|
Mercenaries In India
Mercenaries in India were fighters, primarily peasants, who came from India and abroad, to fight for local rulers in India in the medieval period. This mercenary work became an important source of income for some communities. During the 16th and 17th centuries, a number of mercenaries, arriving from several countries found employment in India. Some of the mercenaries emerged to become independent rulers. Purbiyas and Pindaris In the medieval period, Purbiya mercenaries from Bihar and Eastern Uttar Pradesh were a common feature in Kingdoms in Western and Northern India. They were also later recruited by the Marathas and the British. They also played a prominent role in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. In the 18th and 19th centuries, the Pindaris were irregular military men who were recruited by the elites of the Mughal Empire and the Deccan sultanates, and later by the Maratha Confederacy. They were disbanded in the Third Anglo-Maratha War. African mercenaries in India The Sidd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janjira State
Janjira State was a princely state in India during the British Raj. It was governed by the Siddi Khan dynasty of Habesha peoples, Habesha descent and the state was under the suzerainty of the Bombay Presidency. Janjira State was located on the Konkan coast in the present-day Raigad district of Maharashtra. The state included the towns of Murud, Raigad, Murud and Shrivardhan, as well as the fortified island of Murud-Janjira, just off the coastal village of Murud, which was the capital and the residence of the rulers. The state had an area of 839 km2, not counting Jafarabad State, Jafarabad, and a population of 110,389 inhabitants in 1931. Jafarabad State (also spelled Jafrabad) was a dependency of the Nawab of Janjira State, and located 320 km to its north-northwest. History Establishment According to legend, Janjira Invaded in the year 1489 the Ahmadnagar Sultanate sent its admiral Piram Khan (of Ethiopian descent) with orders to capture the Murud-Janjira from Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of the river Tapti near its confluence with the Arabian Sea, it used to be a large seaport. It is now the commercial and economic centre of South Gujarat, and one of the largest urban areas of western India. It has well-established diamond and textile industry, and is a major supply centre for apparels and accessories. About 90% of the world's diamonds are cut and polished in Surat. It is the second largest city in Gujarat after Ahmedabad and the List of most populous cities in India, eighth largest city by population and List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, ninth largest urban agglomeration in India. It is the administrative capital of the Surat district. The city is located south of the state capital, Gandhinagar; south of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South Asia and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company gained Company rule in India, control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent and British Hong Kong, Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world by various measures and had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British Army at certain times. Originally Chartered company, chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies," the company rose to account for half of the world's trade during the mid-1700s and early 1800s, particularly in basic commodities including cotton, silk, indigo dye, sugar, salt, spices, Potass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Goa
The State of India, also known as the Portuguese State of India or Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded seven years after the discovery of the sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the Kingdom of Portugal. The capital of Portuguese India served as the governing centre of a string of military forts and maritime ports scattered along the coasts of the Indian Ocean. The first viceroy Francisco de Almeida established his base of operations at Fort Manuel in the Malabar region, after the Kingdom of Cochin negotiated to become a protectorate of Portugal in 1505. With the Portuguese conquest of Goa from the Bijapur Sultanate in 1510, Goa became the major anchorage for the Armadas arriving in India. The capital of the viceroyalty was transferred from Cochin to Goa in 1530. From 1535, Mumbai (Bombay) was a harbour of Portuguese India, known as '' Bom Bahia'', until it was handed over, through the dowry of Catherine de Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Shah I
Muhammad Shah I, born Tatar Khan, was a ruler of the Muzaffarid dynasty, who reigned over the Gujarat Sultanate briefly from 1403 (when he deposed his father, Zafar Khan), until 1404, when Zafar Khan regained the throne. Early life About 1396, Tatar Khan, leaving his baggage in the fort of Panipat, made an attempt to capture Delhi. But Iqbál Khán took the fort of Pánipat, captured Tátár Khán's baggage, and forced him to withdraw to Gujarát. On the death of Nasir ud din Muhammad Shah III in 1392, Nasir's son Sikandar assumed the throne but died after just after 45 days. Sikandar was succeeded by his brother Mahmud II but their cousin Nusrat Khan also claimed similar rank in Firuzabad. In the prevailing situation, Tamerlane invaded India and marched on Delhi in 1398. In early 1399, Tamerlane defeated Mahmud II and looted and destroyed much of Delhi. Sultan Mahmud II escaped and after many wanderings, reached Patan. Mahmud II hoped to secure Zafar Khan's alliance to mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belonging to the Yadava clan of Lunar dynasty, Chandravamsa lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts by the southern powers to ward off Muslim invasions of India, Muslim invasions by the end of the 13th century. At its peak in the early 16th century under Krishnadevaraya, it subjugated almost all of Southern India's ruling dynasties and pushed the Deccan sultanates beyond the Tungabhadra River, Tungabhadra-Krishna River, Krishna River doab region, in addition to annexing the Gajapati Empire (Odisha) up to the Krishna River, becoming one of the most prominent states in India. The empire's territory covered most of the lands of the modern-day Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Goa, and some pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellion of Ismail Mukh against Muhammad bin Tughlaq, the Sultan of Delhi. Ismail Mukh then abdicated in favour of Zafar Khan, who established the Bahmani Sultanate. The Bahmani Kingdom was perpetually at war with its neighbours, including its rival to the south, the Vijayanagara Empire, which outlasted the sultanate. The Mahmud Gawan Madrasa was created by Mahmud Gawan, the vizier regent who was prime minister of the sultanate from 1466 until his execution in 1481 during a conflict between the foreign (Afaqis) and local (Deccanis) nobility. Bidar Fort was built by Ahmad Shah I (), who relocated the capital to the city of Bidar. Ahmad Shah led campaigns against Vijayanagara and the sultanates of Malwa and Gujarat. His campaign against Vijayanag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik Ambar
Malik Ambar (1548–1626) was a military leader and statesman who served as the Peshwa (Prime Minister) of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate and its ''de facto'' ruler from 1600 until his death in 1626. Originally a slave from modern day Ethiopia, ''Chapu'', as he was known then, was sold from place to place by many slave merchants, one of whom renamed him Ambar and converted him to Islam. He was eventually brought to India, where he was bought by his last owner, the Peshwa of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate. Ambar rose through the ranks at Ahmadnagar, where he created a mercenary force numbering greater than 50,000 men. He was eventually given the title "Malik"(ملِك) meaning King in arabic. He was based in the Deccan region and was hired by local kings. Ambar became a popular Prime Minister of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate, showing administrative acumen. He is also regarded as a pioneer in guerrilla warfare in the region. He is credited with carrying out a revenue settlement of much of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Razia Sultana
Raziyyat-Ud-Dunya Wa Ud-Din ( Hindustani (Hindi): रज़िय्यत उद दुन्या व उद दीन, ; 1205 – 15 October 1240, ), popularly known as Razia Sultan, was a ruler of the Delhi Sultanate in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent. She was the first female Muslim ruler of the subcontinent, and the only female Muslim ruler of Delhi. A daughter of Mamluk Sultan Shamsuddin Iltutmish, Razia administered Delhi during 1231–1232 when her father was busy in the Gwalior campaign. According to a possibly apocryphal legend, impressed by her performance during this period, Iltutmish nominated Razia as his heir apparent after returning to Delhi. Iltutmish was succeeded by Razia's half-brother Ruknuddin Firuz, whose mother Shah Turkan planned to execute her. During a rebellion against Ruknuddin, Razia instigated the general public against Shah Turkan, and ascended the throne after Ruknuddin was deposed in 1236. Razia's ascension was challenged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut
Jamal ud-Din Yaqut (also Yakut; died 1240) was an African Siddi slave-turned- nobleman who was a close confidant of Razia Sultan, the first and only female monarch of the Delhi Sultanate in India. Yakut was the puppet of Razia Sultan's stepmother but after sometime he became a trustworthy soldier of the Delhi Sultanate. Razia Sultan's patronage made him an influential member of the court, provoking racial antagonism amongst the nobles and clergy, who were both primarily Turkic and already resentful of the rule of a female monarchy. Ethnic background Not much is known regarding Jamal ud-Din Yaqut's early life, primarily due to his slave status. It is speculated that ''Jamal ud-Din Yaqut'' was the Turkic name given to him by his Mamluk overlords. Yaqut lived during the time of Sultan Iltutmish and then Razia Sultan, sometime from 1200 to 1240 CE, when he was slain in a revolt against Razia Sultan. Yaqut belonged to the habshis, a group of enslaved Africans of East African ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
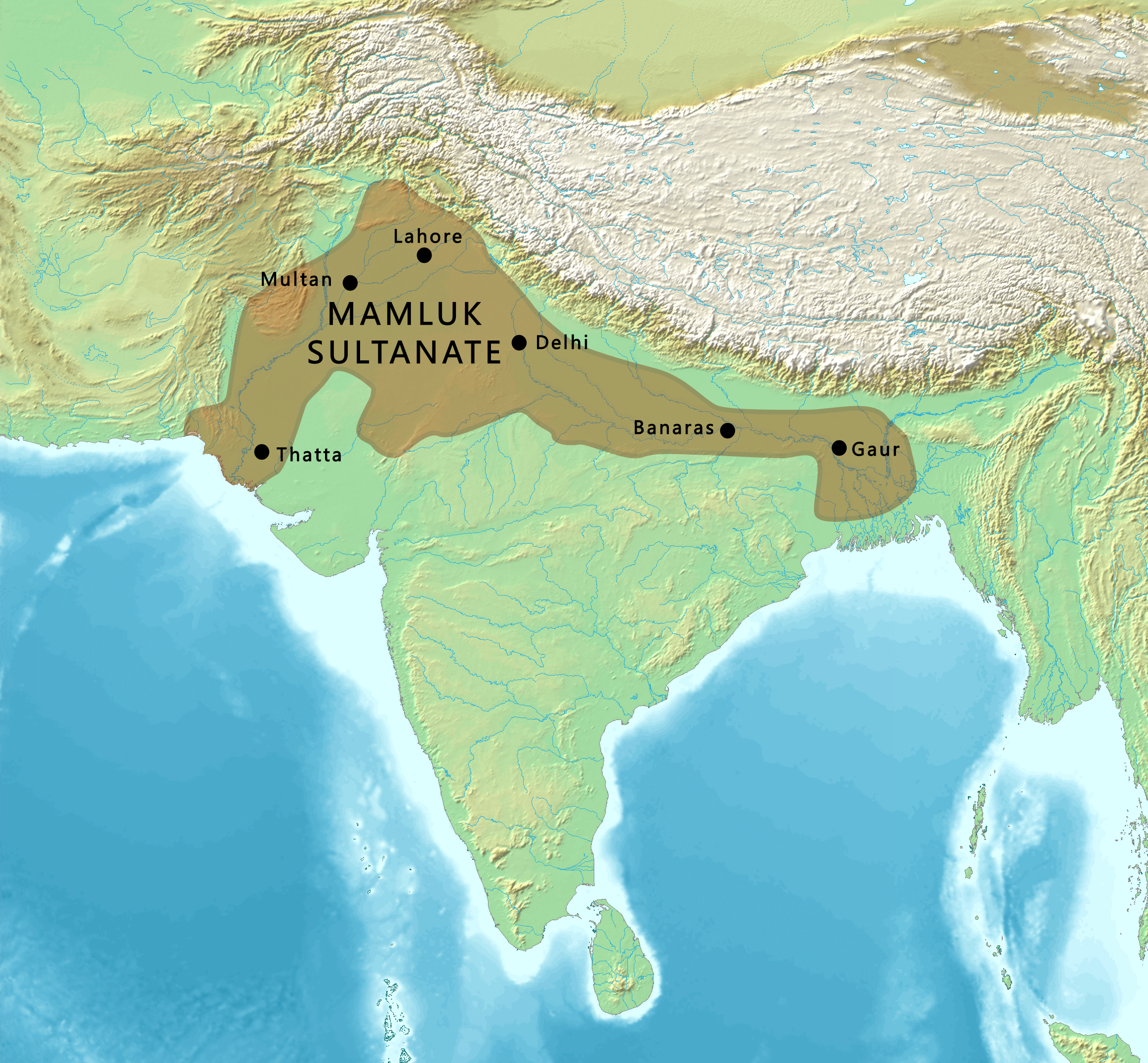
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |