|
Mesquitol
Mesquitol is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. '' Prosopis juliflora'', an invasive New World mesquite now found in Kenya, has unusually high levels of (−)-mesquitol in its heartwood. Mesquitol, with its pyrogallol-type A-ring, is more susceptible to quinone formation at this ring, leading to aryl–aryl bond formation at carbon 5. The structural moieties constitute the proteracacinidin class of proanthocyanidins. Mesquitol-(5→8)-catechin atropisomer Atropisomers are stereoisomers arising because of hindered rotation about a covalent bond, single bond, where Gibbs free energy, energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to all ...s can be isolated from '' Prosopis glandulosa''. References Flavanols Catechols {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Juliflora
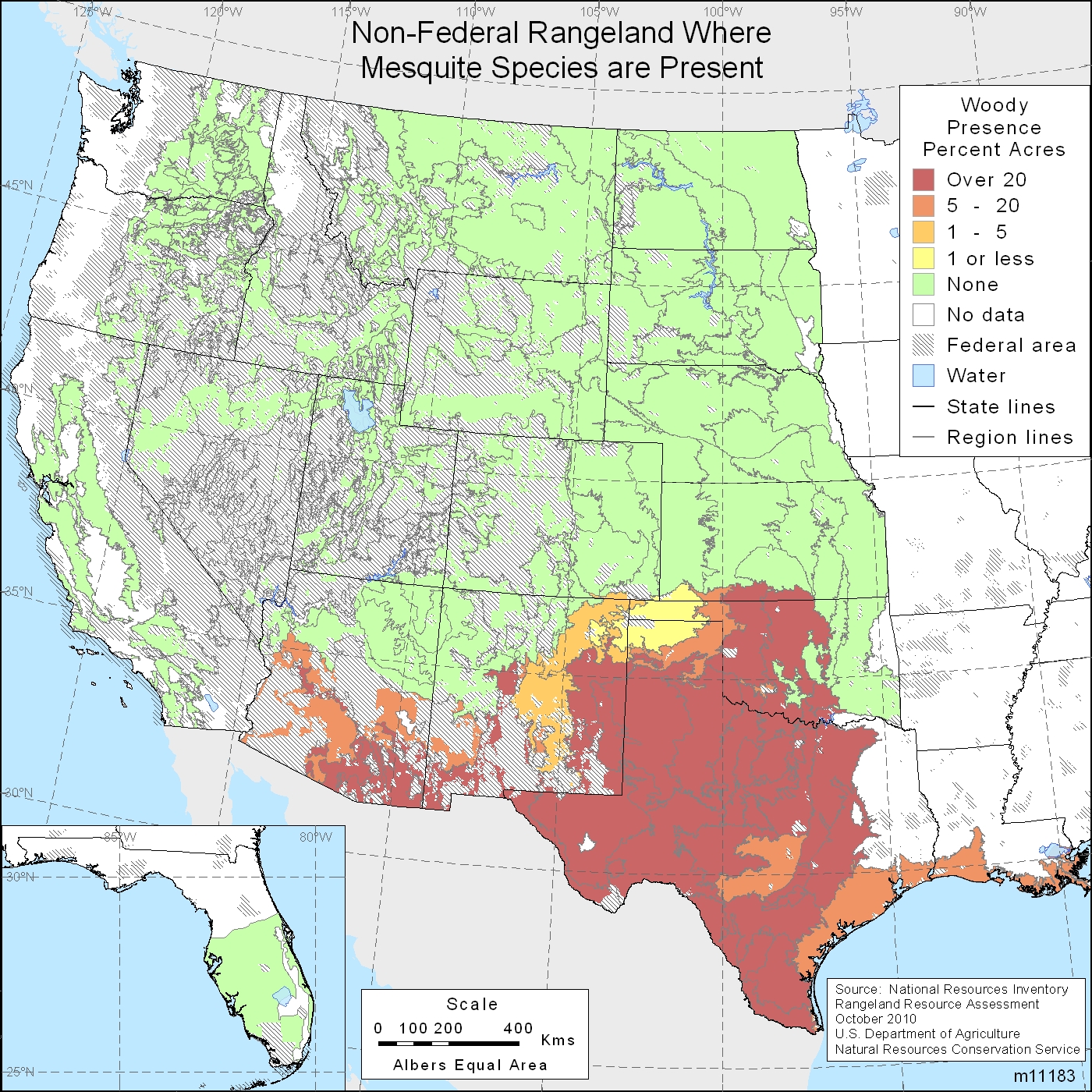
''Neltuma juliflora '' (, ''Cuji'' in Venezuela, ''Trupillo'' in Colombia, ''Aippia'' in the Wayuunaiki language and long-thorn kiawe in Hawaii), formerly ''Prosopis juliflora'', is a shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae, a kind of mesquite. It is native to Mexico, South America and the Caribbean. It has become established as an invasive weed in Africa, Asia, Australia and elsewhere. It is a contributing factor to continuing transmission of malaria, especially during dry periods when sugar sources from native plants are largely unavailable to mosquitoes. Description Growing to a height of up to , ''N. juliflora'' has a trunk diameter of up to . Its leaves are deciduous, geminate-pinnate, light green, with 12 to 20 leaflets. Flowers appear shortly after leaf development. The flowers are in long green-yellow cylindrical spikes, which occur in clusters of 2 to 5 at the ends of branches. Pods are long and contain between 10 and 30 seeds per pod. A mature plant can produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteracacinidin
Proteracacinidins are polymeric condensed tannins composed of mesquitol. This type of tannin can be found in hook-thorn tree (''Senegalia afra''). The oxidative depolymerization of proteracacinidins yields the anthocyanidin Anthocyanidins are common plant pigments, the aglycones of anthocyanins. They are based on the flavylium cation, an oxonium ion, with various groups substituent, substituted for its hydrogen atoms. They generally change color from red through p ... teracacinidin. References Condensed tannins Senegalia {{phenol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavan-3-ol
Flavan-3-ols (sometimes referred to as flavanols) are a subgroup of flavonoids. They are derivatives of flavans that possess a 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2''H''-chromen-3-ol skeleton. Flavan-3-ols are structurally diverse and include a range of compounds, such as catechin, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, proanthocyanidins, theaflavins, thearubigins. They play a part in plant defense and are present in the majority of plants. Chemical structure The single-molecule (monomer) catechin, or isomer epicatechin (see diagram), adds four hydroxyls to flavan-3-ol, making building blocks for concatenated polymers (proanthocyanidins) and higher order polymers (anthocyanidins). Flavan-3-ols possess two chiral carbons, meaning four diastereoisomers occur for each of them. They are distinguished from the yellow, ketone-containing flavonoids such as quercitin and rutin, which are called flavonol, flavonols. Early use of the term bioflavonoid was imprecisely applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16th century, the term "New World" has been used to describe the Western Hemisphere, often referred to as the Americas. Since the 18th century, it has come to represent the United States, which was initially colonial British America until it established independence following the American Revolutionary War. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term arose in the early 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesquite
Mesquite is a common name for some plants in the genera ''Neltuma'' and '' Strombocarpa'', which contain over 50 species of spiny, deep-rooted leguminous shrubs and small trees. They are native to dry areas in the Americas. Until 2022, these genera were traditionally included in a broad view of the genus '' Prosopis'', but that genus is now restricted to a few species native to the Old World. Mesquites have extremely long roots to seek water from very far under ground. As they are legumes, mesquites are one of the few sources of fixed nitrogen in the desert habitat. The trees bloom from spring to summer. They often produce fruits known as "pods". Mesquites are able to grow up to tall, depending on site and climate. They are deciduous and depending on location and rainfall have either deep or shallow roots. Mesquites are considered long-lived because of the low mortality rate after the dicotyledonous stage and juveniles are also able to survive in conditions with low light and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrogallol
Pyrogallol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a water-soluble, white solid although samples are typically brownish because of its sensitivity toward oxygen. It is one of three isomers of benzenetriols. Production and reactions It is produced in the manner first reported by Scheele in 1786: heating gallic acid to induce decarboxylation. Gallic acid is also obtained from tannin. Many alternative routes have been devised. One preparation involves treating ''para''-chlorophenoldisulfonic acid with potassium hydroxide, a variant on the time-honored route to phenols from sulfonic acids. Polyhydroxybenzenes are relatively electron-rich. One manifestation is the easy C-acetylation of pyrogallol. Uses It was once used in hair dyeing, dyeing of suturing materials. It also has antiseptic properties. In alkaline solution, pyrogallol undergoes deprotonation. Such solutions absorb oxygen from the air, turning brown. This conversion can be used to determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinone
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds benzene.html" ;"title="uch as benzene">uch as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully Conjugated system, conjugated cyclic diketone, dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone" (thus the name of the class). Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (''ortho''-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone. The name is derived from that of quinic acid (with the suffix "-one" indicating a ketone), since it is one of the compounds obtained upon oxidation of quinic acid. Quinic acid, like quinine is obtained from cinchona bark, called quinaquina in the indigenous languages of Peruvian tribes. Properties Quinones are oxidized derivatives of aromatic compounds an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proanthocyanidin
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in many plants, such as cranberry, blueberry, and grape seeds. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More complex polyphenols, having the same polymeric building block, form the group of Condensed tannin, condensed tannins. Proanthocyanidins were discovered in 1947 by Jacques Masquelier, who developed and patented techniques for the extraction of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from pine bark and grape seeds. Proanthocyanidins are under preliminary research for the potential to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by consuming cranberries, grape seeds or red wine. Distribution in plants Proanthocyanidins, including the lesser bioactive and bioavailable polymers (four or more catechins), represent a group of condensed flavan-3-ols, such as procyanidins, prodelphinidins and propelargonidins. They can be found in many plants, most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropisomer
Atropisomers are stereoisomers arising because of hindered rotation about a covalent bond, single bond, where Gibbs free energy, energy differences due to steric strain or other contributors create a barrier to rotation that is high enough to allow for isolation of individual rotamers. They occur naturally and are of occasional importance in pharmaceutical design. When the substituents are achiral, these conformers are enantiomers (''atropoenantiomers''), showing axial chirality; otherwise they are diastereomers (''atropodiastereomers''). Etymology and history The word ''atropisomer'' (, , meaning "not to be turned") was coined in application to a theoretical concept by German biochemist Richard Kuhn for Karl Freudenberg's seminal ''Stereochemie'' volume in 1933. Atropisomerism was first experimentally detected in a tetra substituted biphenyl, a diacid, by George Christie and James Kenner in 1922. Michinori Ōki further refined the definition of atropisomers taking into account th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopis Glandulosa
''Neltuma glandulosa'', formerly ''Prosopis glandulosa'', commonly known as honey mesquite, is a species of small to medium-sized, thorny shrub or tree in the legume family (Fabaceae). Distribution The plant is primarily native to the Southwestern United States and Northern Mexico. Its range extends on the northeast through Texas and into southwestern Kansas and Oklahoma and northwestern Louisiana (the South Central states), and west to southern California. It can be part of the Mesquite Bosque plant association community in the Sonoran Desert ecoregion of California and Arizona (U.S.), and Sonora state (México), and in the Chihuahuan Desert of New Mexico and Texas in the US, and Chihuahua in Mexico. Description ''Neltuma glandulosa'' has rounded, big and floppy, drooping branches with feathery foliage and straight, paired thorns on twigs. This tree normally reaches , but can grow as tall as . It is considered to have a medium growth rate. It flowers from March to No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavanols
Flavan-3-ols (sometimes referred to as flavanols) are a subgroup of flavonoids. They are derivatives of flavans that possess a 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2''H''-chromen-3-ol skeleton. Flavan-3-ols are structurally diverse and include a range of compounds, such as catechin, epicatechin gallate, epigallocatechin, epigallocatechin gallate, proanthocyanidins, theaflavins, thearubigins. They play a part in plant defense and are present in the majority of plants. Chemical structure The single-molecule (monomer) catechin, or isomer epicatechin (see diagram), adds four hydroxyls to flavan-3-ol, making building blocks for concatenated polymers (proanthocyanidins) and higher order polymers (anthocyanidins). Flavan-3-ols possess two chiral carbons, meaning four diastereoisomers occur for each of them. They are distinguished from the yellow, ketone-containing flavonoids such as quercitin and rutin, which are called flavonols. Early use of the term bioflavonoid was imprecisely applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |