Mean Airway Pressure on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mean airway pressure typically refers to the mean pressure applied during
 In
In
positive-pressure
Modes of mechanical ventilation are one of the most important aspects of the usage of mechanical ventilation. The mode refers to the method of inspiratory support. In general, mode selection is based on clinician familiarity and institutional pre ...
mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
. Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar
Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
ventilation, arterial oxygenation, hemodynamic
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously ...
performance, and barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or in contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in ...
. It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance.
Equations
There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure.Volume control ventilation
In ventilation with a square flow waveform this equation can be used: where: * = mean airway pressure * = peak inspiratory pressure * = peak end expiratory pressure * = inspiratory time * = cycle timePressure control ventilation
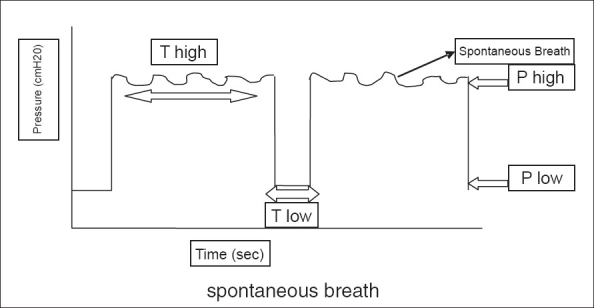
During pressure control ventilation this variant of the equation can be used: where: * = mean airway pressure * = peak inspiratory pressure * = peak end expiratory pressure * = inspiratory time * = cycle timeAirway pressure release ventilation
 In
In airway pressure release ventilation
Airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) is a pressure control mode of mechanical ventilation that utilizes an inverse ratio ventilation strategy. APRV is an applied continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) that at a set timed interval rel ...
(APRV) a variation of the previous equation must be used for the variables:
:
:where:
:* = mean airway pressure
:* = peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)
:* = peak end expiratory pressure
:* = time spent at
:* = time spent at
Other equations
: : : : :Clinical significance
Mean airway pressure has been shown to have a similar correlation as plateau pressure to mortality. MAP is closely associated with mean alveolar pressure and shows the stresses exerted on the lung parenchyma on mechanical ventilation. In high frequency oscillatory ventilation, it has been suggested to set the mean airway pressure six above the lower inflection point on the lungs P-V curve.See also
*Ventilators
A ventilator is a type of breathing apparatus, a class of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathi ...
* Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, wit ...
* Modes of ventilation
* Mean systemic pressure
References