|
Maxillary Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the maxillary nerve (V) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (CN V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of Sense, sensation from the maxilla, nasal cavity, Sinus (anatomy), sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 180 Structure It begins at the middle of the trigeminal ganglion as a flattened plexiform band then it passes through the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. It leaves the skull through the foramen rotundum, where it becomes more cylindrical in form, and firmer in texture. After leaving foramen rotundum it gives two branches to the pterygopalatine ganglion. It then crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, inclines lateralward on the back of the maxilla, and enters the orbit through the inferior orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
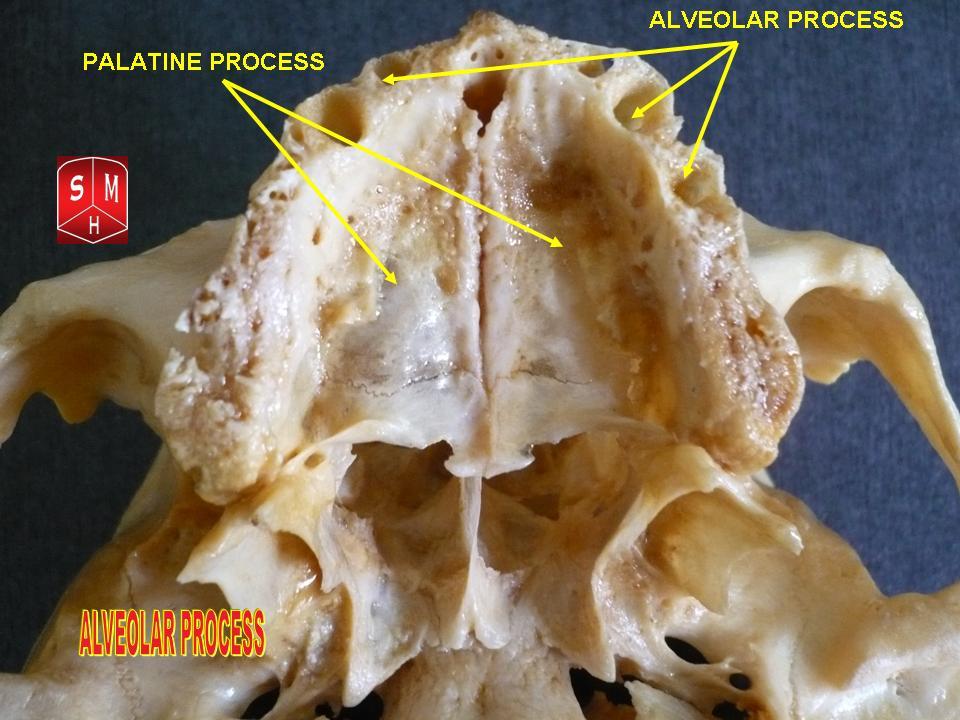
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called a ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow", especially "the socket of a tooth", from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity", diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship", from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe"; Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street", originally "narrow opening"; Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmic Nerve
The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face and anterior scalp, as well as other structures of the head. Structure Origin The ophthalmic nerve is the first branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), the first and smallest of its three divisions. It arises from the superior part of the trigeminal ganglion. Course It passes anterior-ward along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus inferior to the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and trochlear nerve (N IV). It exits the skull into the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. Branches Within the skull, the ophthalmic nerve produces: * meningeal branch (tentorial nerve) The ophthalmic nerve divides into three major branches which pass through the superior orbital fissure: * frontal nerve ** supraorbital nerve ** supratrochlea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenopalatine Foramen
The sphenopalatine foramen is a foramen of the skull that connects the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa. It gives passage to the sphenopalatine artery, nasopalatine nerve, and the superior nasal nerve (all passing from the pterygopalatine fossa into the nasal cavity). Structure The processes of the superior border of the palatine bone are separated by the ''sphenopalatine notch'', which is converted into the sphenopalatine foramen by the under surface of the body of the sphenoid. The sphenopalatine foramen is situated posterior to the middle nasal meatus orbital process of palatine bone, anterior to the sphenoidal process of palatine bone, inferior to the body and of the sphenoid bone, and superior to the superior margin of the perpendicular plate of palatine bone. Relations The ethmoid crest (a reliable surgical landmark A landmark is a recognizable natural or artificial feature used for navigation, a feature that stands out from its near environment and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasopalatine
The nasopalatine nerve (also long sphenopalatine nerve) is a nerve of the head. It is a sensory branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that passes through the pterygopalatine ganglion (without synapsing) and then through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity, and finally out of the nasal cavity through the incisive canal and then the incisive fossa to enter the hard palate. It provides sensory innervation to the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum, and gingiva just posterior to the upper incisor teeth. The nasopalatine nerve is the largest of the medial posterior superior nasal nerves. Structure Course It exits the pterygopalatine fossa through the sphenopalatine foramen to enter the nasal cavity. It passes across the roof of the nasal cavity below the orifice of the sphenoidal sinus to reach the posterior part of the nasal septum. It passes anteroinferiorly upon the nasal septum along a groove upon the vomer, running between the periosteum and mucous membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Orbital Fissure
The inferior orbital fissure is a gap between the Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wing of sphenoid bone, and the maxilla. It connects the Orbit (anatomy), orbit (anteriorly) with the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (posteriorly). Anatomy The medial end of the inferior orbital fissure diverges laterally from the medial end of the superior orbital fissure. It is situated between the lateral wall of the orbit and the floor of the orbit. Contents The fissure gives passage to multiple structures, including: * Infraorbital nerve, Infraorbital artery, artery and Infraorbital vein, vein * Inferior ophthalmic vein * Zygomatic nerve * Orbital branches of the pharyngeal nerve * Maxillary nerve Additional images File:Gray189.png, Left infratemporal fossa. File:Gray191.png, Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. File:Gray787.png, Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure. File:Slide2rome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaticofacial Nerve
The zygomaticofacial nerve (or zygomaticofacial branch of zygomatic nerve or malar branch of zygomatic nerve) is a cutaneous ( sensory) branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2) that arises within the orbit. The zygomaticofacial nerve penetrates the inferolateral angle of the orbit, emerging into the face through the zygomaticofacial foramen, then penetrates the orbicularis oculi muscle to reach and innervate the skin of the prominence of the cheek. Anatomy Communications The zygomaticofacial nerve forms a nerve plexus A nerve plexus is a plexus (branching network) of intersecting nerves. A nerve plexus is composed of afferent and efferent fibers that arise from the merging of the anterior rami of spinal nerves and blood vessels. There are five spinal nerve ple ... with the zygomatic branches of facial nerve (CN VII), and the inferior palpebral branches of maxillary nerve (V2). Variation The nerve may sometimes be absent. References External links * * Maxill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaticotemporal Nerve
The zygomaticotemporal nerve (zygomaticotemporal branch, temporal branch) is a cutaneous ( sensory) nerve of the head. It is a branch of the zygomatic nerve (itself a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2)). It arises in the orbit and exits the orbit through the zygomaticotemporal foramen in the zygomatic bone to enter the temporal fossa. It is distributed to the skin of the side of the forehead. It also contains a parasympathetic secretomotor component for the lacrimal gland which it confers to the lacrimal nerve (which then delivers it to the gland). Structure Origin The zygomaticotemporal nerve is a branch of the zygomatic nerve. Course It passes along the lateral wall of the orbit in a groove in the zygomatic bone. It passes through the zygomaticotemporal foramen of the zygomatic bone to emerge (at the anterior portion of) the temporal fossa. In the temporal fossa, it passes superior-ward between the two layers of the temporal fascia, between the temporal bone an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Nerve
The zygomatic nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve (itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It arises in the pterygopalatine fossa and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure before dividing into its two terminal branches: the zygomaticotemporal nerve and zygomaticofacial nerve. Through its branches, the zygomatic nerve provides sensory invervation to skin over the zygomatic bone and the temporal bone. It also carries post-ganglionic parasympathetic axons to the lacrimal gland. It may be blocked by anaesthetising the maxillary nerve. Structure Origin The zygomatic nerve is a branch of the maxillary nerve (CN V2). It arises at the pterygopalatine ganglion. Course It exits from the pterygopalatine fossa through the inferior orbital fissure to enter the orbit. In the orbit, it travels anteriorly along its lateral wall. Branches Soon after the zygomatic nerve enters the orbit, it divides into its branches. These include: * Zygomaticotemporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges is to protect the central nervous system. Structure Dura mater The dura mater (), is a thick, durable membrane, closest to the Human skull, skull and vertebrae. The dura mater, the outermost part, is a loosely arranged, fibroelastic layer of cells, characterized by multiple interdigitating cell processes, no extracellular collagen, and significant extracellular spaces. The middle region is a mostly fibrous portion. It consists of two layers: the endosteal layer, which lies closest to the skull, and the inner meningeal layer, which lies closer to the brain. It contains larger blood vessels that split into the capillaries in the pia mater. It is composed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Meningeal Nerve
The middle meningeal nerve (meningeal or dural branch) is given off from the maxillary nerve (CN V2) directly after its origin from the trigeminal ganglion, before CN V2 enters the foramen rotundum. It accompanies the middle meningeal artery and vein Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ... once the artery and vein enter the cranium through the foramen spinosum and supplies the dura mater. Additional images File:Gray138.png, Left temporal bone. Inner surface. References Maxillary nerve {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Foramen
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is one of two small holes in the skull's upper jawbone ( maxillary bone), located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose. Both holes are used for blood vessels and nerves. In anatomical terms, it is located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. It is typically from the infraorbital margin. Structure Forming the exterior end of the infraorbital canal, the infraorbital foramen communicates with the infraorbital groove, the canal's opening on the interior side. The ramifications of the three principal branches of the trigeminal nerve—at the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramen—are distributed on a vertical line (in anterior view) passing through the middle of the pupil. The infraorbital foramen is used as a pressure point to test the sensitivity of the infraorbital nerve. Palpation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Orbital Fissure
The inferior orbital fissure is a gap between the Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wing of sphenoid bone, and the maxilla. It connects the Orbit (anatomy), orbit (anteriorly) with the infratemporal fossa and pterygopalatine fossa (posteriorly). Anatomy The medial end of the inferior orbital fissure diverges laterally from the medial end of the superior orbital fissure. It is situated between the lateral wall of the orbit and the floor of the orbit. Contents The fissure gives passage to multiple structures, including: * Infraorbital nerve, Infraorbital artery, artery and Infraorbital vein, vein * Inferior ophthalmic vein * Zygomatic nerve * Orbital branches of the pharyngeal nerve * Maxillary nerve Additional images File:Gray189.png, Left infratemporal fossa. File:Gray191.png, Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. File:Gray787.png, Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure. File:Slide2rome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |