|
Memory Effect
Memory effect, also known as battery effect, lazy battery effect, or battery memory, is an effect observed in nickel-cadmium rechargeable batteries that causes them to hold less charge. It describes the situation in which nickel-cadmium batteries gradually lose their maximum energy capacity if they are repeatedly recharged after being only partially discharged. The battery appears to "remember" the smaller capacity. True memory effect The term "memory" came from an aerospace nickel-cadmium application in which the cells were repeatedly discharged to 25% of available capacity (give or take 1%) by exacting computer control, then recharged to 100% capacity without overcharge. This long-term, repetitive cycle régime, with no provision for overcharge, resulted in a loss of capacity beyond the 25% discharge point. True memory cannot exist if any one (or more) of the following conditions holds: * batteries achieve full overcharge. * discharge is not exactly the same each cycle, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechargeable Battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or primary battery, which is supplied fully charged and discarded after use. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. The term "accumulator" is used as it accumulates and stores energy through a reversible electrochemical reaction. Rechargeable batteries are produced in many different shapes and sizes, ranging from button cells to megawatt systems connected to stabilize an electrical distribution network. Several different combinations of electrode materials and electrolytes are used, including lead–acid, zinc–air, nickel–cadmium (NiCd), nickel–metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and lithium-ion polymer (Li-ion polymer). Rechargeable batteries typically initially cost more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procter & Gamble
The Procter & Gamble Company (P&G) is an American multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble. It specializes in a wide range of personal health/consumer health, personal care and hygiene products; these products are organized into several segments including beauty; grooming; health care; fabric and home care; and baby, feminine, and family care. Before the sale of Pringles and Duracell to Kellogg's and Berkshire Hathaway, respectively, its product portfolio also included food, snacks, beverages, and batteries. P&G is incorporated in Ohio. In 2014, P&G recorded $83.1 billion in sales. On August 1, 2014, P&G announced it was streamlining the company, dropping and selling off around 100 brands from its product portfolio in order to focus on the remaining 65 brands, which produced 95% of the company's profits. A.G. Lafley, the company's chairman and CEO until October 2015, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge Cycle
A charge cycle is the process of charging a rechargeable battery and discharging it as required into a load. The term is typically used to specify a battery's expected life, as the number of charge cycles affects life more than the mere passage of time. Discharging the battery fully before recharging may be called "deep discharge"; partially discharging then recharging may be called "shallow discharge". A "charge cycle" is not a unit of time; the length of time spent charging or discharging does not affect the number of charge cycles. Each battery is affected differently by charge cycles. In general, number of cycles for a rechargeable battery (the cycle life) indicates how many times it can undergo the process of complete charging and discharging until failure or starting to lose capacity. Apple Inc. clarifies that a charge cycle means using all the battery's capacity, but not necessarily by discharging it from 100% to 0%: "You complete one charge cycle when you’ve used (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms/molecules in the sintered material diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating a solid piece. Since the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy, metallurgical powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compacting of snowfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Camera
A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in Digital data storage, digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs. Digital and digital movie cameras share an optical system, typically using a Camera lens, lens with a variable Diaphragm (optics), diaphragm to focus light onto an image pickup device. The diaphragm and Shutter (photography), shutter admit a controlled amount of light to the image, just as with film, but the image pickup device is electronic rather than chemical. However, unlike film cameras, digital cameras can display images on a screen immediately afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solvent like water. Upon dissolving, the substance separates into cations and anions, which disperse uniformly throughout the solvent. Solid-state electrolytes also exist. In medicine and sometimes in chemistry, the term electrolyte refers to the substance that is dissolved. Electrically, such a solution is neutral. If an electric potential is applied to such a solution, the cations of the solution are drawn to the electrode that has an abundance of electrons, while the anions are drawn to the electrode that has a deficit of electrons. The movement of anions and cations in opposite directions within the solution amounts to a current. Some gases, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), under conditions of high temperature or low pressure can also functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trickle Charging
Trickle charging is the process of Battery charger, charging a fully charged battery (electricity), battery at a rate equal to its self-discharge rate, enabling the battery to remain at its fully charged level. This state occurs almost exclusively when the battery is not loaded, as trickle charging will not keep a battery charged if current is being drawn by a load. A battery under continuous float voltage charging is said to be float-charging. For lead–acid batteries under no-load float charging (such as in SLI battery, SLI batteries), trickle charging happens naturally at the end-of-charge, when the lead–acid battery internal resistance to the charging current increases enough to reduce additional charging current to a trickle, hence the name. In such cases, the trickle charging equals the energy expended by the lead–acid battery splitting the water in the electrolyte into hydrogen and oxygen gases. Other battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion battery technology, cannot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium-ion Battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy density, and energy efficiency and a longer cycle life and calendar life than other types of rechargeable batteries. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991; over the following 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold. In late 2024 global demand passed per year, while production capacity was more than twice that. The invention and commercialization of Li-ion batteries has had a large impact on technology, as recognized by the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Li-ion batteries have enabled portable consumer electronics, laptop computers, cellular phones, and electric cars. Li-ion batteries also see signifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
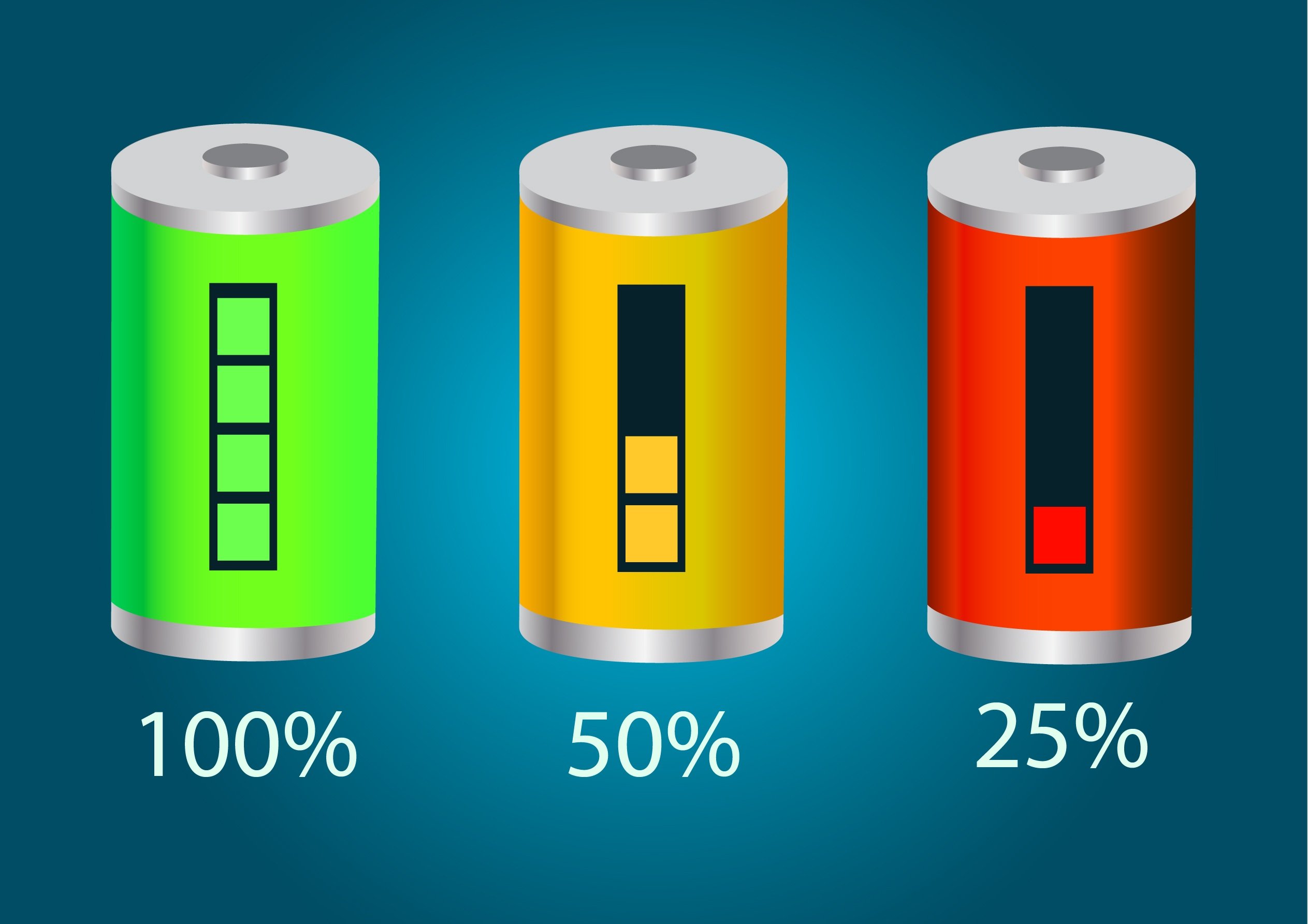
State Of Charge
State of charge (SOC) quantifies the remaining capacity available in a battery at a given time and in relation to a given state of ageing. It is usually expressed as percentage (0% = empty; 100% = full). An alternative form of the same measure is the depth of discharge (DOD), calculated as 1 − SOC (100% = empty; 0% = full). It refers to the amount of charge that may be used up if the cell is fully discharged. State of charge is normally used when discussing the present state of a battery in use, while depth of discharge is most often used to discuss a constant variation of state of charge during repeated cycles. In electric vehicles In a battery electric vehicle (BEV), the state of charge indicates the remaining energy in the battery pack. It is the equivalent of a fuel gauge. The state of charge can help to reduce electrical car owners' anxiety when they are waiting in the line or stay at home since it will reflect the progress of charging and let owners know when it wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battery Charging
A battery charger, recharger, or simply charger, is a device that energy storage, stores energy in an electric battery by running electric current, current through it. The charging protocol—how much voltage and current, for how long and what to do when charging is complete—depends on the size and type of the battery being charged. Some battery types have high tolerance for overcharging after the battery has been fully charged and can be recharged by connection to a constant voltage source or a constant current source, depending on battery type. Simple chargers of this type must be manually disconnected at the end of the charge cycle. Other battery types use a timer to cut off when charging should be complete. Other battery types cannot withstand over-charging, becoming damaged (reduced capacity, reduced lifetime), over heating or even exploding. The charger may have temperature or voltage sensing circuits and a microprocessor controller to safely adjust the charging current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |