: * ''Aelurostrongylus''Ohlweiler F. P., Guimarães M. C. de A., Takahasi F. Y. & Eduardo J. M. (2010). "Current distribution of ''Achatina fulica'', in the State of São Paulo including records of ''Aelurostrongylus abstrusus'' (Nematoda) larvae infestation". '' Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de Sao Paulo'' 52(4): 211-214. PDF *''Metastrongylus ''Metastrongylus'' is a genus of nematodes of the family Metastrongylidae, usually found as lungworms in pigs and sometimes causing parasitic bronchitis. It causes a disease called metastrongylosis. Species *'' Metastrongylus elongatus'' ...'' *'' Skrjabingylus'' References Strongylida Nematode families {{Rhabditida-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Bronchitis
Parasitic bronchitis, also known as hoose, husk, or verminous bronchitis, is a disease of sheep, cattle, goats, and swine caused by the presence of various species of parasite, commonly known as lungworms, in the bronchial tubes or in the lungs. It is marked by cough, dyspnea, anorexia and constipation. Lungworms which cause parasitic bronchitis include nematodes of the genera '' Dictyocaulus'', ''Metastrongylus'', and ''Protostrongylus''. Hoose is essentially an infantile disease, almost always afflicting animals under one year of age. It can be diagnosed through fecal examination or taking a sputum sample and treated by killing the nematode larvae and adults. In severe cases, additional antibiotics may be needed. The most effective prevention is via vaccination, especially important for cattle. Cause The cause for parasitic bronchitis is the nematode called '' Dictyocaulus viviparus''. In the infected animal's fecal matter the larvae later become infective. When anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungworm
Lungworms are parasitic nematode worms of the order Strongylida that infest the lungs of vertebrates. The name is used for a variety of different groups of nematodes, some of which also have other common names; what they have in common is that they migrate to their hosts' lungs or respiratory tracts, and cause bronchitis or pneumonia. The lungworm will gradually damage the airways or lung tissue by inciting an inflammatory reaction inside the tissue. Ultimately, the parasites survive and reproduce in the respiratory tissues. The category is thus more a descriptive than a precisely taxonomic one. The most common lungworms belong to one of two groups, the superfamily Trichostrongyloidea or the superfamily Metastrongyloidea, but not all the species in these superfamilies are lungworms. The lungworms in the superfamily Trichostrongyloidea include several species in the genus '' Dictyocaulus'' which infest hoofed animals, including most common domestic species. Different specie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |