|
Megiddo, Israel
Megiddo (، ) is a kibbutz in northern Israel, built in 1949. Located in the Jezreel Valley, it falls under the jurisdiction of Megiddo Regional Council. In , it had a population of . The kibbutz is located near Megiddo Junction, the intersection of highways 65, from Hadera to Afula, and 66, running from Haifa south to the West Bank. The junction is the site of a bus terminal and a high-security prison. The kibbutz was built 600 metres north-east of the site of the depopulated Arab village of Lajjun, now known as Einot Kobi. In Christian apocalyptic literature, Mount Megiddo, the hill overlooking the valley where the current kibbutz is located, is identified as the site of the final battle between the forces of good and evil at the end of time, known as Armageddon and mentioned in the New Testament in Revelation 16:16. Geography The kibbutz is located near the site of the several Battles of Megiddo and Tel Megiddo, a rich archeological site. According to the Bible, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Israeli-occupied territories, It occupies the Occupied Palestinian territories, Palestinian territories of the West Bank in the east and the Gaza Strip in the south-west. Israel also has a small coastline on the Red Sea at its southernmost point, and part of the Dead Sea lies along its eastern border. Status of Jerusalem, Its proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, while Tel Aviv is the country's Gush Dan, largest urban area and Economy of Israel, economic center. Israel is located in a region known as the Land of Israel, synonymous with the Palestine (region), Palestine region, the Holy Land, and Canaan. In antiquity, it was home to the Canaanite civilisation followed by the History of ancient Israel and Judah, kingdoms of Israel and Judah. Situate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Megiddo (other)
Battle of Megiddo may refer to: *Battle of Megiddo (15th century BC), between the Egyptians and the Canaanites *Battle of Megiddo (609 BC), between the Egyptians and the Judahites *Battle of Megiddo (1918), between the United Kingdom and the Ottoman Empire *Armageddon Armageddon ( ; ; ; from ) is the prophesied gathering of armies for a battle during the end times, according to the Book of Revelation in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. Armageddon is variously interpreted as either a literal or a ... ( ), a prophesied catastrophic end-of-the-world battle in the Abrahamic religions See also * Megiddo (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
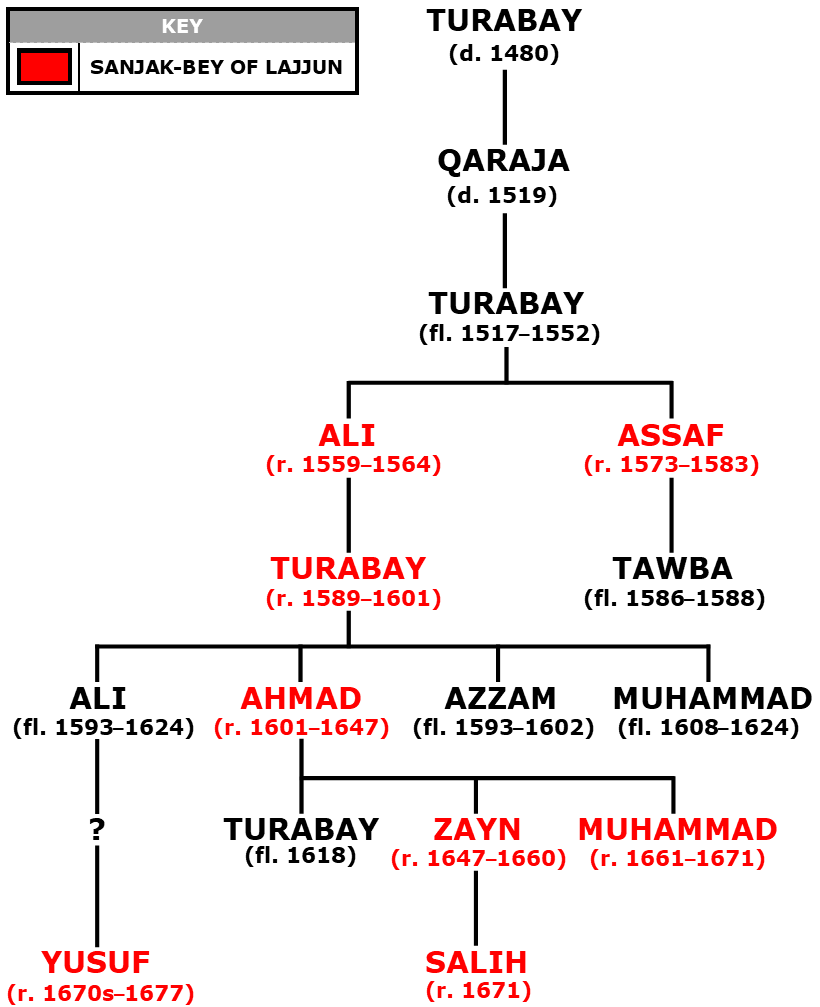
Turabay Dynasty
The Turabay dynasty () was a family of Bedouin emirs in northern Palestine (region), Palestine who served as the (tax farmers) and (district governors) of Lajjun Sanjak during Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rule in the 16th–17th centuries. The sanjak (district) spanned the towns of Lajjun, Jenin and Haifa, and the surrounding countryside. The progenitors of the family had served as chiefs of Jezreel Valley, Marj ibn Amir (the Plain of Esdraelon or Jezreel Valley) under the Egypt-based Mamluk Sultanate (Cairo), Mamluks in the late 15th century. During the Battle of Marj Dabiq, conquest of the Levant and Egypt by the Ottoman Empire in 1516–1517, the Turabay chief Qaraja and his son Turabay aided the forces of Ottoman Sultan Selim I. The Ottomans kept them in their Mamluk-era role as guardians of the strategic Via Maris and Damascus–Jerusalem highways and rewarded them with Farm (revenue leasing), tax farms in northern Palestine. Their territory became a sanjak in 1559 and Turabay' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Period
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interactions between the Middle East and Europe for six centuries. Ruling over so many peoples, the empire granted varying levels of aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disturbance (archaeology)
A disturbance is any change to an archaeological site due to events which occurred after the site was laid down. Disturbances may be caused by natural events or human activity, and may result in loss of archaeological value. In some cases, it can be difficult to distinguish between features caused by human activity in the period of interest, and features caused by later human activity or natural processes. Causes Natural causes The soil science, soil scientist Francis D. Hole identified nine natural processes resulting in soil disturbance, including the movements of animals and plants (known as bioturbation, and including burrowing, root growth and tree uprooting, treefalls); freezing and thawing; movement under gravity (including earthflow and rockslides); swelling and shrinking of clays; the actions of wind and water; the growth and dissolution of salt crystals; and movement caused by earthquakes. Different sites are subject to different degrees, combinations, and interactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to develop writing. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, (1479–1425 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. He is regarded as one of the greatest warriors, military commanders, and military strategists of all time; as Egypt's preeminent warrior pharaoh and conqueror; and as a dominant figure in the New Kingdom period. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt from his coronation on 28 April 1479 BC at the age of two until his death on 11 March 1425 BC. But for the first 22 years of his reign, he was coregent with his stepmother and aunt, Hatshepsut, who was named the pharaoh.Partridge, R., 2002. Fighting Pharaohs: Weapons and warfare in ancient Egypt. Manchester: Peartree. pp. 202–203 He became sole ruler after Hatshepsut's death in 1458. Thutmose III conducted between 17 and 20 military campaigns, all victorious, which brought ancient Egypt's empire to its zenith. They are detailed in the inscriptions known as the Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, following the Stone Age and preceding the Iron Age. Conceived as a global era, the Bronze Age follows the Neolithic, with a transition period between the two known as the Chalcolithic. The final decades of the Bronze Age in the Mediterranean basin are often characterised as a period of widespread societal collapse known as the Late Bronze Age collapse (), although its severity and scope are debated among scholars. An ancient civilisation is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age if it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to develop writing. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Chalcolithic ( ) (also called the Copper Age and Eneolithic) was an archaeological period characterized by the increasing use of smelted copper. It followed the Neolithic and preceded the Bronze Age. It occurred at different periods in different areas, but was absent in some parts of the world, such as Russia, where there was no well-defined Copper Age between the Stone and Bronze Ages. Stone tools were still predominantly used during this period. The Chalcolithic covers both the early cold working (hammering) of near pure copper ores, as exhibited by the likes of North American Great Lakes Old Copper complex, from around 6,500 BC, through the later copper smelting cultures. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from . The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionally synonymous with what is known as the Land of Israel ( Zion) or the Promised Land in a biblical or religious context, or as Canaan or Palestine in a secular or geographic context—referring to a region that is mostly between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. Today, it chiefly overlaps with the combined territory of the modern states of Israel and Palestine. Most notable among the religions that tie substantial spiritual value to the Holy Land are Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. A considerable part of the Holy Land's importance derives from Jerusalem, which is regarded as extremely sacred in and of itself. It is the holiest city in Judaism and Christianity and the third-holiest city in Islam (behind Mecca and Medina in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |