|
Mesa Verde
Mesa Verde National Park is a national park of the United States and UNESCO World Heritage Site located in Montezuma County, Colorado, and the only World Heritage Site in Colorado. The park protects some of the best-preserved Ancestral Puebloan ancestral sites in the United States. Established by Congress and President Theodore Roosevelt in 1906, the park occupies near the Four Corners region of the American Southwest. With more than 5,000 sites, including 600 cliff dwellings, it is the largest archaeological preserve in the United States. Mesa Verde (Spanish for "green table", or more specifically "green table mountain") is best known for structures such as Cliff Palace, one of the largest cliff dwellings in North America. Starting BC Mesa Verde was seasonally inhabited by a group of nomadic Paleo-Indians known as the Foothills Mountain Complex. The variety of projectile points found in the region indicates they were influenced by surrounding areas, including the Great B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National Parks Of The United States
The United States has 63 national parks, which are congressionally designated protected areas operated by the National Park Service, an agency of the Department of the Interior. National parks are designated for their natural beauty, unique geological features, diverse ecosystems, and recreational opportunities, typically "because of some outstanding scenic feature or natural phenomena." While legislatively all units of the National Park System are considered equal with the same mission, national parks are generally larger and more of a destination, and hunting and extractive activities are prohibited. National monuments, on the other hand, are also frequently protected for their historical or archaeological significance. Eight national parks (including six in Alaska) are paired with a national preserve, areas with different levels of protection that are administered together but considered separate units and whose areas are not included in the figures below. The units of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montezuma County, Colorado
Montezuma County is a county located in the southwest corner of the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 25,849. The county seat is Cortez, Colorado, Cortez. Montezuma County contains many archaeologically significant Amerindian structures, which notably can be found in Mesa Verde National Park, Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Yucca House National Monument, and Hovenweep National Monument. Montezuma County is also home to most of the Ute Mountain Indian Reservation, home of the Weeminuche Band of the Ute Nation, known as the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe, with its headquarters at Towaoc, Colorado, Towaoc. History Montezuma County has been settled since approximately AD 600, and had an estimated population of approximately 100,000, four times its current population, in the 12th century. However, a series of events caused virtually all permanent settlements to be abandoned between 1200 and 1300, and the area was contes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
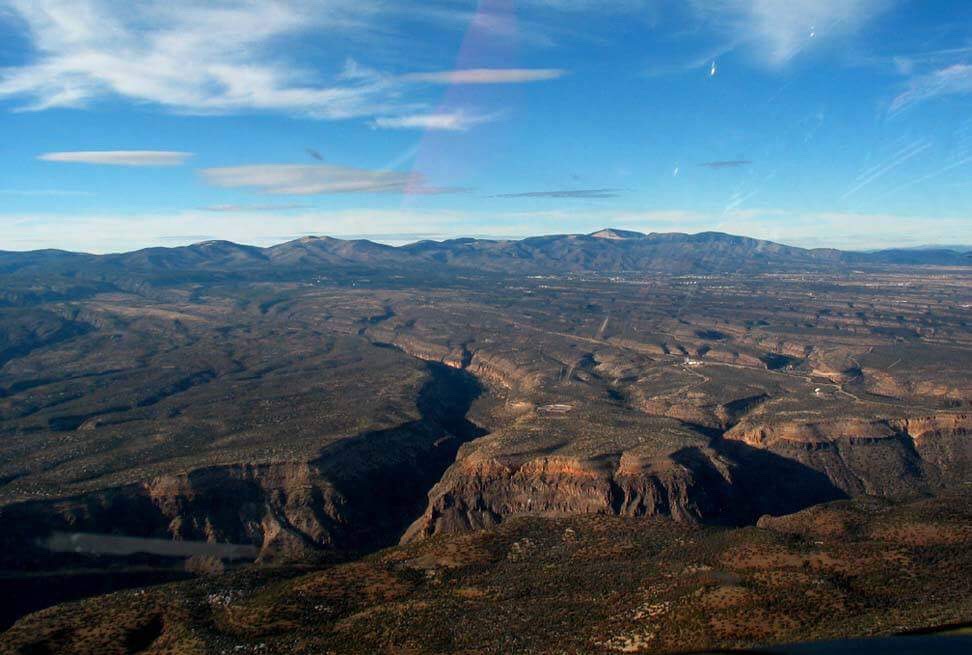
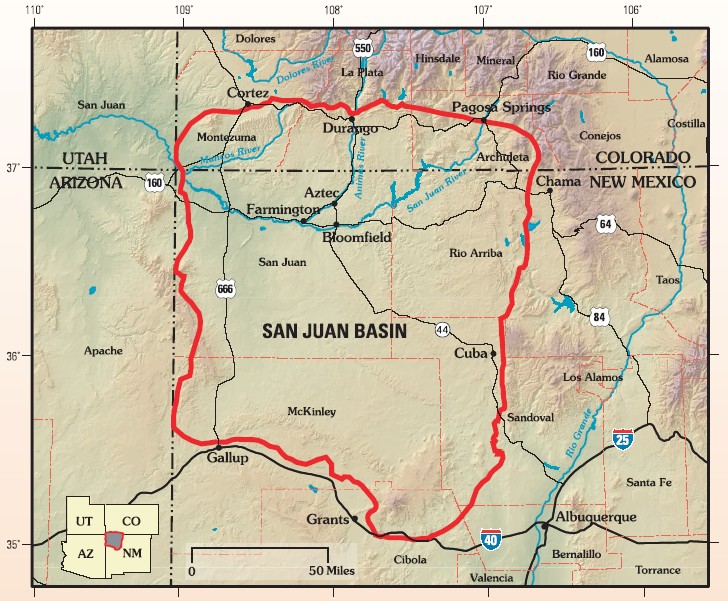
San Juan Basin
The San Juan Basin is a geologic structural basin located near the Four Corners region of the Southwestern United States. The basin covers 7,500 square miles and resides in northwestern New Mexico, southwestern Colorado, and parts of Utah and Arizona. Specifically, the basin occupies space in the San Juan, Rio Arriba, Sandoval, and McKinley counties in New Mexico, and La Plata and Archuleta counties in Colorado. The basin extends roughly N-S and E-W. The San Juan Basin is an asymmetric structural depression in the Colorado Plateau province, with varying elevation and nearly in topographic relief. Its most striking features include Chaco Canyon (northwestern New Mexico, between Farmington and Santa Fe) and Chacra Mesa. The basin lies west of the Continental Divide, and its main drainage is the southwest- to west-flowing San Juan River, which eventually joins the Colorado River in Utah. Climate of the basin is arid to semiarid, with an annual precipitation of and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan Mountains
The San Juan Mountains is a high and rugged mountain range in the Rocky Mountains in southwestern Colorado and northwestern New Mexico. The area is highly mineralized (the Colorado Mineral Belt) and figured in the gold and silver mining industry of early Colorado. Major towns, all old mining camps, include Creede, Lake City, Silverton, Ouray, and Telluride. Large scale mining has ended in the region, although independent prospectors still work claims throughout the range. The last large-scale mines were the Sunnyside Mine near Silverton, which operated until late in the 20th century, and the Idarado Mine on Red Mountain Pass, which closed in the 1970s. Famous old San Juan mines include the Camp Bird and Smuggler Union mines, both located between Telluride and Ouray. The Summitville mine was the scene of a major environmental disaster in the 1990s when the liner of a cyanide-laced tailing pond began leaking heavily. Summitville is in the Summitville caldera, one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyptodon Old Drawing
''Glyptodon'' (; ) is a genus of glyptodont, an extinct group of large, herbivorous armadillos, that lived from the Pliocene, around 3.2 million years ago, to the early Holocene, around 11,000 years ago, in South America. It is one of, if not the, best known genus of glyptodont. ''Glyptodon'' has a long and storied past, being the first named extinct Cingulata, cingulate and the type genus of the subfamily Glyptodontinae. Fossils of ''Glyptodon'' have been recorded as early as 1814 from Pleistocene aged deposits from Uruguay, though many were incorrectly referred to the ground sloth ''Megatherium'' by early paleontologists. The type species, ''G. clavipes'', was described in 1839 by notable British Paleontology, paleontologist Richard Owen, Sir Richard Owen. Later in the 19th century, dozens of complete skeletons were unearthed from localities and described by paleontologists such as Florentino Ameghino and Hermann Burmeister. During this era, many species of ''Glyptodon'' were d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangre De Cristo Mountains
The Sangre de Cristo Mountains (Spanish language, Spanish for "Blood of Christ") are the southernmost mountain range, subrange of the Rocky Mountains. They are located in southern Colorado and northern New Mexico in the United States. The mountains run from Poncha Pass in South-Central Colorado, trending southeast and south, ending at Glorieta Pass, southeast of Santa Fe, New Mexico. The mountains contain a number of fourteeners, fourteen thousand foot peaks in the Colorado portion, as well as several peaks in New Mexico which are over thirteen thousand feet. The name of the mountains may refer to the occasional reddish hues observed during sunrise and sunset, and when alpenglow occurs, especially when the mountains are covered with snow. Although the particular origin of the name is unclear, it has been in use since the early 19th century. Before that time the terms "La Sierra Nevada", "La Sierra Madre", "La Sierra", and "The Snowies" (used by English speakers) were used. Accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pajarito Plateau
The Pajarito Plateau is a volcanic plateau in north central New Mexico, United States. The plateau, part of the Jemez Mountains, is bounded on the west by the Sierra de los Valles, the range forming the east rim of the Valles Caldera, and on the east by the Puye escarpment, which rises about above the Rio Grande valley about a mile (1.6 km) west of the river. The Rio Grande passes through White Rock, New Mexico, White Rock Canyon to the southeast, and the Caja del Rio (Cerros del Rio) across the river is sometimes regarded as part of the plateau. The plateau is occupied by several notable entities, including Bandelier National Monument, the town of Los Alamos, New Mexico, Los Alamos and its remote suburb White Rock, New Mexico, White Rock, and Los Alamos National Laboratory. Elevations range from about at the river to about where the plateau merges into the mountain range. The Pajarito Plateau is primarily composed of Bandelier Tuff, a voluminous deposit of volcanic tuff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albuquerque Basin
The Albuquerque Basin (or Middle Rio Grande Basin) is a structural basin and ecoregion within the Rio Grande rift in central New Mexico. It contains the city of Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque. Geologically, the Albuquerque Basin is a half-graben that slopes down towards the east to terminate on the Sandia Mountains, Sandia and Manzano Mountains, Manzano mountains. The basin is the largest and oldest of the three major basins in the Rio Grande rift, containing sediments whose depth ranges from . The basin has a semi-arid climate, with large areas that count as semi-desert. Paleo-Indian traces dating back 12,000 years show that the climate used to be wetter and more fertile than it is today. The Rio Grande flows through the basin from north to south, and Rio Grande Valley (New Mexico), its valley has been irrigated for at least 1,000 years. Intense irrigation began in the late nineteenth century with new dams, levees and ditches which has caused environmental problems. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chama River (Rio Grande)
The Rio Chama, a major tributary river of the Rio Grande, is located in the U.S. states of Colorado and New Mexico. The river is about long altogether. From its source to El Vado Dam its length is about , from El Vado Dam to Abiquiu Dam is about , and from Abiquiu Dam to its confluence with the Rio Grande is about .Calculated in Google Earth The name "Chama" is a shortened version of the Tewa term , meaning "wrestling pueblo-ruin". Course The Rio Chama originates in south-central Colorado, just above the New Mexico border in the San Juan Mountains and Rio Grande National Forest. The main stem Rio Chama begins at the confluence of two short headwater tributaries called West Fork and East Fork. The West Fork flows eastward from the Continental Divide. Across the divide lies the Navajo River, one of the headwater tributaries of the Colorado River. The East Fork extends a few miles into Conejos County, Colorado to a source near one of the headwater tributaries of the Conejos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pueblo
Pueblo refers to the settlements of the Pueblo peoples, Native American tribes in the Southwestern United States, currently in New Mexico, Arizona, and Texas. The permanent communities, including some of the oldest continually occupied settlements in the United States, are called pueblos (lowercased). Spanish explorers of northern New Spain used the term ''pueblo'' to refer to permanent Indigenous towns they found in the region, mainly in New Mexico and parts of Arizona, in the former province of Santa Fe de Nuevo México, Nuevo México. This term continued to be used to describe the communities housed in apartment structures built of stone, adobe, and other local material. The structures were usually multistoried buildings surrounding an open plaza. Many rooms were accessible only through ladders raised and lowered by the inhabitants, thus protecting them from break-ins and unwanted guests. Larger pueblos are occupied by hundreds to thousands of Puebloan people. Several federall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Sisters (agriculture)
The Three Sisters () are the three main agricultural crops of various indigenous people of Central and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North America: Cucurbita, squash, maize ("corn"), and climbing Bean, beans (typically Phaseolus acutifolius, tepary beans or Phaseolus vulgaris, common beans). In a technique known as companion planting, the maize and beans are often planted together in mounds formed by hilling soil around the base of the plants each year; squash is typically planted between the mounds. The cornstalk serves as a Trellis (architecture), trellis for climbing beans, the beans Nitrogen fixation#Root nodule symbioses, fix nitrogen in their root nodules and stabilize the maize in high winds, and the wide leaves of the squash plant shade the ground, keeping the soil moist and helping prevent the establishment of Weed, weeds. Indigenous peoples throughout North America cultivated different varieties of the Three Sisters, adapted to varying local environments. The ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |