|
Mechanical Heat Treatment
Mechanical heat treatment (MHT) is an alternative waste treatment technology. This technology is also commonly termed autoclaving. MHT involves a mechanical sorting or pre-processing stage with technology often found in a material recovery facility. The mechanical sorting stage is followed by a form of thermal treatment. This might be in the form of a waste autoclave or processing stage to produce a refuse derived fuel pellet. MHT is sometimes grouped along with mechanical biological treatment. MHT does not however include a stage of biological degradation (anaerobic digestion or composting). Configurations Different MHT systems may be configured to meet various objectives with regard to the waste outputs from the process. The alternatives (depending on the system employed) may be one or more of the following: |
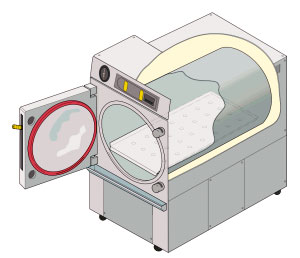
Autoclaving
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for 30–60 minutes at a gauge pressure of 103 kPa depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclaves are widely used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department For Environment, Food And Rural Affairs
The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) is a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, ministerial department of the government of the United Kingdom. It is responsible for environmental quality, environmental protection, food production and standards, agriculture, fisheries and rural communities in the entire United Kingdom. Memorandum of understanding, Concordats set out agreed frameworks for cooperation, between it and the Scottish Government, Welsh Government and Northern Ireland Executive, which have devolved responsibilities for these matters in their respective nations. Defra also leads for the United Kingdom on agricultural, fisheries and environmental matters in international negotiations on sustainable development and climate change, although a new Department of Energy and Climate Change was created on 3 October 2008 to take over the last responsibility; later transferred to the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Biological Treatment
A mechanical biological treatment (MBT) system is a type of waste processing facility that combines a sorting facility with a form of biological treatment such as composting or anaerobic digestion. MBT plants are designed to process municipal solid waste, mixed household waste as well as commercial waste, commercial and industrial wastes. Process The terms ''mechanical biological treatment'' or ''mechanical biological pre-treatment'' relate to a group of list of solid waste treatment technologies, solid waste treatment systems. These systems enable the recovery of materials contained within the mixed waste and facilitate the stabilisation of the biodegradable component of the material. Twenty two facilities in the UK have implemented MBT/BMT treatment processes. The sorting component of the plants typically resemble a materials recovery facility. This component is either configured to recover the individual elements of the waste or produce a refuse-derived fuel that can be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Recovery Facility
A materials recovery facility, materials reclamation facility, materials recycling facility or multi re-use facility (MRF, pronounced "murf") is a specialized waste sorting and recycling system that receives, separates and prepares recyclable materials for marketing to end-user manufacturers. Generally, the main recyclable materials include ferrous metal, non-ferrous metal, plastics, paper, glass. Organic food waste is used to assist anaerobic digestion or composting. Inorganic inert waste is used to make building materials. Non-recyclable high calorific value waste is used to making refuse-derived fuel (RDF) and solid recovered fuel (SRF). Industry and locations In the United States, there are over 300 materials recovery facilities. The total market size is estimated at $6.6B as of 2019. As of 2016, the top 75 were headed by Sims Municipal Recycling out of Brooklyn, New York. Waste Management operated 95 MRF facilities total, with 26 in the top 75. ReCommunity operated 6 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Solid Waste Treatment Technologies
The article contains a list of different forms of solid waste treatment technologies and facilities employed in waste management infrastructure. Waste handling facilities * Civic amenity site (CA site) * Transfer station (waste management), Transfer station Established waste treatment technologies * Incineration * Landfill * Recycling * Specific to organic waste: ** Anaerobic digestion ** Composting *** Windrow composting Alternative waste treatment technologies In the UK some of these are sometimes termed advanced waste treatment technologies * Biodrying * Gasification ** Plasma gasification: Gasification assisted by plasma torches * Hydrothermal carbonization * Hydrothermal liquefaction * Mechanical biological treatment (sorting into selected fractions) ** Refuse-derived fuel * Mechanical heat treatment * Molten salt oxidation * Pyrolysis * UASB (applied to solid wastes) * Waste autoclave * Specific to organic waste: ** Bioconversion of biomass to mixed alcohol fuels ** In-vesse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composting
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or Humic acids, humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of green waste (nitrogen-rich materials such as leaves, grass, and food scraps) and brown waste (woody ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to Waste management, manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the Fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation used industrially to produce food and drink products, as well as home fermentation, uses anaerobic digestion. Anaerobic digestion occurs naturally in some soils and in lake and oceanic basin sediments, where it is usually referred to as "anaerobic activity". This is the source of Methane#Occurrence, marsh gas methane as discovered by Alessandro Volta in 1776. Anaerobic digestion comprises four stages: * Hydrolysis *Acidogenesis *Acetogenesis *Methanogenesis The digestion process begins with bacterial hydrolysis of the input materials. Insoluble organic polymers, such as carbohydrates, are broken down to soluble derivatives that become available for other bacteria. Acidogenesis, Acidogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window panes, tableware, and optics. Some common objects made of glass are named after the material, e.g., a Tumbler (glass), "glass" for drinking, "glasses" for vision correction, and a "magnifying glass". Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the Melting, molten form. Some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring, and obsidian has been used to make arrowheads and knives since the Stone Age. Archaeological evidence suggests glassmaking dates back to at least 3600 BC in Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, or Syria. The earliest known glass objects were beads, perhaps created accidentally during metalworking or the production of faience, which is a form of pottery using lead glazes. Due to its ease of formability int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recycling
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the properties it had in its original state. It is an alternative to "conventional" waste disposal that can save material and help lower greenhouse gas emissions. It can also prevent the waste of potentially useful materials and reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reducing energy use, air pollution (from incineration) and water pollution (from landfilling). Recycling is a key component of modern waste reduction and represents the third step in the "Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle" waste hierarchy, contributing to environmental sustainability and resource conservation. It promotes environmental sustainability by removing raw material input and redirecting waste output in the economic system. There are some ISO standards related to recycling, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Process
Biological processes are those processes that are necessary for an organism to live and that shape its capacities for interacting with its environment. Biological processes are made of many chemical reactions or other events that are involved in the persistence and transformation of life forms. Regulation of biological processes occurs when any process is modulated in its frequency, rate or extent. Biological processes are regulated by many means; examples include the control of gene expression, protein modification or interaction with a protein or substrate molecule. * Homeostasis: regulation of the internal environment to maintain a constant state; for example, sweating to reduce temperature * Biological organization, Organization: being structurally composed of one or more cell (biology), cells – the basic units of life * Metabolism: transformation of energy by converting chemicals and energy into cellular components (anabolism) and decomposing organic matter (catabolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |