|
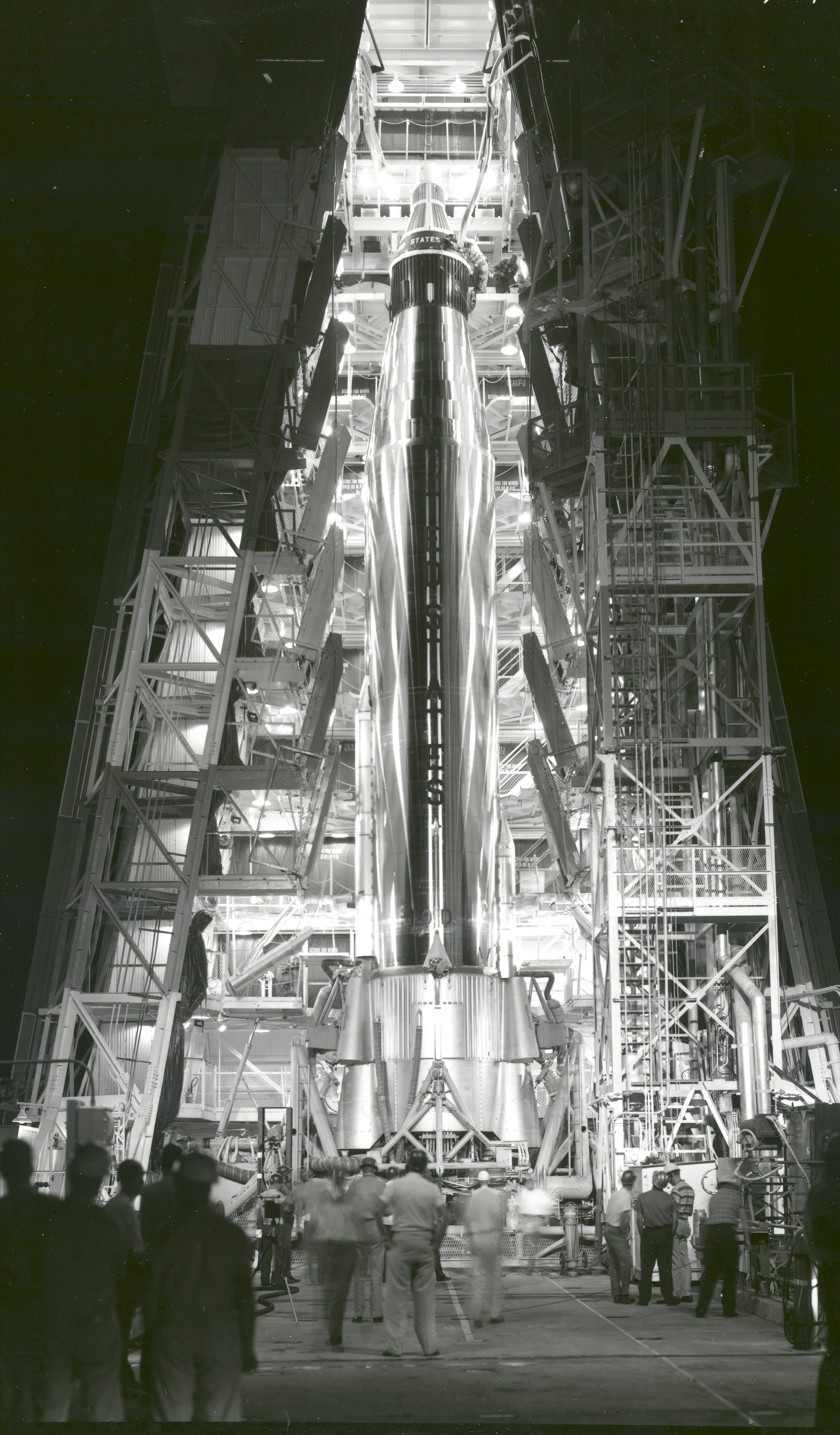
Mercury-Atlas 8
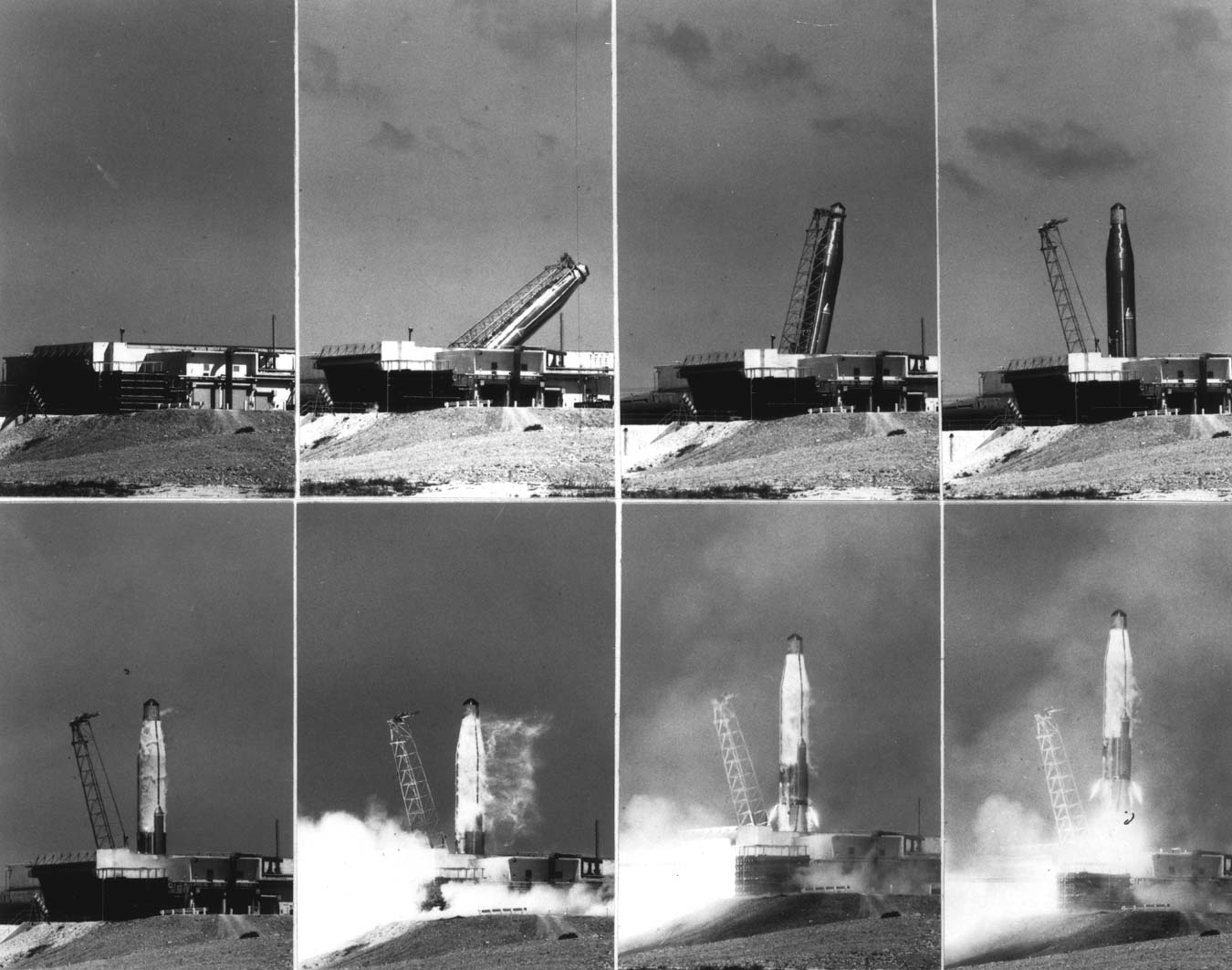
Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) was the fifth United States crewed space mission, part of NASA's Mercury program. Astronaut Wally Schirra, Walter M. Schirra Jr., orbited the Earth six times in the ''Sigma 7'' spacecraft on October 3, 1962, in a nine-hour flight focused mainly on technical evaluation rather than on scientific experimentation. This was the longest U.S. crewed orbital flight yet achieved in the Space Race, though well behind the several-day record set by the Soviet Union, Soviet Vostok 3 earlier in the year. It confirmed the Mercury spacecraft's durability ahead of the one-day Mercury-Atlas 9 mission that followed in 1963. Planning began for the third U.S. orbital mission in February 1962, aiming for a six-or-seven-orbit flight to build on the previous three-orbit missions. NASA officially announced the mission on June 27, and the flight plan was finalized in late July. The mission focused on engineering tests rather than on scientific experimentation. The mission finally lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas LV-3B
The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas D Mercury Launch Vehicle or Mercury-Atlas Launch Vehicle, was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, and was a member of the Atlas (rocket family), Atlas family of rockets. With the Atlas having been originally designed as a weapon system, testing and design changes were made to the missile to make it a safe and reliable launch vehicle. After the changes were made and approved, the US launched the LV-3B nine times, four of which had human spaceflight, crewed Mercury spacecraft. Design The Atlas LV-3B was a Human-rating certification, human-rated expendable launch system used as part of the United States Project Mercury to send astronauts into low Earth orbit. Manufactured by American aircraft manufacturing company Convair, it was derived from the SM-65D Atlas missile, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok 3
Vostok 3 () and Vostok 4 (, 'Orient 4' or 'East 4') were Soviet space program flights in August 1962, intended to determine the ability of the human body to function in conditions of weightlessness, test the ground control capability to launch and manage two separate, concurrent flights, and test the endurance of the Vostok 3KA spacecraft over longer flights. Cosmonaut Andriyan Nikolayev orbited the Earth 64 times in Vostok 3 over nearly four days in space, August 11–15, 1962, a feat which would not be matched by NASA until the Gemini program (1965–1966). Pavel Popovich was launched on Vostok 4 on August 12, and made 48 Earth orbits. The two capsules were launched on trajectories that brought the spacecraft within approximately of each another. They also communicated with each other via radio, the first ship-to-ship communications in space. These missions marked the first time that more than one crewed spacecraft was in orbit at the same time, giving Soviet mission con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury-Atlas 5
Mercury-Atlas 5 was an American spaceflight of the Mercury program. It was launched on November 29, 1961, with Enos, a chimpanzee, aboard. The craft orbited the Earth twice and splashed down about south of Bermuda, and Enos became the first primate from the United States and the third great ape to orbit the Earth. History By November 1961, the Soviet Union had launched Yuri Gagarin and Gherman Titov into orbit during the Vostok 1 and Vostok 2 crewed orbital flights while the United States had managed only suborbital ones. At that time NASA was still debating placing a chimpanzee in orbit as part of the Mercury-Atlas subprogram, with NASA headquarters questioning the wisdom of the Manned Spacecraft Center launching another uncrewed Mercury mission. The NASA Public Affairs Office issued a press release prior to the flight, stating "The men in charge of Project Mercury have insisted on orbiting the chimpanzee as a necessary preliminary checkout of the entire Mercury program be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SM-65D Atlas
The SM-65D Atlas, or Atlas D, was the first operational version of the U.S. Atlas missile. Atlas D was first used as an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) to deliver a nuclear weapon payload on a suborbital trajectory. It was later developed as a launch vehicle to carry a payload to low Earth orbit on its own, and later to geosynchronous orbit, to the Moon, Venus, or Mars with the Agena or Centaur upper stage. Atlas D was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, at Launch Complexes 11, 12, 13 and 14, and Vandenberg Air Force Base at Launch Complex 576. The fully operational D-series Atlas was similar to the R&D model Atlas B and C, but incorporated a number of design changes implemented as a result of lessons learned during test flights. In addition, the D-series had the full-up Rocketdyne MA-2 propulsion system with of thrust versus the of thrust in the Atlas B/C's engines. Operational Atlas D missiles retained radio ground guidance aside from a few R& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok 2
Vostok 2 (, ) was a Soviet space mission which carried cosmonaut Gherman Titov into orbit for a full day on August 6, 1961, to study the effects of a more prolonged period of weightlessness on the human body. Titov orbited the Earth over 17 times, exceeding the single orbit of Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1 − as well as the suborbital spaceflights of American astronauts Alan Shepard and Gus Grissom aboard their respective Mercury-Redstone 3 and 4 missions. Titov's number of orbits and flight time would not be surpassed by an American astronaut until Gordon Cooper's Mercury-Atlas 9 spaceflight in May 1963. After the flight of Vostok 1, Sergei Korolev took a short vacation in Crimea where he began working out the flight plan for the next mission. There were considerable arguments over the duration of the mission as flight doctors argued for no more than three orbits. The flight of Korabl-Sputnik 2 nine months earlier had carried two dogs on a six orbit mission, during which the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborbital
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity. For example, the path of an object launched from Earth that reaches the Kármán line (about – above sea level), and then falls back to Earth, is considered a sub-orbital spaceflight. Some sub-orbital flights have been undertaken to test spacecraft and launch vehicles later intended for orbital spaceflight. Other vehicles are specifically designed only for sub-orbital flight; examples include crewed vehicles, such as the X-15 and SpaceShipTwo, and uncrewed ones, such as ICBMs and sounding rockets. Flights which attain sufficient velocity to go into low Earth orbit, and then de-orbit before completing their first full orbit, are not considered sub-orbital. Examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit. For celestial objects in general, the orbital period is determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, ''e.g.'' Earth around the Sun. Periods in astronomy are expressed in units of time, usually hours, days, or years. Its reciprocal is the orbital frequency, a kind of revolution frequency, in units of hertz. Small body orbiting a central body According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period ''T'' of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: :T = 2\pi\sqrt where: * ''a'' is the orbit's semi-major axis * ''G'' is the gravitationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |