|
Medullipin
Medullipin is a hormone created by the interstitial cells of renal papilla, which is converted to medullipin II in the liver. This, in turn, results in vasodilation and decreased blood pressure Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r .... There are two kinds of medullipin, known as medullipin 1 and medullipin 2. The structure of this substance remains unknown, but its existence has been strongly inferred from multiple experiments in animals, wherein a rise in renal perfusion causes blood pressure to fall. This hypotensive response depends on an intact renal medulla and is not altered by renal denervation or the inhibition of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) or autonomic nervous function Kaplan NM. Kaplan's Clinical Hypertension, 9th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
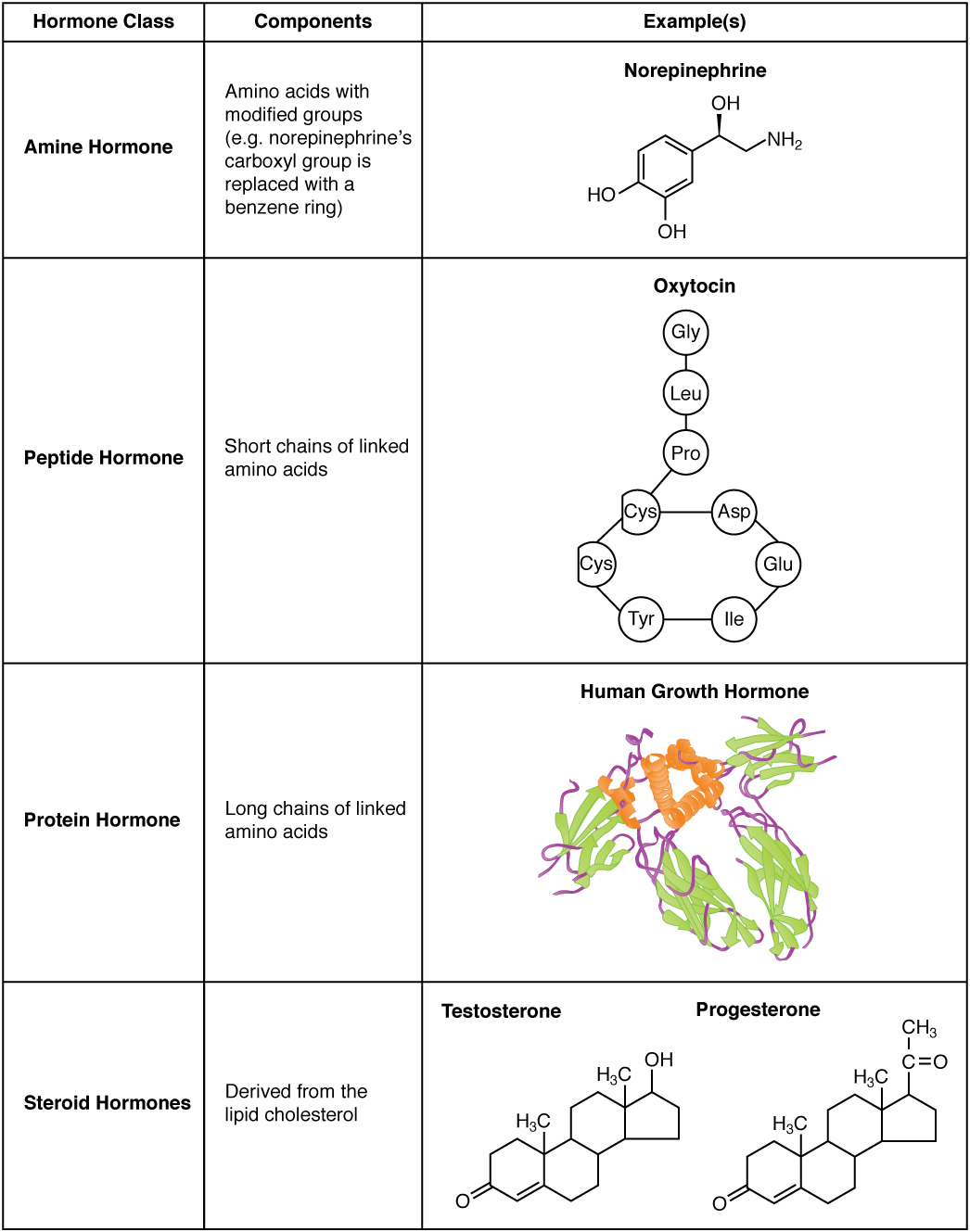
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as diges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstitial Cell
Interstitial cell refers to any cell that lies in the spaces between the functional cells of a tissue. Examples include: * Interstitial cell of Cajal (ICC) * Leydig cells, cells present in the male testes responsible for the production of androgen (male sex hormone) * A portion of the stroma of ovary * Certain cells in the pineal gland * Renal interstitial cells * neuroglial cells See also *List of human cell types derived from the germ layers This is a list of cells in humans derived from the three embryonic germ layers – ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Cells derived from ectoderm Surface ectoderm Skin * Trichocyte * Keratinocyte Anterior pituitary * Gonadotrope * Corticot ... References *Sybil B Parker (ed). "Interstitial cell". McGraw Hill Dictionary of Scientific and Technical Terms. Fifth Edition. International Edition. 1994. Page 1041. {{DEFAULTSORT:Interstitial cells Cell biology Biology-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renin–angiotensin System
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance. When renal blood flow is reduced, juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys convert the precursor prorenin (already present in the blood) into renin and secrete it directly into the circulation. Plasma renin then carries out the conversion of angiotensinogen, released by the liver, to a decapeptide called angiotensin I. Angiotensin I is subsequently converted to angiotensin II (an octapeptide) by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) found on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, predominantly those of the lungs. Angiotensin II has a short life of about 1 to 2 minutes. Then, it is rapidly degraded into a heptapeptide called angiotensin III by angiotensinases which are present in red blood cells and vascular beds in many tissues. Angiotensin III increases blood pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response. The autonomic nervous system is regulated by integrated reflexes through the brainstem to the spinal cord and organs. Autonomic functions include control of respiration, cardiac regulation (the cardiac control center), vasomotor activity (the vasomotor center), and certain reflex actions such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing and vomiting. Those are then subdivided into other areas and are also linked to autonomic subsystems and the peripheral nervous syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormones Of The Liver
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the correct development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organs and tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating a variety of physiological processes and behavioral activities such as digestion, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |