|
Mean Airway Pressure
Mean airway pressure typically refers to the mean pressure applied during positive-pressure mechanical ventilation. Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation, hemodynamic performance, and barotrauma. It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance. Equations There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure. Volume control ventilation In ventilation with a square flow waveform this equation can be used: \bar_=0.5\times(PIP - PEEP) \times (T_I/T_)+PEEP where: * \bar_ = mean airway pressure * PIP= peak inspiratory pressure * PEEP= peak end expiratory pressure * T_I= inspiratory time * T_= cycle time Pressure control ventilation During pressure control ventilation this variant of the equation can be used: \bar_= (PIP - PEEP) \times (T_I/T_)+PEEP where: * \bar_ = mean airway pressure * PIP= peak inspiratory pressure * PEEP= peak end expira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-pressure
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilation. The mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. In general, mode selection is based on clinician familiarity and institutional preferences, since there is a paucity of evidence indicating that the mode affects clinical outcome. The most frequently used forms of volume-limited mechanical ventilation are intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV) and continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV). Terminology There have been substantial changes in the nomenclature of mechanical ventilation over the years, but more recently it has become standardized by many respirology and pulmonology groups. Writing a mode is most proper in all capital letters with a dash between the control variable and the strategy (i.e. PC-IMV, or VC-MMV etc.). Taxonomy for mechanical ventilation The taxonomy is a logical classification system based on 10 maxims of ventilator design: 10 maxims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
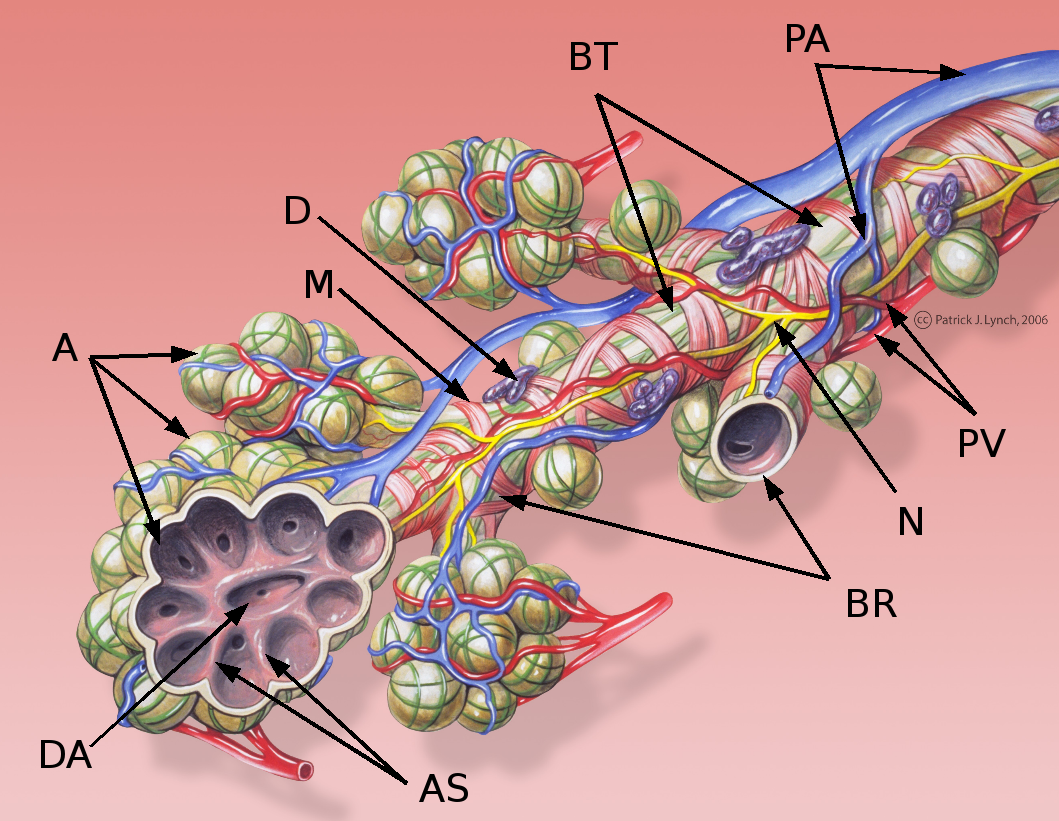
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Oxygen is diffused across the membrane into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is released fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemodynamic
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based on the use of classical viscometers are not capable of explaining haemodynamics. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or in contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in tension or shear, either directly by an expansion of the gas in the closed space or by pressure difference hydrostatically transmitted through the tissue. Tissue rupture may be complicated by the introduction of gas into the local tissue or circulation through the initial trauma site, which can cause blockage of circulation at distant sites or interfere with the normal function of an organ by its presence. The term is usually applied when the gas volume involved already exists prior to decompression. Barotrauma can occur during both compression and decompression events. Barotrauma generally manifests as sinus or middle ear effects, lung overpressure injuries and injuries resulting from external squeezes. Decompression sickness is indir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Mandatory Ventilation
Continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV) is a mode of mechanical ventilation in which breaths are delivered based on set variables. Still used in the operating room, in previous nomenclature, CMV referred to "controlled mechanical ventilation" ("control mode ventilation"), a mode of ventilation characterized by a ventilator that makes no effort to sense patient breathing effort. In continuous mandatory ventilation, the ventilator can be triggered either by the patient or mechanically by the ventilator. The ventilator is set to deliver a breath according to parameters selected by the operator. "Controlled mechanical ventilation" is an outdated expansion for "CMV"; "continuous mandatory ventilation" is now accepted standard nomenclature for mechanical ventilation. CMV today can assist or control itself dynamically, depending on the transient presence or absence of spontaneous breathing effort. Thus, today's CMV would have been called ACV (assist-control ventilation) in older nomenclatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airway Pressure Release Ventilation Figure 2007
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, that bran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
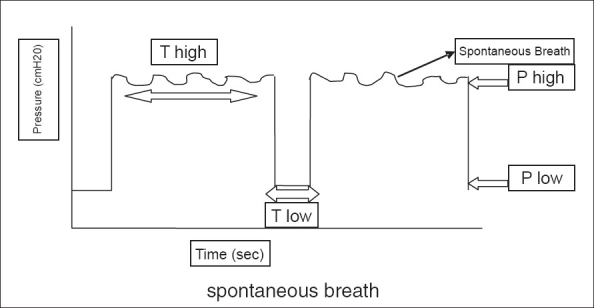
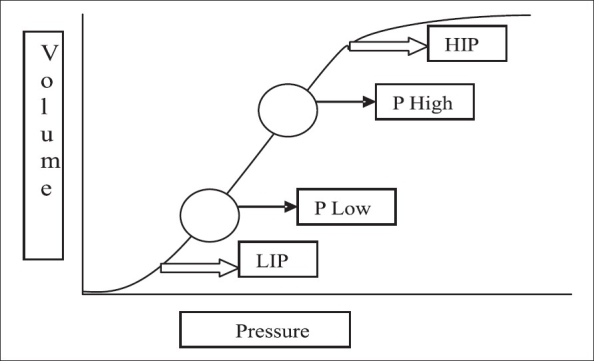
Airway Pressure Release Ventilation
Airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) is a pressure control mode of mechanical ventilation that utilizes an inverse ratio ventilation strategy. APRV is an applied continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) that at a set timed interval releases the applied pressure. Depending on the ventilator manufacturer, it may be referred to as BiVent. This is just as appropriate to use, since the only difference is that the term APRV is copyrighted. History Airway pressure release ventilation was described initially by Stock and Downs in 1987 as a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) with an intermittent release phase. APRV begins at a pressure higher than the baseline pressure and follows with a deflation to accomplish tidal ventilation. Fundamentally APRV is a time-cycled alternant between two levels of positive airway pressure, with the main time on the high level and a brief expiratory release to facilitate ventilation. Indications Based on clinical and experimental d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modes Of Mechanical Ventilation
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilation. The mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. In general, mode selection is based on Respiratory therapist, clinician familiarity and institutional preferences, since there is a paucity of evidence indicating that the mode affects clinical outcome. The most frequently used forms of volume-limited mechanical ventilation are intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV) and continuous mandatory ventilation (CMV). Terminology There have been substantial changes in the nomenclature of mechanical ventilation over the years, but more recently it has become standardized by many respirology and pulmonology groups. Writing a mode is most proper in all capital letters with a dash between the control variable and the strategy (i.e. PC-IMV, or VC-MMV etc.). Taxonomy for mechanical ventilation The taxonomy is a logical classification system based on 10 maxims of ventilator d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
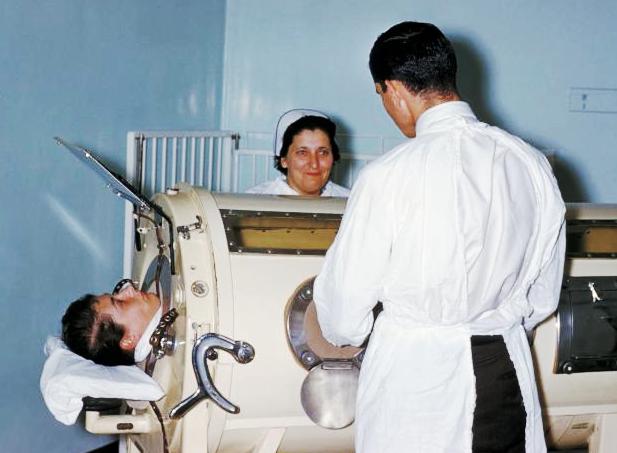
Ventilator
A ventilator is a type of breathing apparatus, a class of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators may be computerized microprocessor-controlled machines, but patients can also be ventilated with a simple, hand-operated bag valve mask. Ventilators are chiefly used in intensive-care medicine, home care, and emergency medicine (as standalone units) and in anesthesiology (as a component of an anesthesia machine). Ventilators are sometimes called "respirators", a term commonly used for them in the 1950s (particularly the "Bird respirator"). However, contemporary medical terminology uses the word "respirator" to refer to a face-mask that protects wearers against hazardous airborne substances. Function In its simplest form, a modern positive pressure ventilator, consists of a compressible air reservoir o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Systemic Pressure
In medicine, the mean systemic pressure (MSP) or mean systemic filling pressure (MSFP) is defined as the mean pressure that exists in the circulatory system when there is no blood motion. A similar term, mean circulatory filling pressure, (MCFP) is defined as the mean pressure that exists in the combined circulatory system & pulmonary system when there is no blood motion. The value of MSP in animal experimental models is approximately 7 mm Hg. It is an indicator of how full the circulatory system is (i.e. the volume of blood in the system compared to the capacity of the system), and is influenced by the volume of circulating blood and the smooth muscle tone in the walls of the venous system (which determines the capacity of the system). MSP is measured in two ways experimentally, and as a result has two alternative naming conventions. MSFP is measured after clamping the aortic root and the great veins at point of entry to right atrium. On the other hand, MCFP is measured exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |