|
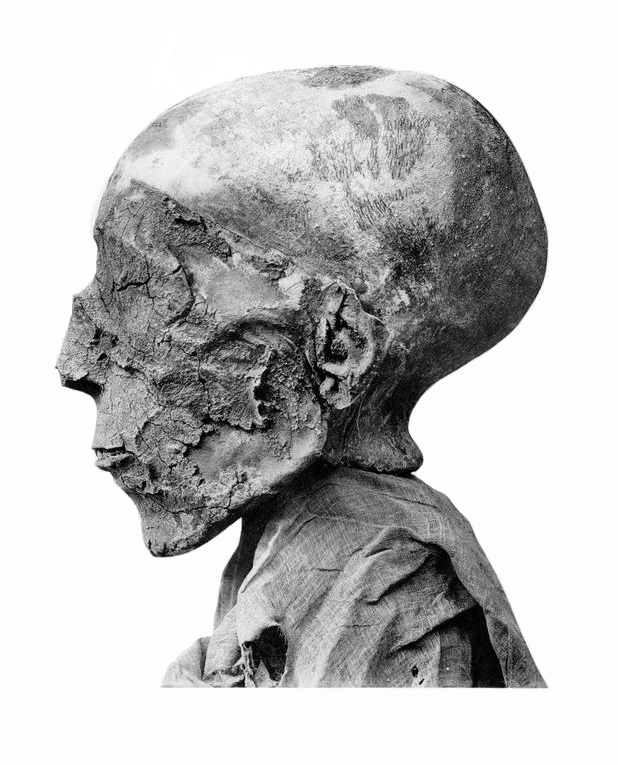
Merenptah
Merneptah () or Merenptah (reigned July or August 1213–2 May 1203 BCE) was the fourth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. According to contemporary historical records, he ruled Egypt for almost ten years, from late July or early August 1213 until his death on 2 May 1203.Jürgen von Beckerath, ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten'', Mainz, (1997), pp.190 He was the first royal-born pharaoh since Tutankhamun of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Merneptah was the thirteenth son of Ramesses II,Gae Callender, ''The Eye Of Horus: A History of Ancient Egypt'', Longman Cheshire (1993), p.263 only coming to power because all of his older brothers had died, including his full brother Khaemweset. He was around seventy years old when he ascended to the throne. He is arguably best known for the Merneptah Stele, featuring the first known mention of the name Israel. His throne name was ''Ba-en-re Mery-netjeru'', which means "Soul of Ra, Beloved of the Gods". Early years F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merenptah Israel Stele Cairo
Merneptah () or Merenptah (reigned July or August 1213–2 May 1203 BCE) was the fourth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. According to contemporary historical records, he ruled Egypt for almost ten years, from late July or early August 1213 until his death on 2 May 1203.Jürgen von Beckerath, ''Chronologie des Pharaonischen Ägypten'', Mainz, (1997), pp.190 He was the first royal-born pharaoh since Tutankhamun of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Merneptah was the thirteenth son of Ramesses II,Gae Callender, ''The Eye Of Horus: A History of Ancient Egypt'', Longman Cheshire (1993), p.263 only coming to power because all of his older brothers had died, including his full brother Khaemweset. He was around seventy years old when he ascended to the throne. He is arguably best known for the Merneptah Stele, featuring the first known mention of the name Israelites, Israel. His throne name was ''Ba-en-re Mery-netjeru'', which means "ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merneptah Stele
The Merneptah Stele, also known as the Israel Stele or the Victory Stele of Merneptah, is an inscription by Merneptah, a pharaoh in ancient Egypt who reigned from 1213 to 1203 BCE. Discovered by Flinders Petrie at Thebes, Egypt, Thebes in 1896, it is now housed at the Egyptian Museum in Cairo. The text is largely an account of Merneptah's victory over the ancient Libyans and their allies, but the last three of the 28 lines deal with a separate campaign in Canaan, then part of Egypt's imperial possessions. It is sometimes referred to as the "Israel Stele" because a majority of scholars translate a set of hieroglyphs in line 27 as "Israelites, Israel". Alternative translations have been advanced but are not widely accepted. The stele represents the earliest textual reference to Israel and the only reference from ancient Egypt. It is one of four known inscriptions from the Iron Age that date to the time of and mention History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel by name, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merenptah (prince)
Merenptah was an ancient Egyptian prince during the 19th Dynasty, and was likely a son of Pharaoh Merenptah (reigned 1213-1203 BCE). He is known from two statues of Senusret I usurped by Pharaoh Merenptah − found in Tanis and Alexandria, respectively − and from three statue fragments from Bubastis. Since he shares a name with Pharaoh Merenptah, and his name is similar to that of the crown prince and eventual successor, Seti Merenptah, and he wears an ''uraeus drawing of a Uraeus The Uraeus () or Ouraeus (Ancient Greek: , ; Egyptian: ', "rearing cobra", plural: ''Uraei'') is the stylized, upright form of an Egyptian cobra, used as a symbol of sovereignty, royalty, deity and divine authority in anci ...'' usually worn by pharaohs only. It is a possibility that he is in fact the same as either of these two. However, Prince Merenptah's titles slightly differ from those of the pharaoh and the crown prince, and the Senusret statues were usurped by Merenptah when he was already ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isetnofret II
Isetnofret (or Isis-nofret or Isitnofret) (Ancient Egyptian: "the beautiful Isis") was a royal woman of Ancient Egypt and, as the Great Royal Wife of Pharaoh Merenptah, she became Isetnofret II. Family Isetnofret II may have been the daughter of Prince Khaemwaset. If so, she married her uncle Merneptah. Another possibility is that Isetnofret II is a daughter of King Ramesses II and his second great royal wife, Queen Isetnofret I. Her children include: * Seti Merenptah, who assume the throne as Seti II * Merenptah, King's son, Executive at the Head of the Two Lands, and Generalissimo Dodson & Hilton, p.178, 182 * Khaemwaset, King's son, Depicted in Karnak Temple * Isetnofret, King's daughter mentioned in the Leiden ship log Titles The titles of Isetnofret II include: Lady of The Two Lands (nbt-t3wy), Great King’s Wife (hmt-niswt-wrt), Mistress of Upper and Lower Egypt (hnwt-Shm’w -mhw), King’s Wife (hmt-nisw). Life Isetnofret II grew up during the reign of Ramesses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siptah
Akhenre Setepenre Siptah or Merneptah Siptah was the penultimate ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. His father's identity is currently unknown. Both Seti II and Amenmesse have been suggested although the fact that Siptah later changed his royal name or Nomen (Ancient Egypt), nomen to Merneptah Siptah after his Year 2 suggests rather that his father was Merneptah. If correct, this would make Siptah and Seti II half-brothers since both of them were sons of Merneptah. He was not the crown prince, but succeeded to the throne as a child after the death of Seti II. His accession date occurred on I Season of the Emergence, Peret day 2 around the month of December. Origins Historically, it was believed that Tiaa (wife of Seti II), Tiaa, a wife of Seti II, was the mother of Siptah. This view persisted until it was eventually realized that a relief in the Louvre Museum (E 26901) "pairs Siptah's name together with the name of his mother" a certain Sutailya or Soteraya. Sutailya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isetnofret
Isetnofret (or Isis-nofret or Isitnofret) (Ancient Egyptian: "the beautiful Isis") was one of the Great Royal Wives of Pharaoh Ramesses II and was the mother of his successor, Merneptah. She was one of the most prominent of the royal wives, along with Nefertari, and was the chief queen after Nefertari's death (around the 24th year of the pharaoh's reign). Family The parents of Isetnofret are not known. She must have married Ramesses II even before he came to the throne as her eldest children already appear in scenes from the time of Seti I. She had at least three sons and one daughter. Her children include: * Prince Ramesses, Crown Prince from Year 25 to 50 of Ramesses II * Princess-Queen Bintanath, firstborn daughter and later wife of RamessesDodson & Hilton, p.170 * Prince Khaemwaset, High Priest of Ptah. Crown Prince from Year 50 to 55 of Ramesses II * Pharaoh Merneptah, Ramesses' 13th son and ultimate successor (he outlived the first 12 princes) * Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seti II
Seti II (or Sethos II) was the fifth pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt and reigned from 1203 BC to 1197 BC. His throne name, Userkheperure Setepenre, means "Powerful are the manifestations of Ra, Re, the chosen one of Re." He was the son of Merneptah and Isetnofret II and occupied the throne during a period known for dynastic intrigue and short reigns, and his rule was no different. Seti II had to deal with many serious plots, most significantly the accession of a rival king named Amenmesse, possibly a half brother, who seized control over Thebes, Egypt, Thebes and Nubia in Upper Egypt during his second to fourth regnal years. Contest for the throne Evidence that Amenmesse was a direct contemporary with Seti II's rule—rather than Seti II's immediate predecessor—includes the fact that Seti II's royal KV15 tomb at Thebes was deliberately vandalised with many of Seti's royal names being carefully erased here during his reign. The erasures were sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age. Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations and other peoples.Mark Smith in "The Early History of God: Yahweh and Other Deities of Ancient Israel" states "Despite the long regnant model that the Canaanites and Israelites were people of fundamentally different culture, archaeological data now casts doubt on this view. The material culture of the region exhibits numerous common points between Israelites and Canaanites in the Iron I period (c. 1200–1000 BCE). The record would suggest that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture ... In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature. Given the information available, one cannot maintain a radical cultural separation between Canaanites and Israelites for the Iron I period." (pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesses II
Ramesses II (sometimes written Ramses or Rameses) (; , , ; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was an Pharaoh, Egyptian pharaoh. He was the third ruler of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty. Along with Thutmose III of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty, he is often regarded as the greatest, most celebrated, and most powerful pharaoh of the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom, which itself was the most powerful period of ancient Egypt. He is also widely considered one of ancient Egypt's most successful warrior pharaohs, conducting no fewer than 15 military campaigns, all resulting in victories, excluding the Battle of Kadesh, generally considered a stalemate. In Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek sources, he is called Ozymandias, derived from the first part of his Egyptian-language regnal name: . Ramesses was also referred to as the "Great Ancestor" by successor pharaohs and the Egyptian people. For the early part of his reign, he focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Royal Wife
Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife () is the title that was used to refer to the Queen consort, principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official functions. Description While most ancient Egyptians were monogamy, monogamous, a male pharaoh would have had other, lesser wives and concubines in addition to the Great Royal Wife. This arrangement would allow the pharaoh to enter into diplomatic marriages with the daughters of allies, as was the custom of ancient kings. In the past the order of succession in Ancient Egypt was thought to pass through the royal women. This theory, referred to as the Heiress Theory, has been rejected regarding the Eighteenth Dynasty ever since a 1980s study of its royalty.O'Connor and Cline (Editors), Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign, pg 6 The throne likely passed to the eldest living son of those pharaohs. The mother of the heir to the throne was not always the Great Royal Wife, but once a pharaoh was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn Museum
The Penn Museum is an archaeology and anthropology museum at the University of Pennsylvania. It is located on Penn's campus in the University City, Philadelphia, University City neighborhood of Philadelphia, at the intersection of 33rd and South Streets. Housing over 1.3 million artifacts, the museum features one of the most comprehensive collections of Middle and Near-Eastern art in the world. History The Penn Museum, originally called the "University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology", was founded in 1887 following a successful archaeological expedition to the ancient site of Nippur in modern-day Iraq (then part of the Ottoman Empire). Provost William Pepper persuaded the trustees of the University of Pennsylvania to erect a fireproof building to house artifacts from the excavation. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, North American and European museums regularly sponsored such excavations throughout the Mediterranean and Near East, sharing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (, ; Bohairic ; ), or Men-nefer, was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt that was known as ''mḥw'' ("North"). Its ruins are located in the vicinity of the present-day village of Mit Rahina (), in markaz (county) Badrashin, Giza, Egypt. Along with the Memphite Necropolis, pyramid fields that stretch on a desert plateau for more than on its west, including the famous Giza pyramid complex, Pyramids of Giza, Memphis and its necropolis have been listed as a World Heritage Site. The site is open to the public as an open-air museum. According to legends related in the early third century BC by Manetho, a priest and historian who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the Hellenistic period of ancient Egypt, the city was founded by Pharaoh, King Menes. It was the List of Egyptian capitals, capital of ancient Egypt (''Kemet'' or ''Kumat'') during both the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom and remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |