|
Metacheiromyinae
Metacheiromyidae ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct paraphyletic family of myrmecophagous placental mammals within extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.R. M. Schoch (1984."Revision of ''Metacheiromys'' (Wortman, 1903) and a review of the Palaeanodonta."Postilla 192:1-28 Classification and phylogeny Taxonomy * Family: †Metacheiromyidae (paraphyletic family) (Pilgrim, 1932) ** Genus: †'' Brachianodon'' (Gunnell & Gingerich, 1993) *** †''Brachianodon westorum'' (Gunnell & Gingerich, 1993) ** Genus: †'' Mylanodon'' (Secord, 2002) *** †''Mylanodon rosei'' (Secord, 2002) ** Subfamily: † Metacheiromyinae (paraphyletic subfamily) (Wortman, 1903) *** Genus: †''Metacheiromys'' (Wortman, 1903) **** †''Metacheiromys dasypus'' (Osborn, 1904) **** †''Metacheiromys marshi'' (Wortman, 1903) *** Genus: †'' Palaeanodon'' (Matthew, 1918) **** †''Palaeanodon ignavus'' (Matthew, 1918) **** †''Palaeano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
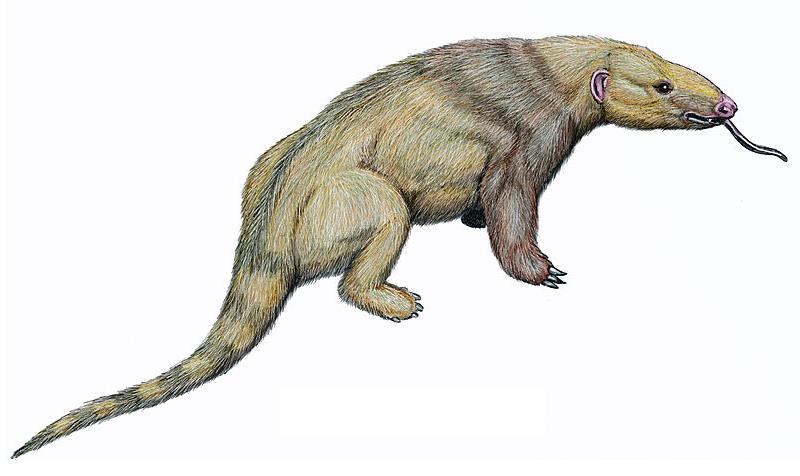
Metacheiromys
''Metacheiromys'' ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct genus of placental mammals from extinct paraphyletic subfamily Metacheiromyinae within extinct paraphyletic family Metacheiromyidae in extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America (what is now Wyoming) from the early to middle Eocene. Etymology The generic name means "next to ''Cheiromys''" because the scientist who saw the bones mistakenly thought that the animal was a primate with hands like those of the lemurs from genus ''Daubentonia'', whose synonym is ''Cheiromys''. Characteristics of taxa ''Metacheiromys'' was a small creature, and measured around long. It had long claws and a narrow head similar in shape to that of an armadillo or an anteater (though it was actually related to the modern pangolins). The shape of its claws suggests that it probably dug through the soil in search of food, most likely small invertebrates. Unlike modern anteaters or pangolins, it had powerful canine teeth, but only a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeanodonta
Palaeanodonta ("ancient toothless animals") is an extinct clade of stem-pangolins. They were insectivorous (Myrmecophagy, myrmecophagous), possibly fossorial, and lived from the middle Paleocene to early Oligocene in North America, Europe and Asia. While the taxonomic grouping of Palaeanodonta has been debated,Averianov, A. O. & Lopatin, A. V. (2014."High-level systematics of placental mammals: Current status of the problem."Biology Bulletin, 41(9), 801–816. it is widely thought that they are a sister group to pangolins. Anatomy Skull Palaeanodonts generally have low and caudally-broad skulls, with notable Lambdoid suture, lambdoid crests and inflated Tympanic part of the temporal bone, bullae and Squamosal bone, squamosals. Teeth Despite the name of the group and contrary to their pangolin relatives, palaeanodonts are known to have had teeth. Early palaeanodonts retained minimal Molar (tooth)#Tribosphenic, tribosphenic post-canines while later species had peglike or othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacheiromyinae
Metacheiromyidae ("next to ''Cheiromys''") is an extinct paraphyletic family of myrmecophagous placental mammals within extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to middle Eocene.R. M. Schoch (1984."Revision of ''Metacheiromys'' (Wortman, 1903) and a review of the Palaeanodonta."Postilla 192:1-28 Classification and phylogeny Taxonomy * Family: †Metacheiromyidae (paraphyletic family) (Pilgrim, 1932) ** Genus: †'' Brachianodon'' (Gunnell & Gingerich, 1993) *** †''Brachianodon westorum'' (Gunnell & Gingerich, 1993) ** Genus: †'' Mylanodon'' (Secord, 2002) *** †''Mylanodon rosei'' (Secord, 2002) ** Subfamily: † Metacheiromyinae (paraphyletic subfamily) (Wortman, 1903) *** Genus: †''Metacheiromys'' (Wortman, 1903) **** †''Metacheiromys dasypus'' (Osborn, 1904) **** †''Metacheiromys marshi'' (Wortman, 1903) *** Genus: †'' Palaeanodon'' (Matthew, 1918) **** †''Palaeanodon ignavus'' (Matthew, 1918) **** †''Palaeano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoicotheriinae
Epoicotheriinae ("strange beasts") is an extinct paraphyletic subfamily of insectivorous placental mammals within extinct paraphyletic family Epoicotheriidae in extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America and Europe from the early Eocene to early Oligocene. Epoicotheriins were fossorial mammals. Late Eocene/early Oligocene genera were highly specialized animals that were convergent with the talpids, golden moles and marsupial mole in the structure of their skulls and forelimbs, and would have had a similar lifestyle as subterranean burrowers.Kenneth D. Rose, Robert J. Emry (1983"Extraordinary fossorial adaptations in the oligocene palaeanodonts ''Epoicotherium'' and ''Xenocranium'' (Mammalia)"Journal of Morphology 175(1):33 - 56 Classification and phylogeny Classification * Subfamily: †Epoicotheriinae (paraphyletic subfamily) (Simpson, 1927) ** Genus: †'' Pentapassalus'' (Gazin, 1952) *** †''Pentapassalus pearcei'' (Gazin, 1952) *** †''Pentapassalus woodi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoicotheriidae
Epoicotheriidae ("strange beasts") is an extinct paraphyletic family of insectivorous placental mammals within extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America, Asia and Europe from the late Paleocene to early Oligocene. Epoicotheriids were fossorial mammals. Late Eocene/early Oligocene genera were highly specialized animals that were convergent with the Talpidae, talpids, golden moles and marsupial mole in the structure of their skulls and forelimbs, and would have had a similar lifestyle as subterranean burrowers.Kenneth D. Rose, Robert J. Emry (1983"Extraordinary fossorial adaptations in the oligocene palaeanodonts ''Epoicotherium'' and ''Xenocranium'' (Mammalia)"Journal of Morphology 175(1):33 - 56 Classification and phylogeny Taxonomy Epoicotheriidae was named by George Gaylord Simpson, Simpson in 1927. It was assigned to the Palaeanodonta by Rose (1978) and Carroll (1988). Classification * Family: †Epoicotheriidae (Paraphyly, paraphyletic family) (Simpson, 1927) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenocranium
''Xenocranium'' ("strange skull") is an extinct monotypic genus of placental mammal from extinct paraphyletic subfamily Epoicotheriinae within extinct paraphyletic family Epoicotheriidae in extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America during the late Eocene. Etymology The name of genus ''Xenocranium'' comes and , respectively after its unique skull arrangement. The specific epithet is derived and , in reference to the nearby township of Hat Creek, Wyoming, U.S.A. Description ''Xenocranium pileorivale'' was a highly specialized animal that was convergent with the talpids, golden moles and marsupial mole. It possesses many traits indicative of the lifestyle of a subterranean burrower, including small eyes, an upturned snout, muscular arms with large attachment points for the triceps, teres major, and carpal and digital flexor muscles. The dental formula is . Palaeoecology The holotype of ''Xenocranium pileorivale'' was recovered from the Brule Formation, 160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pholidotamorpha
Pholidotamorpha ("pangolin-like forms") is a clade of placental, mostly ant- and termite-eating mammals that (partially) physically resemble anteaters and armadillos. However, those aforementioned species are now placed in the order Xenarthra, along with sloths; Pholidotamorpha is now classified under the mirorder Ferae, which includes the order Carnivora (carnivorous mammals) and the pangolins (Pholidota) as well as the prehistoric order Palaeanodonta, containing only extinct species. Classification and phylogeny History of taxonomy Both the Pholidota and Palaeanodonta orders were formerly placed with other orders of ant-eating mammals, most notably Xenarthra (armadillos, sloths, anteaters, which they superficially resemble); some palaeontologists, throughout the history of zoology, have placed pangolins and palaeanodonts as a suborder, Pholidota, in the greater order Cimolesta, alongside the extinct family Ernanodontidae as a separate suborder Ernanodonta near it. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escavadodon
''Escavadodon'' ("tooth from Escavada") is an extinct genus of pangolin-like myrmecophagous placental mammals of extinct monotypic family Escavadodontidae within extinct order Palaeanodonta, that lived in North America during the middle Paleocene. It contains a single species, ''Escavadodon zygus'', recovered from the Nacimiento Formation of New Mexico. Phylogenetic tree The phylogenetic relationships of genus ''Escavadodon'' is shown in the following cladogram: See also * Mammal classification * Palaeanodonta Palaeanodonta ("ancient toothless animals") is an extinct clade of stem-pangolins. They were insectivorous (Myrmecophagy, myrmecophagous), possibly fossorial, and lived from the middle Paleocene to early Oligocene in North America, Europe and Asi ... References Palaeanodonta Paleocene mammals of North America Torrejonian Fossils of the United States Paleontology in New Mexico Fossil taxa described in 2000 {{Paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin Hardwicke (white Background)
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: ''Manis'', ''Phataginus'', and ''Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . Several extinct pangolin species are also known. In September 2023, nine species were reported. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. Depending on the species, they live in hollow trees or burrows. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangolins superficially resemble ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |