|
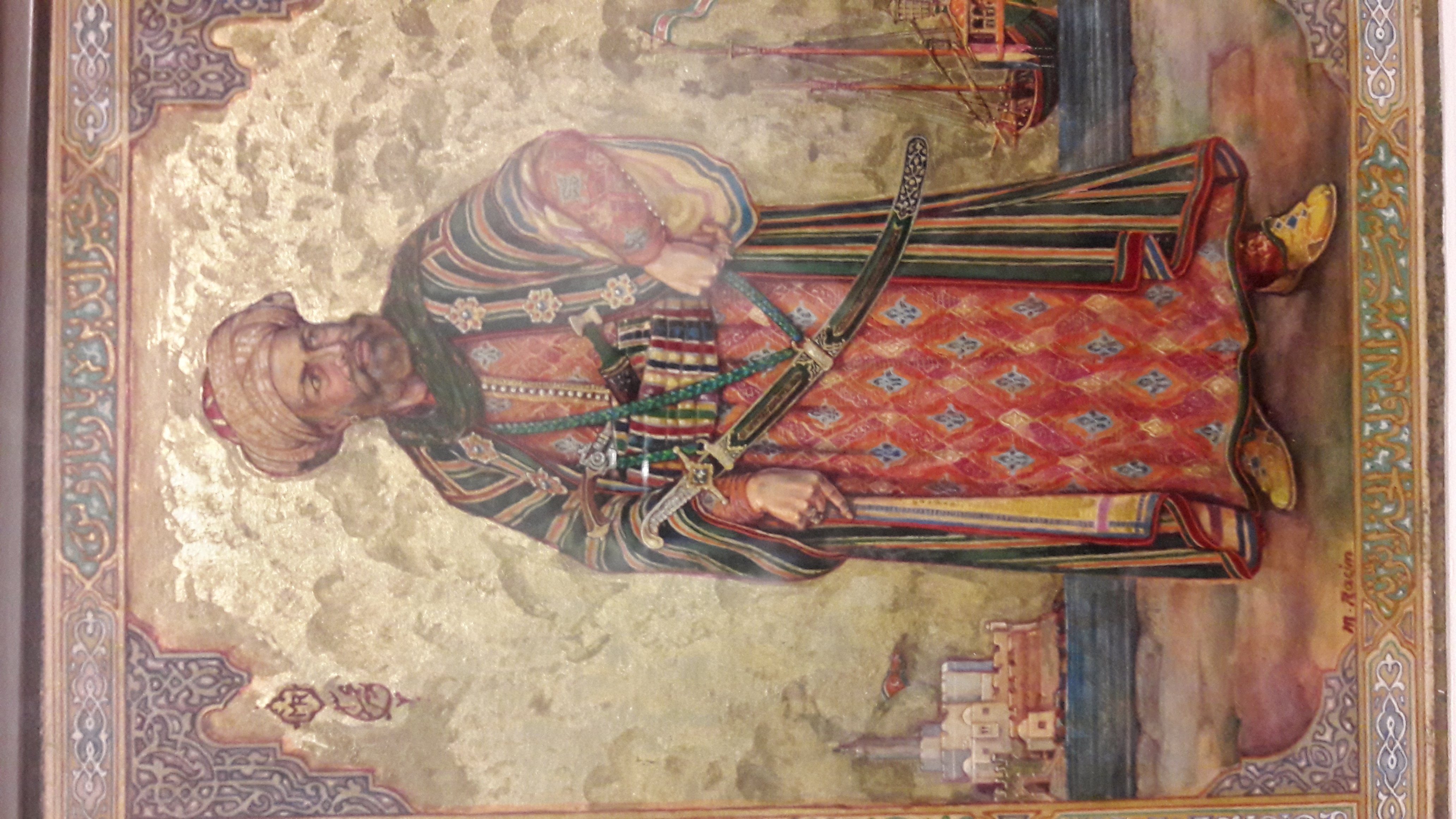
Mehmed III Giray
Mehmed III Giray Crimean Tatar, Ottoman Turkish and (1584–1629, reigned 1623–1628) was a khan of the Crimean Khanate. Much of his life was spent in conflict with nearly everyone around him. Part of the trouble was caused by his over-aggressive brother Shahin Giray. His reign was marked by an unsuccessful Turkish attempt to expel him and by the first treaty between Crimea and the Zaporozhian Cossacks. He was driven out by the Turks in 1628 and died trying to regain his throne. His name in Crimean Tatar is (, ). 1584–1601 Early life His grandfather, khan Mehmed II Giray the fat, was one of the many sons of Devlet I Giray. In 1584 Mehmed II was driven from the throne and killed. A few months later Mehmed's son Saadet II Giray invaded, made himself khan and was driven out. He fled to the Kumyks on the Caspian Sea and died in Astrakhan around 1588, allegedly poisoned by the Russians. Saadet's sons, in order by age, were Devlet, Mehmed and Shahin Giray. Around 1594, during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Crimean Khans
The Crimean Khanate was a state which existed in present-day southern Ukraine from 1441 until 1783. The position of Khan in Crimea was electoral and was picked by beys from four of the most noble families (also known as Qarachi beys: Argyns, Kipchaks, Shirins, and Baryns) at kurultai where the decision about a candidate was adopted.Giray - Khan dynasty of Crimea Khan's Palace website (unavailable currently). The newly elected Khan was raised on a white felt sheet and over him were read Islamic prayers, after that the Khan was triumphantly enthroned. List The following is the chronological table of reigns of Khan (title), Khans of the Crimean Khanate from the Giray dynasty:References < ...
|
Bakhchysarai
Bakhchysarai is a city in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Bakhchysarai Raion (district), as well as the former capital of the Crimean Khanate. Its main landmark is Hansaray, the only extant palace of the Crimean Khans, currently open to tourists as a museum. Population: Since the beginning of the Russo-Ukrainian War in 2014, it has been occupied by the Russian Federation. Geography Bakhchysarai lies in a narrow valley of the river, about 30 Kilometers south-west of Simferopol. History The earliest known man-made objects found in the valley date from the Mesolithic period. Settlements have existed in the valley since Late Antiquity. Before the founding of Bakhchysarai the Qırq Yer fortress (modern Çufut Qale), Salaçıq, and Eski Yurt were built. These have since become incorporated into the urban area of modern Bakhchysarai. Bakhchysarai first appears in historical documents in 1502. In 1532 Sahib I Giray, Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaika (boat)
A chaika (,, , Hungarian language, Hungarian: csajka, , / , or ) was a wooden boat that could have a mast (sailing), mast and sail, a type of galley, used in early modern warfare and cargo transport by the: *Zaporozhian Cossacks in the 16th–17th centuries in Ukraine on the Dnieper River, Dnipro River and the Black Sea. *Serbs in the 16th-19th centuries on the Danube, known as Šajkaši, under the Kingdom of Hungary, Austrian Empire and Habsburgs. *Slovenes from the 16th to the early 20th century on the Drava River. Types Austrian Tschaika were either (Double Tschaika), (Ganz ("Full") Tschaika), (Halb ("Half") Tschaika) or (Quarter Tschaika) in length, operated by sail or oars. Between 30 and 50 men were in service, commanded by an officer, with a helmsman, an armourer, a drummer, two bowsmen, and up to 36 oarsmen.Hollins, p. 11 Zaporizhian Host (Ukraine) Chaikas were between in length, in width, and in depth. The bottom of a chaika was carved out of a single Trunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapudan Pasha
The Kapudan Pasha (, modern Turkish: ), also known as the (, modern: , "Captain of the Sea") was the grand admiral of the Ottoman Navy. Typically, he was based at Galata and Gallipoli during the winter and charged with annual sailings during the summer months. The title of ''Kapudan Pasha'' itself is only attested from 1567 onwards; earlier designations for the supreme commander of the fleet include (" bey of the sea") and ("head captain"). The title ''Derya Bey'' as an official rank within the Ottoman state structure originated during the reign of Bayezid I (). Following the 1453 conquest of Constantinople, Mehmed II raised Baltaoğlu Süleyman Bey to the status of sanjak bey for his efforts against the Byzantines in the Golden Horn.Shaw, Stanford J''History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey'' Vol. 1, pp. 131 ff. Cambridge University Press (Cambridge), 1976. Accessed 12 Sept 2011. Baltaoğlu received the sanjak of Gallipoli (the principal Turkish naval base) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adil Giray
Adil Giray Crimean Tatar, Ottoman Turkish, and was khan of the Crimean Khanate from 1666 to 1671. Family He is said to have been the grandson of Fetih I Giray (see below). His father was killed in battle in 1624 when the Turks tried to overthrow Mehmed III Giray. None of his descendants were khans. His elder brother Fetih was nureddin in 1641-44 during the first reign of Mehmed IV Giray. His kalga and nureddin were Devlet and Gazi, sons of his brother Fetih. Another Adil Giray was one of the many sons of Selâmet I Giray. He served as nureddin under his brothers İslâm III Giray and Mehmed IV Giray circa 1651 to before 1666. His son was Devlet III Giray (1716-1717). He was killed by a fall from a horse. Reign In 1666 he was placed on the throne by the Ottomans, who were displeased with khan Mehmed IV. At the time he was in exile at Rhodes. He came into conflict with his nobles, especially the Shirin clan, because of his questionable ancestry and high taxes. It is said he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahib I Giray
Sahib I Giray Crimean Tatar, Ottoman Turkish and (1501–1551) was Khan of Kazan for three years and Khan of Crimea for nineteen years. His father was the Crimean Khan Meñli I Giray. Sahib was placed on the throne of Kazan by his ambitious brother Mehmed of Crimea and driven out of Kazan by the Russians. He became Khan of Crimea with Ottoman support and was expelled by the Turks for disobedience. During his reign Crimean troops fought for the Turks and also fought in the North Caucasus. In 1532-1584, during the long reigns of Sahib I Giray, Devlet I Giray and Mehmed II Giray, Crimea was at the height of its power. Family and early life Sahib's grandfather was the founder of the Giray dynasty, Hacı I Giray (c. 1441–1466). His father was Mengli Giray (1478–1515). His brothers included Mehmed I Giray (1515–1523), Saadet I Giray (1524–1532) and Mubarak (also spelled Mubarek). Wives Sahib's wives were: *Fatima Sultan; *Khanbike Sultan, sister of the Circassian Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad IV
Murad IV (, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; , 27 July 1612 – 8 February 1640) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Constantinople, the son of Sultan Ahmed I (r. 1603–17) and Kösem Sultan. He was brought to power by a palace conspiracy when he was just 11 years old, and he succeeded his uncle Mustafa I (r. 1617–18, 1622–23). Until he assumed absolute power on 18 May 1632, the empire was ruled by his mother, Kösem Sultan, as ''nāʾib-i salṭanat'' (regent). His reign is most notable for the Ottoman–Safavid War (1623–1639), Ottoman–Safavid War, of which the Treaty of Zuhab, outcome would partition the Caucasus between the two Imperial powers for around two centuries, while it also roughly laid the foundation for the current Turkey–Iran–Iraq borders. Early life Murad IV was born on 27 July 1612 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budjak Horde
The Budjak Horde, also known as the Belgorod or Bilhorod Horde, formed part of the Nogai Horde in the 17th and 18th centuries. It settled in the northern Black Sea coast area under protectorate of the Crimean Khanate and the Ottoman Empire's Sanjak of Ozu ( Yedisan). Its capital was in Căușeni. In the 1620s, the horde migrated from the Pontic steppes to the steppes of the Budjak region. The Bilhorod Tatars (20,000–30,000) were nomadic herdsmen. They made forays for slaves and loot into Right-bank Ukraine and Moldavia. In 1770, the horde became a protectorate of the Russian Empire and soon after was dispersed through resettlement in the Azov steppes. From there its remnants emigrated to Turkey during the Crimean War of 1853–1856. Prominent leaders of the horde included Khan Temir (died 1637), who allegedly established the noble Moldavian family of Cantemirești. Leaders * 1603–1637 Khan Temir * Giray family with rank of Serasker Notes References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan Temir
Khan Temir (before 1594 to 1637) was a steppe warlord and raider. He ruled the Budjak Horde in what is now the southwestern corner of Ukraine (Budjak) along the Romanian border. Budjak is the southwesternmost corner of the Eurasian Steppe. He raided mostly along the eastern frontier of the Polish Commonwealth. Nominally a vassal of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottomans used him to pressure the Poles just as the Poles used the Zaporozhian Cossacks to pressure the Ottomans and Crimeans. His habit of acting independently caused problems. The Ottomans several times tried to move him east from Poland and eventually executed him. The most important event in his life was his conflict with the Crimean khan in 1628. Family He was the first and greatest leader of the Bujak Horde which seems to have formed up about the time he came to power. A connection to the Cantemirești of Moldavia is likely, but cannot be established exactly. He was associated with the Mansur clan which held the northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mere Hüseyin Pasha
Mere Hüseyin Pasha (died July 1624) was an Ottoman statesman of Albanian origin.Uzunçarsılı, İsmail Hakkı, (1954) ''Osmanlı Tarihi III. Cilt, 2. Kısım, XVİ. Yüzyıl Ortalarından XVII. Yüzyıl Sonuna kadar'', Ankara: Türk Tarih Kurumu (Altıncı Baskı 2011 ) p. 380 He was two times Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire in 1622 and 1623,İsmail Hâmi Danişmend, Osmanlı Devlet Erkânı, Türkiye Yayınevi, İstanbul, 1971 (Turkish) and previously the Ottoman governor of Egypt between 1620 and 1622. His epithet "Mere!" comes from the word for "Take it!" in Albanian; he was nicknamed so because of the many times he ordered his men to "take he heads of his opponents, i.e. execute them. He was purportedly the only grand vizier who did not speak Ottoman Turkish or Osmanlica. Life Hüseyin Pasha was an Albanian from the region of İpek, in present-day Kosovo. He may have been a progenitor of the Begolli family. It is purported that he never learned to speak Turkish, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |