|
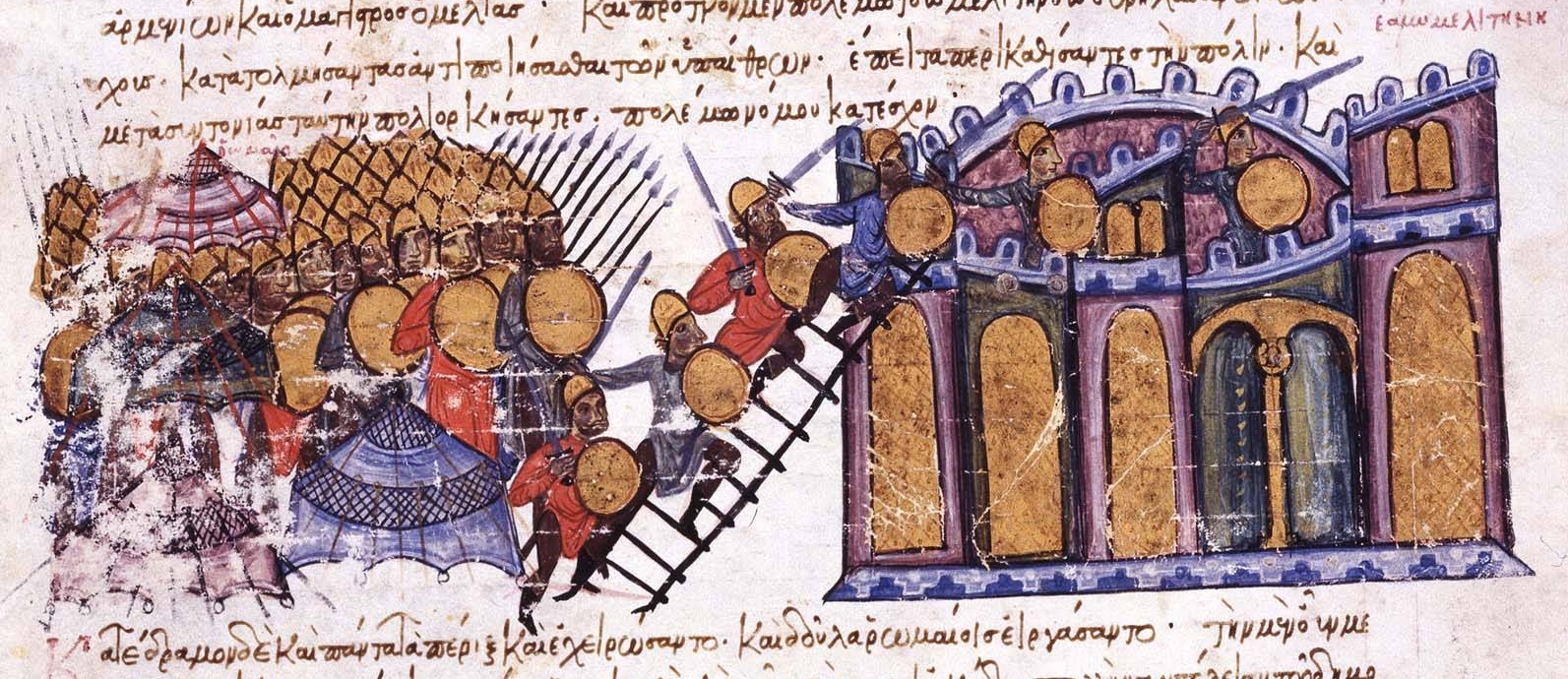
Melias
Melias () or Mleh (, often ''Mleh-mec'', "Mleh the Great" in Armenian sources) was an Armenian prince who entered Byzantine service and became a distinguished general, founding the theme of Lykandos and participating in the campaigns of John Kourkouas against the Arabs. Origin and early career Melias was a member of the lower '' naxarar'' nobility, possibly from the Varazhnuni clan; he was possibly a grandson of Mliah, the prince of Varazhnunik, who was killed by the Arabs in 853. Melias first appears in historical sources as a vassal of Ashot the Long-armed, an Armenian prince (possibly a Bagratid from Taron) who entered Byzantine imperial service in circa 890. As part of Ashot's Armenian contingent, he fought on the Byzantine side at the disastrous Battle of Bulgarophygon against the Bulgarians. Ashot himself perished in this battle, along with the larger part of the Byzantine force.. Melias escaped death and returned to his service at the Byzantine eastern frontier, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lykandos
Lykandos or Lycandus (), known as Djahan in Armenian, was the name of a Byzantine fortress and military-civilian province (or "theme"), known as the Theme of Lykandos (θέμα Λυκανδοῦ), in the 10th–11th centuries. History Origin and early history The fortress of Lykandos was located in the area of modern Elbistan in southeastern Turkey, on the Antitaurus Mountains.. It emerged as a major fortified military centre on the eastern Byzantine frontier under Emperor Leo VI the Wise (), through the actions of the Armenian leader Mleh (Melias in Greek sources), who settled there in 903, establishing a quasi-autonomous lordship. The area was of critical strategic importance, lying directly on the frontier zone between the Byzantines and the Muslim border emirates of Syria and Upper Mesopotamia, and commanding one of the principal routes through the mountains into Byzantine Anatolia. In 905, however, Melias was expelled from the Byzantine Empire (along with other Armenian nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tzamandos
Tzamandos () was a medieval fortress in Anatolia and is today situated in a neighbourhood of Pınarbaşı, Kayseri. It was constructed in 908 by the Byzantine-Armenian general Melias and was a Byzantine and continued as a minor settlement until the early Ottoman period. History Origins Tzamandos was built by the Byzantine Armenian general Melias in 908 in the former no-man's land between the Abbasid Caliphate and the Byzantine Empire. Tzamandos then became a , which included the whole river valley of the Zamantı down to the neighbourhood of Hanköy and the Uzun Yayla, and most likely belonged to the theme of Lykandos which had been created in 914. The town became also soon the seat of a Byzantine bishop. The new region was repopulated by the Byzantine authorities primarily with Armenians and Syrians, which resulted in the establishing of the Syrian Orthodox bishopric of Simandu in 955, which lasted until 1180. When Bardas Skleros revolted in 976, the fortress joined his eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kourkouas
John Kourkouas (, ), also transliterated as Kurkuas or Curcuas, was one of the most important generals of the Byzantine Empire. His success in battles against the Muslim states in the East reversed the course of the centuries-long Arab–Byzantine wars and set the stage for Byzantium's eastern conquests later in the century. Kourkouas belonged to a family of Armenian descent that produced several notable Byzantine generals. As commander of an imperial bodyguard regiment, Kourkouas was among the chief supporters of Emperor Romanos I Lekapenos () and facilitated the latter's rise to the throne. In 923, Kourkouas was appointed commander-in-chief of the Byzantine armies along the eastern frontier, facing the Abbasid Caliphate and the semi-autonomous Arab Muslim border emirates. He kept this post for more than twenty years, overseeing decisive Byzantine military successes that altered the strategic balance in the region. During the 9th century, Byzantium had gradually recovered its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathios Argyros (general Under Leo VI)
Eustathios Argyros (; died ca. 910) was a Byzantine aristocrat and one of the most prominent generals under Emperor Leo VI the Wise (r. 886–912). The first member of the Argyros family to rise to high posts, he fought with distinction against the Arabs in the east, before being disgraced ca. 907, possibly in connection with the flight of Andronikos Doukas to the Arabs. Rehabilitated soon after, he was appointed as ''strategos'' of Charsianon, from which post he oversaw the settlement of Armenian lords as march-wardens along the Empire's eastern frontier. Promoted to commander of the imperial bodyguard in late 908, he again fell into disgrace shortly after and died of poison (apparently a suicide) on his way to his estates. Life Eustathios Argyros was the son of the ''tourmarches'' Leo Argyros, the founder of the noble Argyros family. Nothing is known of his life or prior to the turn of the 10th century, although he may have been in imperial service as early as 866, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rustam Ibn Baradu
Rustam ibn Baradu () or Rustum ibn Bardu, nisba (onomastics), surnamed al-Farghani ("from Ferghana Valley, Farghana"), was a military commander for the Abbasid Caliphate and the governor (''wali'') of Tarsus (city), Tarsus from August 905 to 912/3. Life Rustam was appointed to the post of governor of Tarsus (city), Tarsus and of the Cilician border zone () with the Byzantine Empire on 20 August 905. In this capacity he supervised a Arab–Byzantine prisoner exchanges, prisoner exchange with the Byzantines on the Lamos River soon after. The exchange had already been arranged by his predecessor, Abu'l-Asa'ir Ahmad ibn Nasr, and began on 27 September, but was interrupted after four days after only about 1,200 Arab prisoners had been exchanged, with the Arabs blaming the Byzantines for violating the truce terms. In late October 906, he accompanied the general Ahmad ibn Kayghalagh in an invasion of Byzantine territory. The Abbasid army captured the town of Salandu (Selinus) and advance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
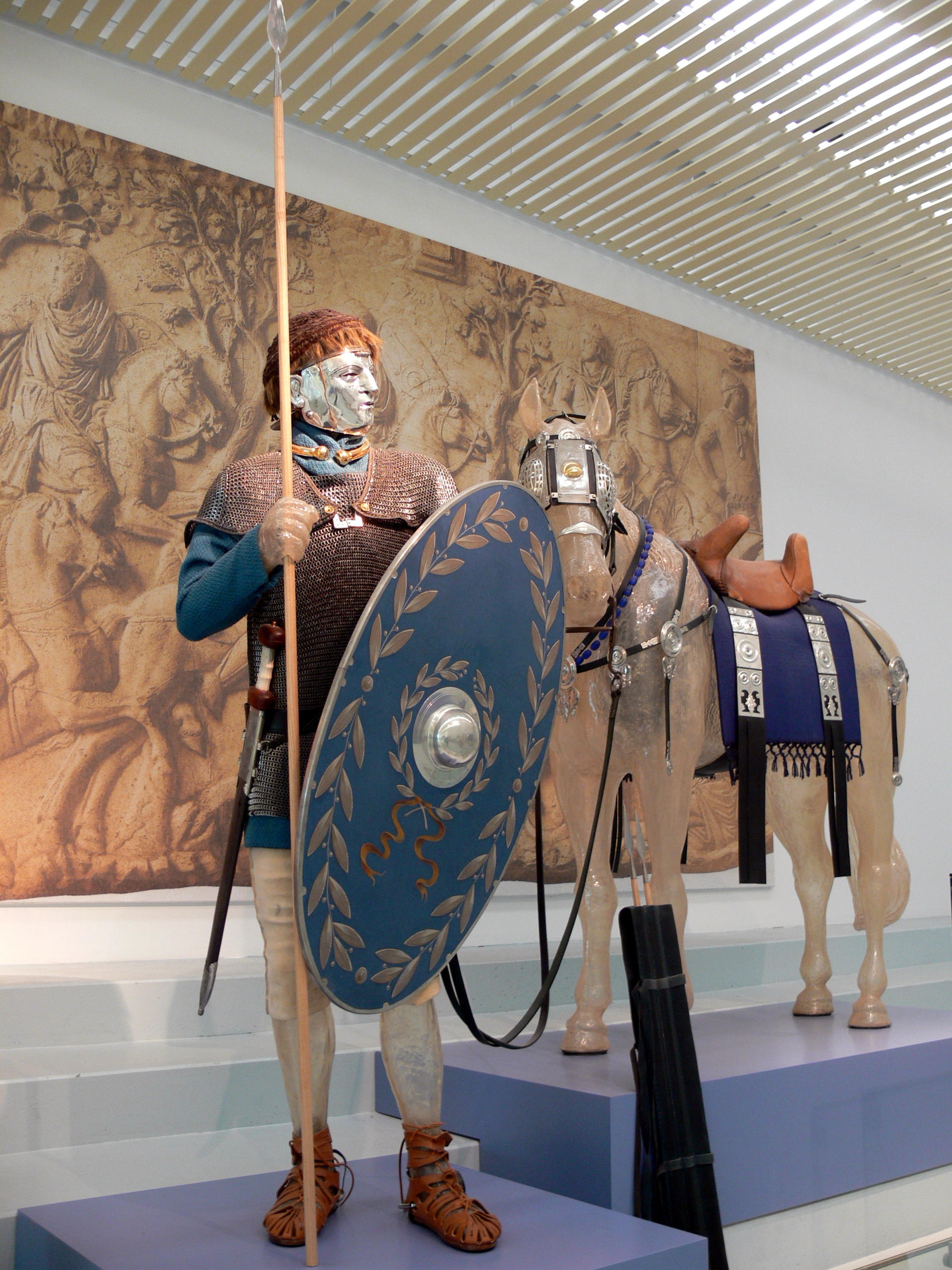
Akritai
The ''Akritai'' (, ''Akrites'', ) is a term used in the Byzantine Empire in the 9th–11th centuries to denote the frontier soldiers guarding the Empire's eastern border, facing the Muslim states of the Middle East. Their exploits, embellished, inspired the Byzantine "national epic" of '' Digenes Akritas'' and the cycle of the Acritic songs. History The term is derived from the Greek word ''akron'' (, in plural ''akra''), meaning or ; similar border guards, the ''limitanei'', were employed in the late Roman and early Byzantine armies to guard the frontiers ('' limes''). In official Byzantine use, the term is non-technical, and used in a descriptive manner, being generally applied to the defenders as well as the inhabitants of the eastern frontier zone, including their Muslim counterparts. The popular image of the ''Akritoi'' has been heavily influenced by their portrayal in the Acritic songs, and refers to the military troops stationed along the Empire's border. In reality, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Doukas (usurper)
Constantine Doukas (or Doux) (; died 913) was a prominent Byzantine general. In 904, he stopped the influential eunuch court official Samonas from defecting to the Arabs. In return, Samonas manipulated his father, Andronikos Doukas (general under Leo VI), Andronikos Doukas, into rebelling and fleeing to the Abbasid court in 906/7. Constantine followed his father to Baghdad, but soon escaped and returned to Byzantium, where he was restored by Leo VI the Wise to favour and entrusted with high military offices. Upon the death of the Emperor Alexander (Byzantine emperor), Alexander, Constantine with the support of several aristocrats unsuccessfully tried to usurp the throne from the young Constantine VII, but was killed in a clash with supporters of the legitimate emperor. Life Early life and career Constantine Doukas was the son of Andronikos Doukas (general under Leo VI), Andronikos Doukas, a prominent general under Emperor Leo VI the Wise () and the first prominent member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadath
Al-Ḥadath al-Ḥamrā' (Arabic for "Hadath the Red") or Adata () was a town and fortress near the Taurus Mountains (modern southeastern Turkey), which played an important role in the Byzantine–Arab Wars. Location The town was located at ca. 1000 m altitude on the southern feet of the Taurus- Antitaurus range, near the upper course of the Aksu River in the Gölbaşı district. Its exact location has been lost, and it has been variously identified with locations north or south of Inekli lake.Ory (1971), pp. 19–20Houtsma (1987), p. 187 History Hadath became important in the early Middle Ages due to its strategic location: it was located in the fortified frontier zone, the '' Thughūr'', that separated the Umayyad and Abbasid empires from the Byzantine Empire. The town lay to the southwest of the important Pass of Hadath/Adata (''darb al-Ḥadath'') which led over the Taurus into Byzantine Anatolia, but was also situated between the two major frontier strongholds of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleisoura (Byzantine District)
In the Byzantine Empire, a ''kleisoura'' (, "enclosure, defile") was a term traditionally applied to a fortified mountain pass and the military district protecting it.; . By the late 7th century, it came to be applied to more extensive frontier districts, distinct from the larger '' themata'', chiefly along the Empire's eastern border with the Caliphate along the line of the Taurus- Anti-Taurus mountains (in the West, only Strymon was in its early days termed a ''kleisoura''). A ''kleisoura'' or ''kleisourarchia'' was an autonomous command, under a ''kleisourarches'' (Greek: κλεισουράρχης). Eventually, most ''kleisourai'' were raised to full ''themata'', and the term fell out of use after the 10th century (in late Byzantine times, '' droungos'' had a similar meaning). Its Islamic counterpart in Cilicia and Mesopotamia Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebasteia (theme)
The Theme of Sebasteia () was a military-civilian province (''thema'' or theme) of the Byzantine Empire located in northeastern Cappadocia and Armenia Minor, in modern Turkey. It was established as a theme in 911 and endured until its fall to the Seljuk Turks in the aftermath of the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. History The theme was formed around the city of Sebasteia (modern Sivas). The region formed part of the Armeniac Theme from the mid-7th century.. The theme is not mentioned in any source prior to the 10th century. In 908, Sebasteia appears for the first time as a distinct fortified frontier district ('' kleisoura''), and by 911 it had been raised to the status of a full theme. As a ''kleisoura'', it was probably subordinate of the newly established theme of Charsianon. The theme comprised the entirety of the Byzantine frontier regions along the middle course of the northern Euphrates. With the expansion of the Byzantine frontier, it was extended south and east as far as Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourma
A ''turma'' (; plural ''turmae''; ) was a cavalry unit in the Roman army of the Republic and Empire. In the Byzantine Empire, it became applied to the larger, regiment-sized military-administrative divisions of a '' thema''. The word is often translated as " squadron" but so is the term '' ala'', a unit that was made up of several ''turmae''. Roman army Republic In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, the time of the Punic Wars and Rome's expansion into Spain and Greece, the core of the Roman army was formed by citizens, augmented by contingents from Rome's allies (''socii''). The organization of the Roman legion of the period is described by the Greek historian Polybius (cf. the so-called " Polybian army"), who writes that each 4,200-strong infantry legion was accompanied by 300 citizen cavalry (''equites''). This contingent was divided into ten ''turmae''.. According to Polybius, the squadron members would elect as their officers three '' decuriones'' ("leaders of 10 men"), of whom the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |