|
Mesocarnivore
A mesocarnivore is an animal whose diet consists of 30–70% meat with the balance consisting of non-vertebrate foods which may include insects, fungi, fruits, other plant material and any food that is available to them. Mesocarnivores are from a large family group of mammalian carnivores and vary from small to medium sized, which are often less than fifteen kilograms, the human is a notable exception.Gary W. Roemer, Matthew E. Gompper, Blaire Van Valkenburgh, "The Ecological Role of the Mammalian Mesocarnivore", ''BioScience'', Volume 59, Issue 2, February 2009, Pages 165–173, https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2009.59.2.9 Mesocarnivores are seen today among the Canidae (coyotes, foxes), Viverridae (civets), Mustelidae (martens, tayra), Procyonidae (ringtail, raccoon), Mephitidae (skunks), and Herpestidae (some mongooses). The red fox is also the most common of the mesocarnivores in Europe and has a high population density in the areas they reside. In North America, some mesocarnivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competition (biology)
Competition is an Biological interaction, interaction between organisms or species in which both require one or more Resource (biological), resources that are in Limiting factor, limited supply (such as food, water, or Territory (animal), territory). Competition lowers the Fitness (biology), fitness of both organisms involved since the presence of one of the organisms always reduces the amount of the resource available to the other. In the study of community ecology, competition within and between members of a species is an important biological interaction. Competition is one of many interacting Biotic component, biotic and Abiotic component, abiotic factors that affect Community (ecology), community structure, species diversity, and population dynamics (shifts in a population over time). There are three major Mechanism (biology), mechanisms of competition: interference, exploitation, and apparent competition (in order from most direct to least direct). Interference and exploitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
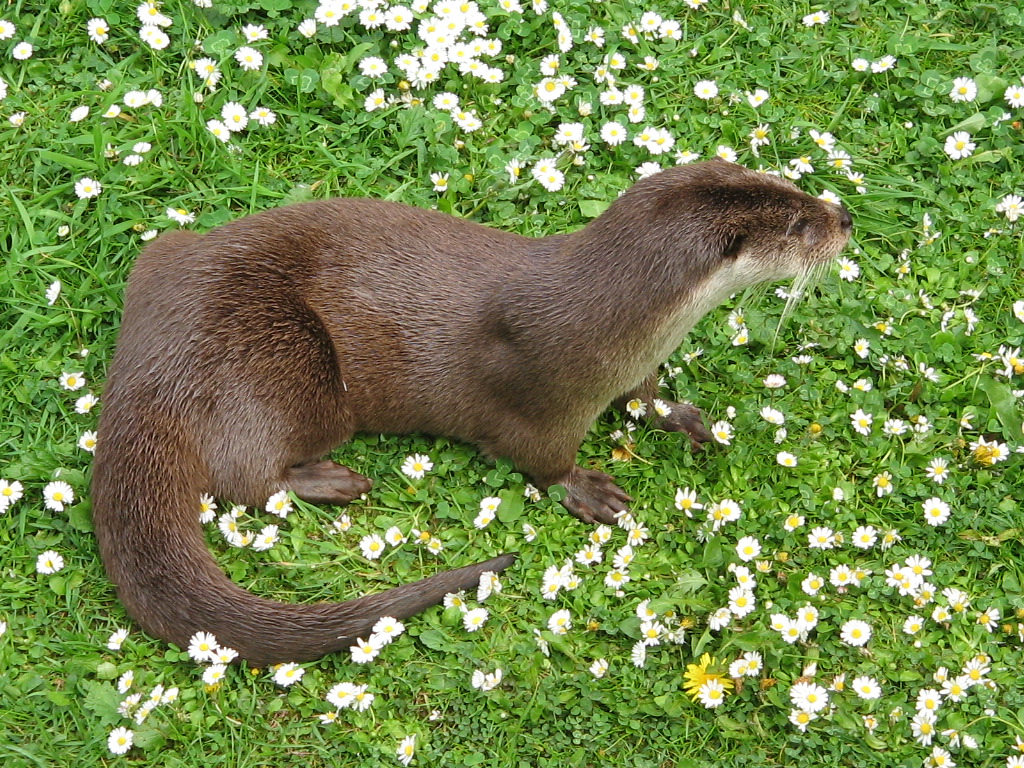
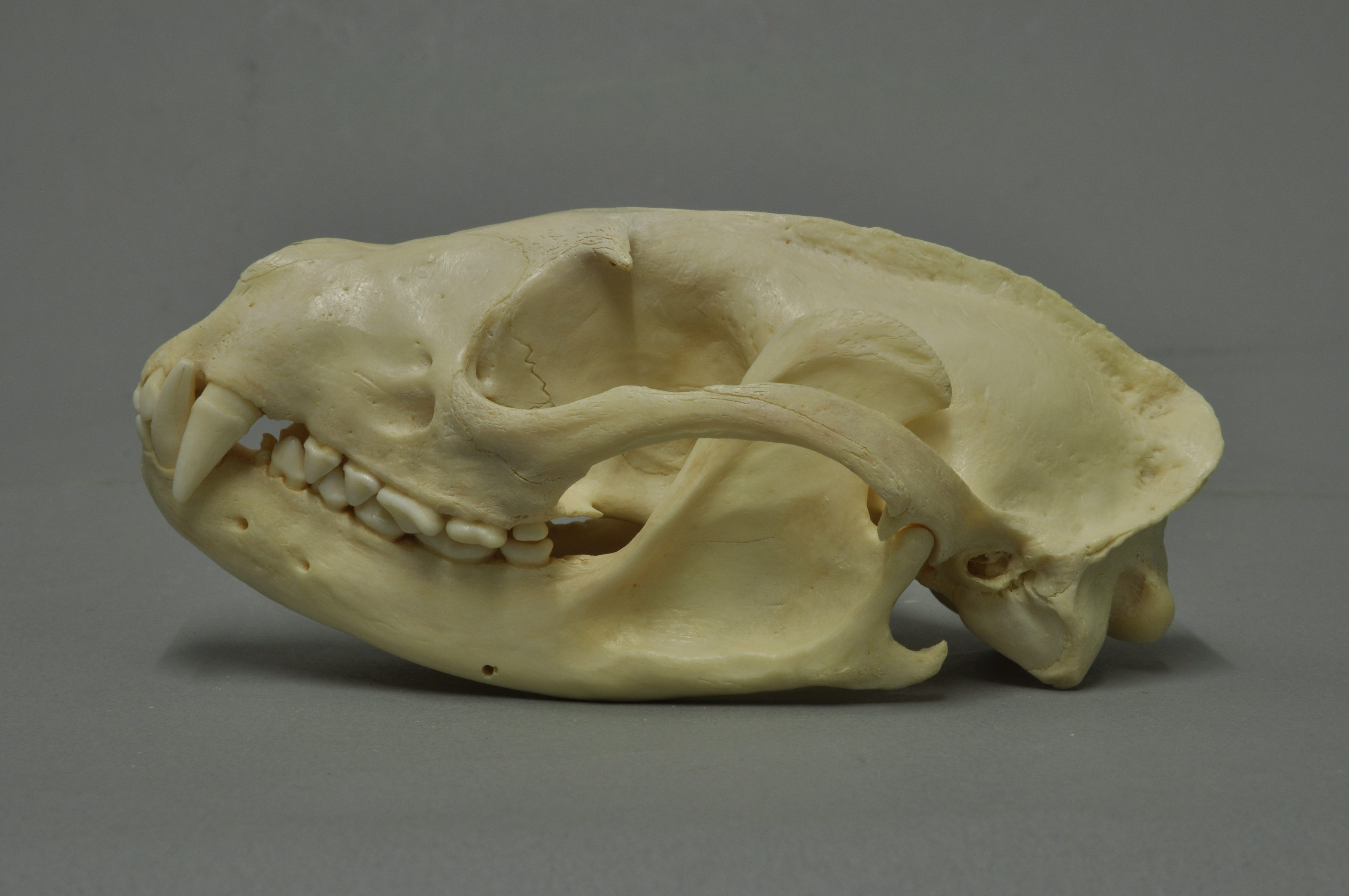
Otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals. Otters' habitats include dens known as holts or couches, with their social structure described by terms such as dogs or boars for males, bitches or sows for females, and pups or cubs for offspring. Groups of otters can be referred to as a bevy, family, lodge, romp, or raft when in water, indicating their social and playful characteristics. Otters are known for their distinct feces, termed spraints, which can vary in smell from freshly mown hay to putrefied fish. Otters exhibit a varied life cycle with a gestation period of about 60–86 days, and offspring typically stay with their family for a year. They can live up to 16 years, with their diet mainly consisting of fish and sometimes frogs, birds, or shellfish, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different things which can interfere with a normal sense of smell, including damage to the nose or smell receptors, anosmia, upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of Eleanor Gamble, published in 1898, which compared olfactory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditionally identified as such (namely Visual perception, sight, Olfaction, smell, Somatosensory system, touch, taste, and hearing), many more are now recognized. Senses used by non-human organisms are even greater in variety and number. During sensation, sense organs collect various stimuli (such as a sound or smell) for Transduction (physiology), transduction, meaning transformation into a form that can be understood by the brain. Sensation and perception are fundamental to nearly every aspect of an organism's cognition, behavior and thought. In organisms, a sensory organ consists of a group of interrelated Sensory neuron, sensory cells that respond to a specific type of physical stimulus. Via Cranial nerves, cranial and spinal nerves (nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating System
A mating system is a way in which a group is structured in relation to sexual behaviour. The precise meaning depends upon the context. With respect to animals, the term describes which males and females mating, mate under which circumstances. Recognised systems include Monogamy in animals, monogamy, Animal sexual behaviour#Polygamy, polygamy (which includes Polygyny in animals, polygyny, Polyandry in animals, polyandry, and polygynandry), and Promiscuity#Other animals, promiscuity, all of which lead to different mate choice outcomes and thus these systems affect how sexual selection works in the species which practice them. In plants, the term refers to the degree and circumstances of outcrossing. In human sociobiology, the terms have been extended to encompass the formation of relationships such as marriage. In plants The primary mating systems in plants are outcrossing (cross-fertilisation), autogamy (self-fertilisation) and apomixis (asexual reproduction without fertilization, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masked Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet or Himalayan palm civet, is a viverrid species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hog Badger
Hog badgers are three species of mustelid in the genus ''Arctonyx''. They represent one of the two genera in the subfamily Melinae, alongside the true badgers (genus ''Meles''). Taxonomy ''Arctonyx'' was formerly considered a monotypic genus containing one species, '' A. collaris'', but a 2008 study found it to comprise 3 distinct species, a finding later followed by the American Society of Mammalogists. Species Three species are known: Conservation The IUCN considers the greater hog badger (''A. collaris''), the northern hog badger (''A. albogularis'') and the Sumatran hog badger (''A. hoevenii'') as three separate species A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), .... The greater hog badger is listed as a Vulnerable species. The other two are listed as Least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masked Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet or Himalayan palm civet, is a viverrid species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans''), also known as the American jackal, prairie wolf, or brush wolf, is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the Wolf, gray wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological niche as the golden jackal does in Eurasia; however, the coyote is generally larger. The coyote is listed as Least Concern, least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, due to its wide distribution and abundance throughout North America. The species is versatile, able to adapt to and expand into environments modified by humans; urban coyotes are common in many cities. The coyote was sighted in eastern Panama (across the Panama Canal from their home range) for the first time in 2013. The coyote has 19 recognized subspecies. The average male weighs and the average female . Their fur color is predominantly light gray and red or fulvous int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. About 31% of Earth's land surface is covered by forests at present. This is one-third less than the forest cover before the expansion of agriculture, with half of that loss occurring in the last century. Between 15 million to 18 million hectares of forest, an area the size of Bangladesh, are destroyed every year. On average 2,400 trees are cut down each minute. Estimates vary widely as to the extent of deforestation in the tropics. In 2019, nearly a third of the overall tree cover loss, or 3.8 million hectares, occurred within humid tropical primary forests. These are areas of mature rainforest that are especially important for biodiversity and carbon storage. The direct cause of most deforestation is agriculture by far. More than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Fragmentation
Habitat fragmentation describes the emergence of discontinuities (fragmentation) in an organism's preferred environment (habitat), causing population fragmentation and ecosystem decay. Causes of habitat fragmentation include geological processes that slowly alter the layout of the physical environment (suspected of being one of the major causes of speciation), and human activity such as land conversion, which can alter the environment much faster and causes the extinction of many species. More specifically, habitat fragmentation is a process by which large and contiguous habitats get divided into smaller, isolated patches of habitats. Definition The term habitat fragmentation includes five discrete phenomena: * Reduction in the total area of the habitat * Decrease of the interior: edge ratio * Isolation of one habitat fragment from other areas of habitat * Breaking up of one patch of habitat into several smaller patches * Decrease in the average size of each patch of habit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |