|
Melancthon Taylor Woolsey
Melancthon Taylor Woolsey (1782 – 18 May 1838) was an officer in the United States Navy during the War of 1812 and battles on the Great Lakes. He supervised warship construction at Navy Point in Sackets Harbor, New York, and later had a full career in the Navy. Early life Woolsey was born near Plattsburgh, New York. He was a son of Melancthon Lloyd Woolsey (1758–1819), a Maj.-Gen. of the New York Militia during the Revolutionary War and Alida ( Livingston) Woolsey (1758–1843), a daughter of the Rev. Henry Gilbert Livingston (a grandson of Robert Livingston, 1st Lord of Livingston Manor). His paternal grandparents were Col. Melancthon Taylor Woolsey and Rebecca Lloyd. Through his father he was a descendant of George Jarvis Woolsey, an emigrant from England who was one of the earliest settlers of New Amsterdam and married Rebecca Cornell (a daughter of Thomas Cornell), Through his mother, he was a descendant of the Livingston, Schuyler, and Van Rensselaer families. Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in three archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, in addition to The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The term is often interchangeable with "Caribbean", although the latter may also include coastal regions of Central America, Central and South American mainland nations, including Mexico, Belize, Honduras, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic island nation of Bermuda, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Terminology The English term ''Indie'' is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Lucas Yeo
Sir James Lucas Yeo, KCB, KBA (7 October 1782 – 21 August 1818) was a Royal Navy officer who served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. Born in Southampton, Hampshire, he joined the British navy at the age of 10 and saw his first action in the Adriatic Sea. Yeo distinguished himself in combat multiple times, most notably during the Portuguese conquest of French Guiana, earning knighthoods in the Portuguese Order of Aviz and the British Order of the Bath. He was subsequently given command of the frigate in 1812, but she was later wrecked in the Bahamas, although he was acquitted of blame for its loss. Yeo was then given command of the British squadron on Lake Ontario and commanded it in several engagements on Lake Ontario with American forces. He died off the African coast in 1818. Service history Early life and career Yeo was born in Southampton, England on 7 October 1782 to a naval victualling agent. Yeo was sent to an academy near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roy Campbell Smith
Roy Campbell Smith (1858 – April 11, 1940) was an American naval officer and the Governor of Guam from 1916 to 1918. Early life On July 16, 1858, Smith was born in Fort Mason, Texas. Smith's father was Charles Henry Smith, an assistant surgeon general of the United States and later of the Confederate States of America. Smith's mother was Maria McGregor Campbell Smith. Education In 1878, Smith graduated from the United States Naval Academy in Annapolis, Maryland. Career Smith was the commanding officer of the from 17 September 1912 to 13 October 1914. In 1916, Smith became the Naval Governor of Guam, until 1918. Smith retired as a U.S. Navy Captain. Awards * Navy Cross Personal life On October 11, 1887, in Annapolis, Maryland, Smith married Margaret Aldrich Sampson, daughter of Rear admiral William Thomas Sampson. They had three children, Roy, Marjorie, and William.() Smith's daughter Marjorie Sampson Smith became a sponsor of USS Sampson (DD-63) on March 4, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
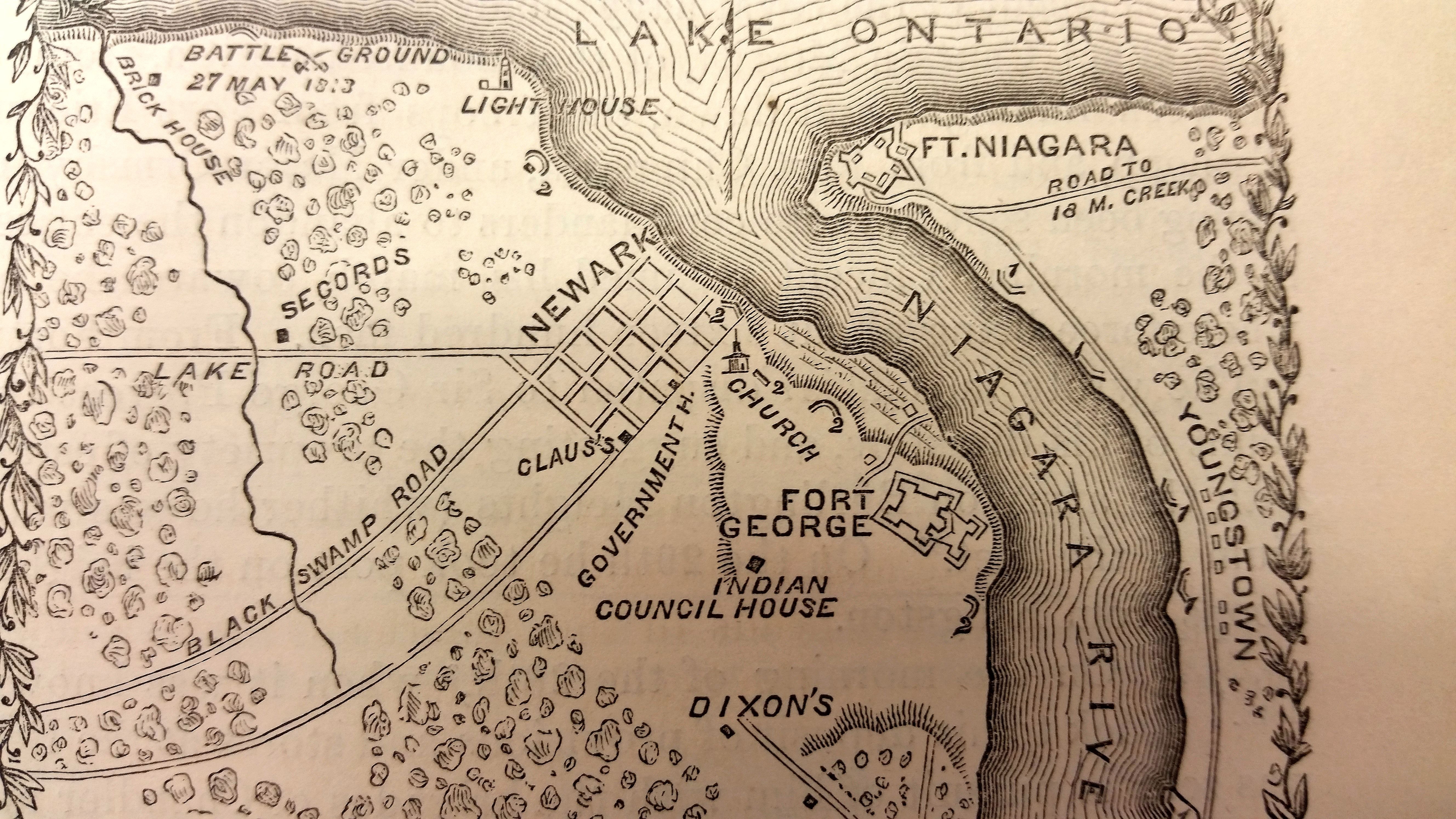
Fort George, Ontario
Fort George was a military fortification in Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. The fort was used by the British Army, the Canadian militia, and the Jeffersonian democracy, Jeffersonian American Republic United States Army, Army for a brief period. The fort was mostly destroyed during the War of 1812. The site of the fort has been a National Historic Sites of Canada, National Historic Site of Canada since 1921, and features a reconstruction of Fort George. The British established Fort George in the 1790s to replace Fort Niagara. Many of its structures were demolished in May 1813, during the Battle of Fort George. After the battle, American forces occupied the fort for seven months before withdrawing in December 1813. Although the British regained the fort shortly afterwards, little effort was put into its reconstruction after they capture of Fort Niagara, captured Fort Niagara the following week. The poor wartime design of Fort George led to its replacement by Fort Mississauga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( , locally pronounced or ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada. It is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of North American cities by population, fourth-most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. As of 2024, the census metropolitan area had an estimated population of 7,106,379. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports, and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multiculturalism, multicultural and cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston, Ontario
Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the northeastern end of Lake Ontario. It is at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River, the south end of the Rideau Canal. Kingston is near the Thousand Islands, a tourist region to the east, and the Prince Edward County, Ontario, Prince Edward County tourist region to the west. Kingston is nicknamed the "Limestone City" because it has many heritage buildings constructed using local limestone. Growing European exploration in the 17th century and the desire for the Europeans to establish a presence close to local Native occupants to control trade led to the founding of a New France, French trading post and military fort at a site known as "Cataraqui" (generally pronounced ) in 1673. The outpost, called Fort Cataraqui, and later Fort Frontenac, became a focus for settlement. After the Conquest of New France (1759–1763), the site of Kingston was relinquished to the British. Cataraqui was renamed K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all unrated warships, including List of gun-brigs of the Royal Navy, gun-brigs and Cutter (boat), cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fire ships were classed by the Royal Navy as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the role of a sloop-of-war when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of the First World War and the highly successful of the Second World War, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capabilities. They performed similar duties to the destroyer escorts of the United States Navy, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner ( ) is a type of sailing ship, sailing vessel defined by its Rig (sailing), rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more Mast (sailing), masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a Topgallant sail, topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a Course (sail), fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are Gaff rig, gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. Etymology The term "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The term may be related to a Scots language, Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. History The exact origins of schooner rigged vessels are obscure, but by early 17th century they appear in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The earliest known il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Chauncey
Isaac Chauncey (February 20, 1772 – January 27, 1840) was a United States Navy officer who served in the Quasi-War, the Barbary Wars and the War of 1812. In the latter part of his naval career he was President of the Board of Navy Commissioners. Involvement in the Quasi-War and First Barbary War Chauncey, born in Black Rock, Connecticut, to Wolcott Chauncy and Ann Brown.Chauncey Fowler, William (1878)Memorials of the Chaunceys: Including President Chauncy Harvard College Library, Henry W. Dutton and Son Printers, Boston, p. 215 His father was the great-great-grandson of Charles Chauncy, the 2nd President of Harvard College. At 19, he was given the command of the ship Jenny, belonging to Peter Schermerhorn, grandfather of Mrs. Astor, and was appointed a lieutenant in the Navy from September 17, 1798. He fought with gallantry in the West Indies during the Quasi-War with France. In a letter dated 21 July, 1802 he was ordered to take command of General Greene for an anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sackett's Harbor
Sackets Harbor (earlier spelled Sacketts Harbor) is a village in Jefferson County, New York, United States, on Lake Ontario. The population was 1,450 at the 2010 census. The village was named after land developer and owner Augustus Sackett, who founded it in the early 1800s. Sackets Harbor is in the western part of the town of Hounsfield and is west of Watertown. The heart of the village, with a Main Street and well-preserved 19th century buildings, has been recognized as the Sackets Harbor Village Historic District and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1983. To support the War of 1812, the US Navy built a major shipyard and its headquarters for the Great Lakes at the village. Within a short period, more than 3,000 men worked at the shipyard. The Army constructed earthworks, forts, barracks and supporting infrastructure to defend the village and navy shipyard, and its troops also camped in the village. The thousands of military personnel made it seem like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warships
A warship or combatant ship is a naval ship that is used for naval warfare. Usually they belong to the navy branch of the armed forces of a nation, though they have also been operated by individuals, cooperatives and corporations. As well as being armed, warships are designed to withstand damage and are typically faster and more maneuverable than merchant ships. Unlike a merchant ship, which carries cargo, a warship typically carries only weapons, ammunition and supplies for its crew. In wartime, the distinction between warships and merchant ships is often blurred. Until the 17th century it was common for merchant ships to be pressed into naval service, and not unusual for more than half of a fleet to be composed of merchant ships—there was not a large difference in construction, unlike the difference between a heavily armoured battleship and an ocean liner. Until the threat of piracy subsided in the 19th century, it was normal practice to arm larger merchant ships such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |