|
Megaloptera
Megaloptera is an order of insects. It contains the alderflies, dobsonflies and fishflies, and there are about 300 known species. The order's name comes from Ancient Greek, from ''mega-'' (μέγα-) "large" + ''pteryx'' (πτέρυξ) "wing", in reference to the large, clumsy wings of these insects. Megaloptera are relatively unknown insects across much of their range, due to the adults' short lives, the aquatic larvae's often-high tolerance of pollution (so they are not often encountered by swimmers etc.), and the generally crepuscular or nocturnal habits. However, in the Americas the dobsonflies are rather well known, as their males have tusk-like mandibles. These, while formidable in appearance, are relatively harmless to humans and other animals; much like a peacock's feathers, they serve mainly to impress females. However, the mandibles are also used to hold females during mating, and some male dobsonflies spar with each other in courtship displays, trying to flip eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alderfly
Alderflies are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together – are part of the subfamily Sialinae, which contains between one and seven extant genera according to different scientists' views. Description Sialinae have a body length of less than 25 mm (1 inch), long filamentous antennae, and four large dark wings of which the anterior pair is slightly longer than the posterior. They lack ocelli and their fourth tarsal segment is dilated and deeply bilobed. Dead alderfly larvae are used as bait in fishing. Life cycle The females lay a vast number of eggs on grass stems near water. When the larvae are born they drop into the water or the ground nearby it and make their way into their new aquatic biome. The larvae are aquatic, active, armed with strong sharp mandibles, and breathe by means of seven pairs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishfly
Fishflies are members of the subfamily Chauliodinae, belonging to the megalopteran family Corydalidae. They are most easily distinguished from their closest relatives, dobsonflies, by the jaws (mandibles) and antennae. In contrast to the large jaws (especially in males) of dobsonflies, fishfly mandibles are not particularly noticeable or distinctive, and the males have feathery antennae similar to many large moths. '' Chauliodes pectinicornis'', the "summer fishfly", is a well-known species in North America. Fishflies lay their eggs upon vegetation overhanging streams, whence the larvae, as soon as hatched, drop into the water, and go about preying upon aquatic animals. When ready to transform to pupae, they crawl out upon the bank and are then found in cavities under stones or even under the bark of trees. Fishflies are quite large, with a wingspan of . They will eat aquatic plants as well as small animals including vertebrates like minnows and tadpoles, and may live up to se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alderfly
Alderflies are megalopteran insects of the family Sialidae. They are closely related to the dobsonflies and fishflies as well as to the prehistoric Euchauliodidae. All living alderflies – about 66 species all together – are part of the subfamily Sialinae, which contains between one and seven extant genera according to different scientists' views. Description Sialinae have a body length of less than 25 mm (1 inch), long filamentous antennae, and four large dark wings of which the anterior pair is slightly longer than the posterior. They lack ocelli and their fourth tarsal segment is dilated and deeply bilobed. Dead alderfly larvae are used as bait in fishing. Life cycle The females lay a vast number of eggs on grass stems near water. When the larvae are born they drop into the water or the ground nearby it and make their way into their new aquatic biome. The larvae are aquatic, active, armed with strong sharp mandibles, and breathe by means of seven pairs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthacorydalis Fruhstorferi
''Acanthacorydalis fruhstorferi'' is a species of dobsonfly native to Vietnam and China. It holds the title of largest aquatic insect by wingspan according to the Guinness Book of World Records at 21.6 cm. The title formerly belonged to the Brazilian damselfly ''Microstigma rotundatum''. ''Acanthacorydalis fruhstorferi'' was first described by Herman Willem van der Weele in 1907 from a specimen from "Than-Moi" (probably in Lạng Sơn Province), Vietnam. It is found throughout Southern China (Fujian, Guangxi, Guangdong, Guizhou, Jiangxi, Yunnan, and Zhejiang) and Northern Vietnam. Liu and associates proposed in 2005 that the species is most closely related to ''Acanthacorydalis sinesis'' citing morphological similarities relative to similar Chinese genera of '' Acanthacorydalis''. Specifically the wing and body colouration, yet differed by ''A.sinesiss lack of sagittal dorsal division. Life history Eggs are deposited between stones near flowing water. Larvae inhabit stream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal life-forms; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ladybugs) eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Beetles typically have a particularly har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endopterygota
Endopterygota (from Ancient Greek ''endon'' 'inner' + ''pterón'' 'wing' + New Latin ''-ota'' 'having'), also known as Holometabola, is a superorder of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult stages. They undergo a radical metamorphosis, with the larval and adult stages differing considerably in their structure and behaviour. This is called holometabolism, or complete metamorphism. Evolution The Endopterygota constitute the most diverse insect superorder, with over 1 million living species divided between 11 orders, containing insects such as butterflies, flies, fleas, bees, ants, and beetles. The earliest endopterygote fossils date from the Carboniferous. The Endopterygota are sometimes divided into three assemblages: Neuropterida (Neuroptera, Megaloptera, Raphidioptera, Strepsiptera and Coleoptera), Hymenopteroida (Hymenoptera), and Panorpida (Siphonaptera, Diptera, Trichoptera, Lepidoptera and Mecoptera). Molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peacock
Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera ''Pavo (genus), Pavo'' and ''Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens, although peafowl of either sex are often referred to colloquialism, colloquially as "peacocks." The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally of the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl of Southeast Asia; the one African species is the Congo peafowl, native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual. The functions of the elaborate iridescent Animal coloration, colouration and large "train" of peacocks have been the subject of extensive scientific debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superorder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
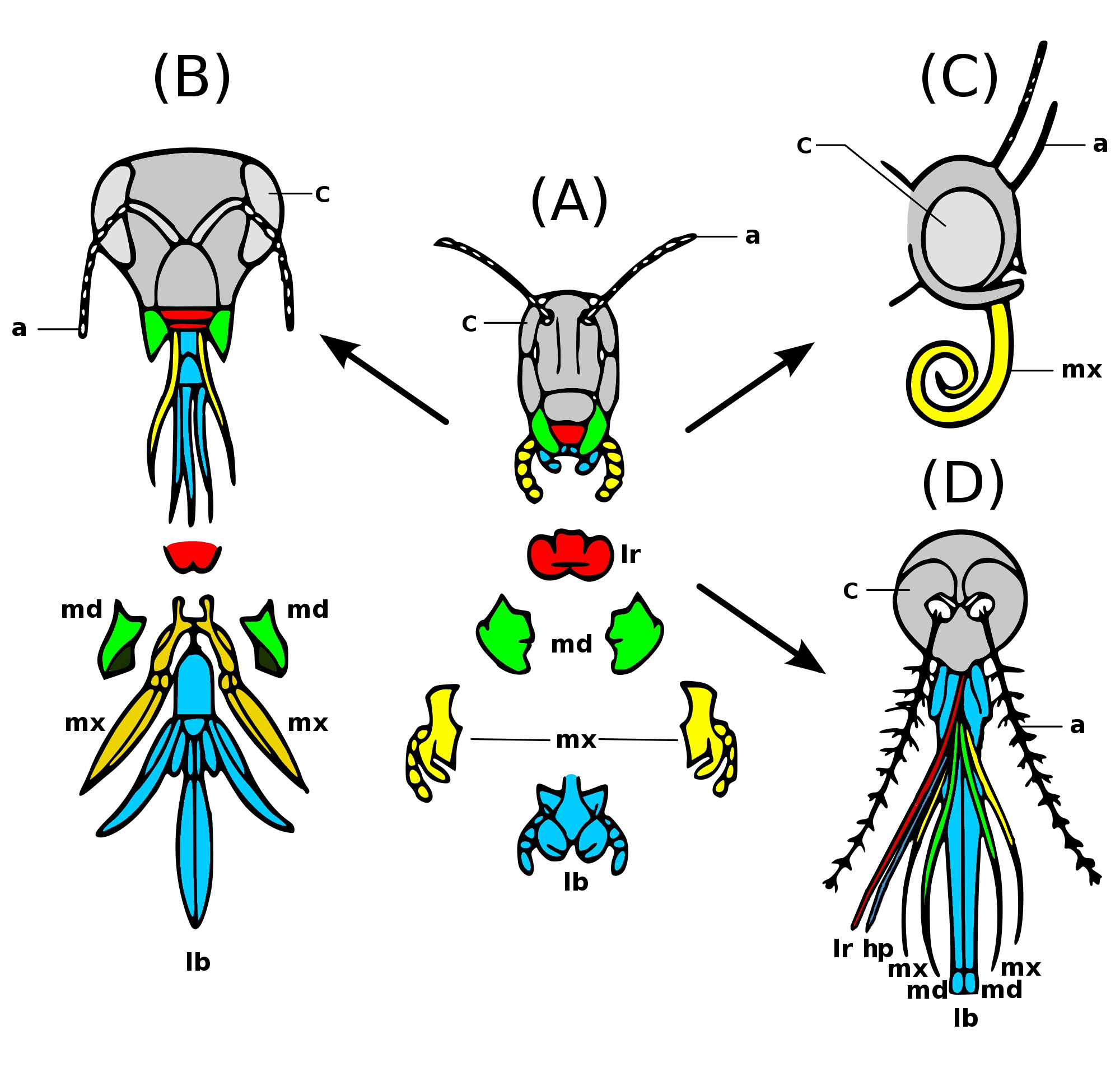
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times idependently. For example, mosquitoes and aphids (which are true bugs) both pierce and suck, however female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identical, they may not be homologous; their analogous functions and appearance might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxonomic Rank
In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While older approaches to taxonomic classification were phenomenological, forming groups on the basis of similarities in appearance, organic structure and behaviour, methods based on genetic analysis have opened the road to cladistics. A given rank subsumes under it less general categories, that is, more specific descriptions of life forms. Above it, each rank is classified within more general categories of organisms and groups of organisms related to each other through inheritance of traits or features from common ancestors. The rank of any ''species'' and the description of its ''genus'' is ''basic''; which means that to identify a particular organism, it is usually not necessary to specify ranks other than these first two. Consider a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |