|
Mechanism Of Anoxic Depolarization In The Brain
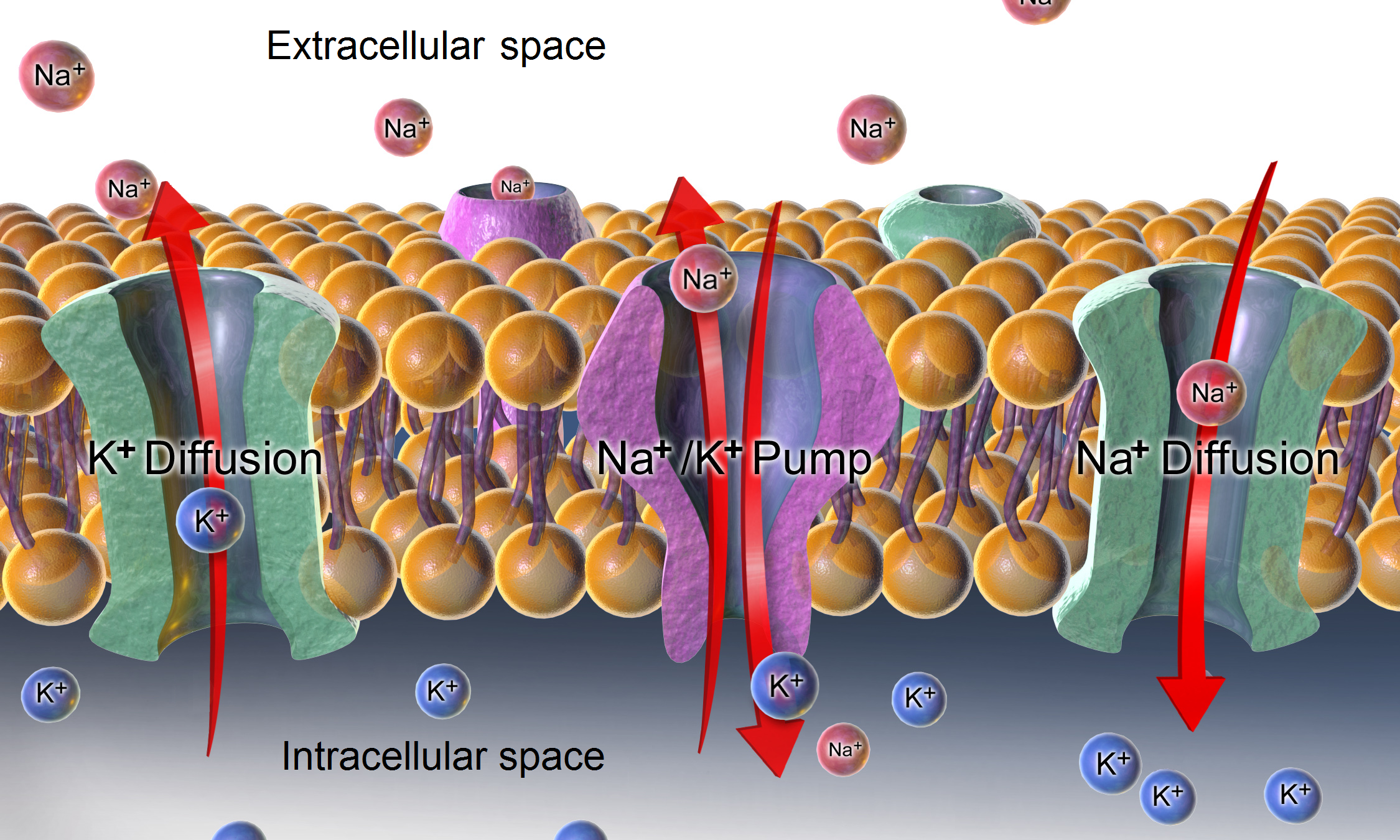
Anoxic depolarization is a progressive and uncontrollable depolarization of neurons during stroke or brain ischemia in which there is an inadequate supply of blood to the brain. Anoxic depolarization is induced by the loss of neuronal selective membrane permeability and the ion gradients across the membrane that are needed to support neuronal activity. Normally, the Na+/K+-ATPase pump maintains the transmembrane gradients of K+ and Na+ ions, but with anoxic brain injury, the supply of energy to drive this pump is lost. The hallmarks of anoxic depolarization are increased concentrations of extracellular K+ ions, intracellular Na+ and Ca2+ ions, and extracellular glutamate and aspartate. Glutamate and aspartate are normally present as the brain's primary excitatory neurotransmitters, but high concentrations activate a number of downstream apoptotic and necrotic pathways. This results in neuronal dysfunction and brain death. Neural signal under normal oxygen uptake Neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell (biology), cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism. Most cells in higher organisms maintain an internal environment that is negatively charged relative to the cell's exterior. This difference in charge is called the cell's membrane potential. In the process of depolarization, the negative internal charge of the cell temporarily becomes more positive (less negative). This shift from a negative to a more positive membrane potential occurs during several processes, including an action potential. During an action potential, the depolarization is so large that the potential difference across the cell membrane briefly reverses polarity, with the inside of the cell becoming p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0011 ActionPotential Nerve
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via hospital o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Transmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), and bind to and react with the receptors on the dendrites of another neuron (the postsynaptic neuron) a short distance away. Changes in the concentration of ions, such as Ca2+, Na+, K+, underlie both chemical and electrical activity in the process. The increase in calcium levels is essential and can be promoted by protons. A similar process occurs in retrograde neurotransmission, where the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron release retrograde neurotransmitters (e.g., endocannabinoids; synthesized in response to a rise in intracellular calcium levels) that signal through receptors that are located on the axon terminal of the presynaptic neuron, mainly at GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses. Neurotransmission is regulated by several d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gap Junctions
Gap junctions are Membrane channel, membrane channels between adjacent cells that allow the direct exchange of cytoplasmic substances, such small molecules, substrates, and metabolites. Gap junctions were first described as ''close appositions'' alongside tight junctions, however, electron microscopy studies in 1967 led to gap junctions being named as such to be distinguished from tight junctions. They bridge a 2-4 nm gap between cell membranes. Gap junctions use protein complexes known as connexons, composed of connexin proteins to connect one cell to another. Gap junction proteins include the more than 26 types of connexin, as well as at least 12 non-connexin components that make up the gap junction complex or ''nexus,'' including the tight junction protein ZO-1—a protein that holds membrane content together and adds structural clarity to a cell, sodium channels, and aquaporin. More gap junction proteins have become known due to the development of next-generation sequencing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) is a long, slender cellular extensions, projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in Vertebrate, vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the Soma (biology), nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the peripheral nervous system, periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the Peripheral nervous system, peripheral and Central nervous system, central ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of Membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and myocyte, muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell interaction, cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward axon terminal, synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-or-none Law
In physiology, the all-or-none law (sometimes the all-or-none principle or all-or-nothing law) is the principle that if a single nerve fibre is stimulated, it will always give a maximal response and produce an electrical impulse of a single amplitude. If the intensity or duration of the stimulus is increased, the height of the impulse will remain the same. The nerve fibre either gives a maximal response or none at all. It was first established by the American physiologist Henry Pickering Bowditch in 1871 for the contraction of heart muscle. An induction shock produces a contraction or fails to do so according to its strength; if it does so at all, it produces the greatest contraction that can be produced by any strength of stimulus in the condition of the muscle at the time. This principle was later found to be present in skeletal muscle by Keith Lucas in 1909. The individual fibres of nerves also respond to stimulation according to the all-or-none principle. Isolation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threshold Potential
In electrophysiology, the threshold potential is the critical level to which a membrane potential must be depolarized to initiate an action potential. In neuroscience, threshold potentials are necessary to regulate and propagate signaling in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Most often, the threshold potential is a membrane potential value between –50 and –55 mV, but can vary based upon several factors. A neuron's resting membrane potential (–70 mV) can be altered to either increase or decrease likelihood of reaching threshold via sodium and potassium ions. An influx of sodium into the cell through open, voltage-gated sodium channels can depolarize the membrane past threshold and thus excite it while an efflux of potassium or influx of chloride can hyperpolarize the cell and thus inhibit threshold from being reached. Discovery Initial experiments revolved around the concept that any electrical change that is brought about in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resting Membrane Potential
The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. The resting membrane potential has a value of approximately −70 mV or −0.07 V. Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. The resting potential exists due to the differences in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells. Because the membrane pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Channels
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of cell functions. Function Potassium channels function to conduct potassium ions down their electrochemical gradient, doing so both rapidly (up to the diffusion rate of K+ ions in bulk water) and selectively (excluding, most notably, sodium despite the sub-angstrom difference in ionic radius). Biologically, these channels act to set or reset the resting potential in many cells. In excitable cells, such as neurons, the delayed counterflow of potassium ions shapes the action potential. By contributing to the regulation of the cardiac action potential duration in cardiac muscle, malfunction of potassium channels may cause life-threatening arrhythmias. Potassium channels may also be involved in maintaining vascular tone. They also regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |