|
Maya Dedication Rituals
The Classic Maya used dedication rituals to sanctify their living spaces and family members by associating their physical world with supernatural concepts through religious practice. The existence of such rituals is inferred from the frequent occurrence of so-called 'dedication' or 'votive' cache deposits in an archaeological context. Caches Caches can be found in the Maya common places and public buildings, which contained objects made or found by commoners.Marcus, Joyce (1978) “Archaeology and Religion: A Comparison of the Zapotec and Maya.” World Archaeology 10(2): 172-191. More specifically, these caches were usually found in fields or family altars, and contained less valuable materials such as ceramic vessels, copal, food, and drink. These dedication cache materials relate more closely to household tasks, such as preparing food or working a field. The content and placement of these caches suggests a request for aid in acquiring daily necessities, such as food, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoard
A hoard or "wealth deposit" is an archaeological term for a collection of valuable objects or artifacts, sometimes purposely buried in the ground, in which case it is sometimes also known as a cache. This would usually be with the intention of later recovery by the hoarder; hoarders sometimes died or were unable to return for other reasons (forgetfulness or physical displacement from its location) before retrieving the hoard, and these surviving hoards might then be uncovered much later by metal detector hobbyists, members of the public, and archaeologists. Hoards provide a useful method of providing dates for artifacts through association as they can usually be assumed to be contemporary (or at least assembled during a decade or two), and therefore used in creating chronologies. Hoards can also be considered an indicator of the relative degree of unrest in ancient societies. Thus conditions in 5th and 6th century Britain spurred the burial of hoards, of which the most famou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structure O-13
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Archaeology
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures. In the 16th century, Eurasian diseases such as smallpox and measles, which were endemic among the colonists but new to North America, caused the deaths of upwards of 90% of the indigenous people, resulting in great losses to their societies and cultures. Mesoamerica is one of the five areas in the world where ancient civilization arose independently (see cradle of civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group of minerals), or jadeite (a silicate of sodium and aluminium in the pyroxene group of minerals). Jade is well known for its ornamental use in East Asian, South Asian, and Southeast Asian art. It is commonly used in Latin America, such as Mexico and Guatemala. The use of jade in Mesoamerica for symbolic and ideological ritual was influenced by its rarity and value among pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Olmecs, the Maya, and other ancient civilizations of the Valley of Mexico. Etymology The English word ''jade'' is derived (via French and Latin 'flanks, kidney area') from the Spanish term (first recorded in 1565) or 'loin stone', from its reputed efficacy in curing ailments of the loins and kidneys. ''Nephrite'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerros
Cerros is an Eastern Lowland Maya archaeological site in northern Belize that functioned from the Late Preclassic to the Postclassic period. The site reached its apogee during the Mesoamerican Late Preclassic and at its peak, it held a population of approximately 1,089 people. The site is strategically located on a peninsula at the mouth of the New River where it empties into Chetumal Bay on the Caribbean coast. As such, the site had access to and served as an intermediary link between the coastal trade route that circumnavigated the Yucatán Peninsula and inland communities. The inhabitants of Cerros constructed an extensive canal system and utilized raised-field agriculture. Site organization The core of the site immediately abuts the bay and consists of several relatively large structures and stepped pyramids, an acropolis complex, and two ballcourts. Bounding the southern side of the site is a crescent-shaped canal network that encloses the central portion of the site an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyph
A glyph () is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical representation, in a particular typeface, of an element of written language. A grapheme, or part of a grapheme (such as a diacritic), or sometimes several graphemes in combination (a composed glyph) can be represented by a glyph. Glyphs, graphemes and characters In most languages written in any variety of the Latin alphabet except English, the use of diacritics to signify a sound mutation is common. For example, the grapheme requires two glyphs: the basic and the grave accent . In general, a diacritic is regarded as a glyph, even if it is contiguous with the rest of the character like a cedilla in French, Catalan or Portuguese, the ogonek in several languages, or the stroke on a Polish " Ł". Although these marks originally had no independent meaning, they have since acquired meaning in the field of mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaxchilan
Yaxchilan () is an ancient Maya city located on the bank of the Usumacinta River in the state of Chiapas, Mexico. In the Late Classic Period Yaxchilan was one of the most powerful Maya states along the course of the Usumacinta River, with Piedras Negras as its major rival.Sharer & Traxler 2006, p. 421 Architectural styles in subordinate sites in the Usumacinta region demonstrate clear differences that mark a clear boundary between the two kingdoms. Yaxchilan was a large center, important throughout the Classic era, and the dominant power of the Usumacinta River area. It dominated such smaller sites as Bonampak, and had a long rivalry with Piedras Negras and at least for a time with Tikal; it was a rival of Palenque, with which Yaxchilan warred in 654. The site is particularly known for its well-preserved sculptured stone lintels set above the doorways of the main structures.Sharer & Traxler 2006, p. 435 These lintels, together with the stelae erected before the major buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Caracol, Chichen Itza
El Caracol, the Observatory, is a unique structure at pre-Columbian Maya civilization site of Chichen Itza. El Caracol, which means 'snail' in Spanish, is so named due to the spiral staircase inside the tower.Sharer & Traxler (2006, p.563) History The structure is dated to around AD 906, the Post Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, by the stele on the Upper Platform. It is suggested that the El Caracol was an ancient Mayan observatory building and provided a way for the Mayan people to observe changes in the sky due to the flattened landscape of the Yucatán with no natural markers for this function around Chichen Itza. The observers could view the sky above the vegetation on the Yucatán Peninsula without any obstruction. Observations Mayan astronomers knew from naked-eye observations that Venus ''appeared'' on the western and ''disappeared'' on the eastern horizons at different times in the year, and that it took 584 days to complete one cycle. They also knew th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
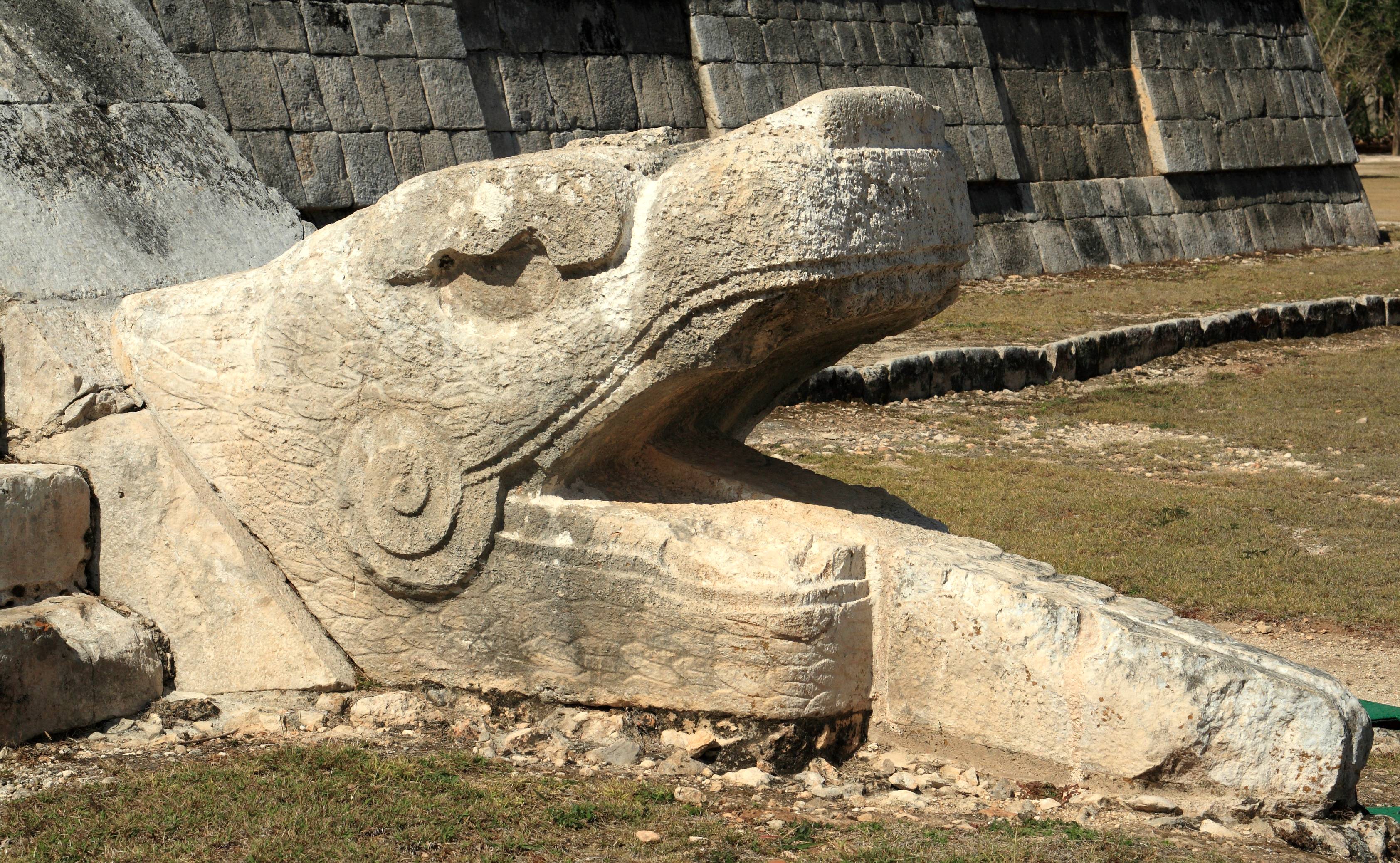
Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with the emphasis reversed in English to ; from yua, Chiʼchʼèen Ìitshaʼ () "at the mouth of the well of the Itza people" was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Terminal Classic period. The archeological site is located in Tinúm Municipality, Yucatán State, Mexico. Chichen Itza was a major focal point in the Northern Maya Lowlands from the Late Classic (c. AD 600–900) through the Terminal Classic (c. AD 800–900) and into the early portion of the Postclassic period (c. AD 900–1200). The site exhibits a multitude of architectural styles, reminiscent of styles seen in central Mexico and of the Puuc and Chenes styles of the Northern Maya lowlands. The presence of central Mexican styles was once thought to have been representative of direct migration or even conquest from central Mexico, but most contemporary interpretations view the presence of these non-Maya styles more as the result of cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which are identifiably Maya date to the 3rd century BCE in San Bartolo, Guatemala. Maya writing was in continuous use throughout Mesoamerica until the Spanish conquest of the Maya in the 16th and 17th centuries. Maya writing used logograms complemented with a set of syllabic glyphs, somewhat similar in function to modern Japanese writing. Maya writing was called "hieroglyphics" or hieroglyphs by early European explorers of the 18th and 19th centuries who found its general appearance reminiscent of Egyptian hieroglyphs, although the two systems are unrelated. Though modern Mayan languages are almost entirely written using the Latin alphabet rather than Maya script, there have been recent developments encouraging a revival of the Maya gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piedras Negras (Maya Site)
Piedras Negras is the modern name for a ruined city of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization located on the north bank of the Usumacinta River in the Petén department of northwestern Guatemala. Piedras Negras is one of the most powerful of the Usumacinta ancient Maya urban centers. Occupation at Piedras Negras is known from the Late Preclassic period onward, based on dates retrieved from epigraphic information found on multiple stelae and altars at the site. Piedras Negras is an archaeological site known for its large sculptural output when compared to other ancient Maya sites. The wealth of sculpture, in conjunction with the precise chronological information associated with the lives of elites of Piedras Negras, has allowed archaeologists to reconstruct the political history of the Piedras Negras polity and its geopolitical footprint. Location Southern Lowlands, Modern-Day: Guatemala Geography Piedras Negras is located along the eastern banks of the Usumacinta River. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures. In the 16th century, Eurasian diseases such as smallpox and measles, which were endemic among the colonists but new to North America, caused the deaths of upwards of 90% of the indigenous people, resulting in great losses to their societies and cultures. Mesoamerica is one of the five areas in the world where ancient civilization arose independently (see cradle of civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |