|
Metabolus
''Metabolus'' is a monotypic genus of bird in the family Monarchidae found in Australia and Melanesia. Taxonomy and systematics Extant species The genus ''Metabolus'' presently contains only a single species: * Chuuk monarch (''Metabolus rugensis'') Former species Formerly, some authorities also considered the following species (or subspecies) as species within the genus ''Metabolus'': *Yap monarch The Yap monarch (''Monarcha godeffroyi''), or Yap Island monarch, is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae. It is endemic to the Yap Main Islands, Micronesia. Some authorities consider the Yap monarch to belong to the genus '' Metabolus ... (as ''Metabolus godeffroyi'') * Tinian monarch (as ''Metabolus takatsukasae'') References Monotypic bird genera Taxa named by Charles Lucien Bonaparte Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Monarchidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuuk Monarch
The Chuuk monarch (''Metabolus rugensis''), or Truk monarch, is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Metabolus''. It is endemic to the islands of Chuuk in Micronesia. Taxonomy and systematics The Chuuk monarch was originally described as belonging to the genus ''Muscicapa''. Description The Chuuk monarch is a large monarch flycatcher, around 20 cm long. The plumage of this species is sexually dimorphic, with the male having almost entirely white plumage with a black face and throat and the female having entirely black plumage. The large bill is pale blue. Distribution and habitat The natural habitats of the Chuuk monarch are subtropical or tropical dry forests, subtropical or tropical mangrove forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, subtropical or tropical moist shrubland, and plantations. Threats It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yap Monarch
The Yap monarch (''Monarcha godeffroyi''), or Yap Island monarch, is a species of bird in the family Monarchidae. It is endemic to the Yap Main Islands, Micronesia. Some authorities consider the Yap monarch to belong to the genus '' Metabolus''. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical mangrove A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ... forests. The natives of Yap Island call it "Gigiy" or "Achgigiy". It is the official state bird of Yap, Federated States of Micronesia. References Yap monarch Birds of Yap Yap monarch Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Taxobox binomials not recognized by IUCN Endemic birds of Yap {{Monarchidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchidae
The monarchs or monarch flycatchers (family Monarchidae) comprise a family of over 100 passerine birds which includes shrikebills, paradise flycatchers, and Grallina, magpie-larks. Monarchids are small insectivore, insectivorous songbirds with long tails. They inhabit forest or woodland across sub-Saharan Africa, south-east Asia, Australasia, and a number of Pacific islands. Only a few species migrate. Many species decorate their cup-shaped nests with lichen. Taxonomy Some of the one hundred or more species making up the family were previously assigned to other groups, largely on the basis of general morphology or behaviour. The magpie-lark, for example, was assigned to the same family as the white-winged chough, since both build unusual nests from mud rather than vegetable matter. That family, Grallinidae, is now considered a Synonym (taxonomy), synonym of Monarchidae. It was formerly considered to have four species. The magpie-lark and the torrent-lark were moved into Monarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Lucien Bonaparte
Charles Lucien Jules Laurent Bonaparte, 2nd Prince of Canino and Musignano (24 May 1803 – 29 July 1857) was a French naturalist and ornithology, ornithologist, and a nephew of Napoleon. Lucien and his wife had twelve children, including Cardinal Lucien Bonaparte (cardinal), Lucien Bonaparte. Life and career Bonaparte was the son of Lucien Bonaparte and Alexandrine de Bleschamp. Lucien was a younger brother of Napoleon I of France, Napoleon I, making Charles the emperor’s nephew. Born in Paris, he was raised in Italy. On 29 June 1822, he married his cousin, Zénaïde Laetitia Julie Bonaparte, Zénaïde, in Brussels. Soon after the marriage, the couple left for Philadelphia in the United States to live with Zénaïde's father, Joseph Bonaparte (who was also the paternal uncle of Charles). Before leaving Italy, Charles had already discovered a Old World warbler, warbler new to science, the moustached warbler, and on the voyage he collected specimens of a new Wilson's storm-petrel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
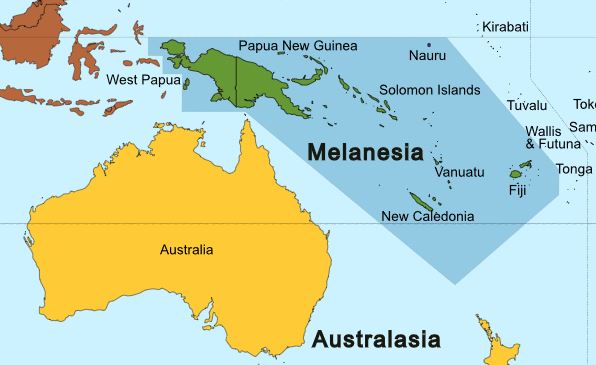
Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea. The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, and Papua New Guinea. It also includes the West New Guinea, Indonesian part of New Guinea, the French overseas collectivity of New Caledonia, and the Torres Strait Islands. Almost all of the region is in the Southern Hemisphere; only a few small islands that are not politically considered part of Oceania—specifically the northwestern islands of Western New Guinea—lie in the Northern Hemisphere. The name ''Melanesia'' (in French, ''Mélanésie'') was first used in 1832 by French navigator Jules Dumont d'Urville: he coined the terms ''Melanesia'' and ''Micronesia'' to go alongside the pre-existing ''Polynesia'' to designate what he viewed as the three main Ethnicity, ethnic and geographical regions forming the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Bird Genera
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. Theoretical implications Monotypic taxa present several important theoretical challenges in biological classification. One key issue is known as "Gregg's Paradox": if a single species is the only member of multiple hierarchical levels (for example, being the only species in its genus, which is the only genus in its family), then each level needs a distinct definition to maintain logical structure. Otherwise, the different taxonomic ranks become effectively identical, which creates problems for organizing biological diversity in a hierarchical system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Charles Lucien Bonaparte
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |