|
Maud Karpeles
Maud Karpeles OBE, (12 November 1885 – 1 October 1976) was a British collector of folksongs and dance teacher. Early life and education Maud Pauline Karpeles was born at Lancaster Gate in Bayswater, London, in 1885. She was the third of five children. Her father, Joseph Nicolaus Karpeles, was a German immigrant who was born in Hamburg, and naturalised as a British subject in 1881. He worked as a tea merchant and stockbroker. Her mother, Emily Karpeles (née Raphael), was born in London. Both her parents were Jewish but nonreligious. Her family moved to Westbourne Terrace, Paddington, when she was about ten. Like her sisters, Karpeles went to boarding school in Tunbridge Wells, where she learned to play the violin and piano, and studied German. In 1906, she spent six months at the Hochschule für Musik in Berlin, taking piano lessons and going to concerts. Volunteer work After returning to England, Karpeles was a volunteer with the Invalid Children's Aid Association. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merry England
"Merry England", or in more jocular, archaic spelling "Merrie England", refers to a utopian conception of English culture, English society and culture based on an idyllic pastoral way of life that was allegedly prevalent in Early Modern Britain at some time between the Middle Ages and the onset of the Industrial Revolution. More broadly, it connotes a putative essentialism, essential Englishness with nostalgic overtones, incorporating such cultural icon, cultural symbols as the thatched cottage, the country inn and the Sunday roast. Folklorist Roy Judge has described the concept as "a world that has never actually existed, a visionary, mythical landscape, where it is difficult to take normal historical bearings." It may be treated both as a product of the sentimental nostalgic imagination and as an ideological or political construct, often underwriting various sorts of conservative world-views. Favourable perceptions of Merry England reveal a nostalgia for aspects of an earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword Dance
Weapon dances incorporating swords or similar weapons are recorded throughout world history. There are various traditions of Solo dance, solo and mock-battle (Pyrrhic dance, Pyrrhic) sword dances in Africa, Asia and Europe. Some traditions use sticks or clubs in place of bladed weapons, while most modern performers employ dulled sword replica, replications to avoid injury. Forms General types of sword dance include: *solo dancers around swords – such as the traditional Scottish sword dances. This general form also encompasses non-sword dances such as the bacca pipes jig in Cotswold morris dance, *mock-battle dances, including many stick dances from non-sword traditions, and such common continental dances as Bouffons or Mattachins as described by Thoinot Arbeau in 1588. *hilt-and-point sword dances – where the dancers are linked together by their swords in a chain. These form the basis for rapper sword and Long Sword dance, long sword forms. China and Vietnam Sword ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contralto
A contralto () is a classical music, classical female singing human voice, voice whose vocal range is the lowest of their voice type, voice types. The contralto's vocal range is fairly rare, similar to the mezzo-soprano, and almost identical to that of a countertenor, typically between the F below middle C (F3 in scientific pitch notation) to the second F above middle C (F5), although, at the extremes, some voices can reach the D below middle C (D3) or the second B above middle C (B5). The contralto voice type is generally divided into the coloratura, lyric, and dramatic contralto. History "Contralto" is primarily meaningful only in reference to classical and operatic singing, as other traditions lack a comparable Voice classification in non-classical music, system of vocal categorization. The term "contralto" is only applied to female singers; men singing in a similar range are called "countertenors". The Italian terms "contralto" and "alto" are not synonymous, "alto" technic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baker Street
Baker Street is a street in the Marylebone district of the City of Westminster in London. It is named after builder James Baker. The area was originally high class residential, but now is mainly occupied by commercial premises. The street is referenced in multiple popular works. Fictional detective Sherlock Holmes lived at 221B Baker Street, a fictional address on the north of the street. A 1978 hit song by Gerry Rafferty was titled " Baker Street". Location Baker Street is a busy thoroughfare, lying in postcode areas NW1/W1 and forming part of the A41. It used to run south from Regent's Park, the junction with Park Road, parallel to Gloucester Place, meeting Marylebone Road, Portman Square and Wigmore Street. In 2019, the until-then one-way street was changed to accommodate lanes running in both directions. At the junction with Wigmore Street, Baker Street turns into Orchard Street, which ends when it meets with Oxford Street. After Portman Square the road continues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea College Of Arts
Chelsea College of Arts is a Colleges of the University of the Arts London, constituent college of the University of the Arts London, a public art and design university in London, England. It offers further education, further and higher education courses in fine art, graphic design, interior design, product design, and textile design up to PhD level. History Polytechnic Chelsea College of Arts was originally an integral school of the South-Western Polytechnic, which opened at Manresa Road, Chelsea, London, Chelsea, in 1895 to provide scientific and technical education to Londoners. Day and evening classes for men and women were held for the domestic worker, domestic economy, mathematics, engineering, natural science, art, and music. Art was taught from the beginning of the Polytechnic (United Kingdom), Polytechnic and included design, weaving, embroidery, and Electrophoretic deposition, electrodeposition. The South-Western Polytechnic became the Chelsea Polytechnic in 1922 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dressmaker
A dressmaker, also known as a seamstress, is a person who makes clothing for women, such as dresses, blouses, and evening gowns. Dressmakers were historically known as mantua-makers, and are also known as a modiste or fabrician. Notable dressmakers *Cristóbal Balenciaga *Pierre Balmain *Coco Chanel *Christian Dior * David Emanuel *Norman Hartnell, royal dressmaker * Elizabeth Keckley, modiste and confidante to Mary Todd Lincoln * Jean Muir, fashion designer * Madame Palmyre, a favorite designer and dressmaker of Eugénie, empress of France * Anna and Laura Tirocchi, Providence, Rhode Island * Isabel Toledo * Madeleine Vionnet * R'Bonney Gabriel, fashion designer and beauty queen of Miss Universe 2022 * Mak Tumang, fashion designer * Michael Cinco, fashion designer * Janet Walker, costumier and dress-making-bust inventor * Charles Frederick Worth Related terms * "Dressmaker" denotes clothing made in the style of a dressmaker, frequently in the term "dressmaker details", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
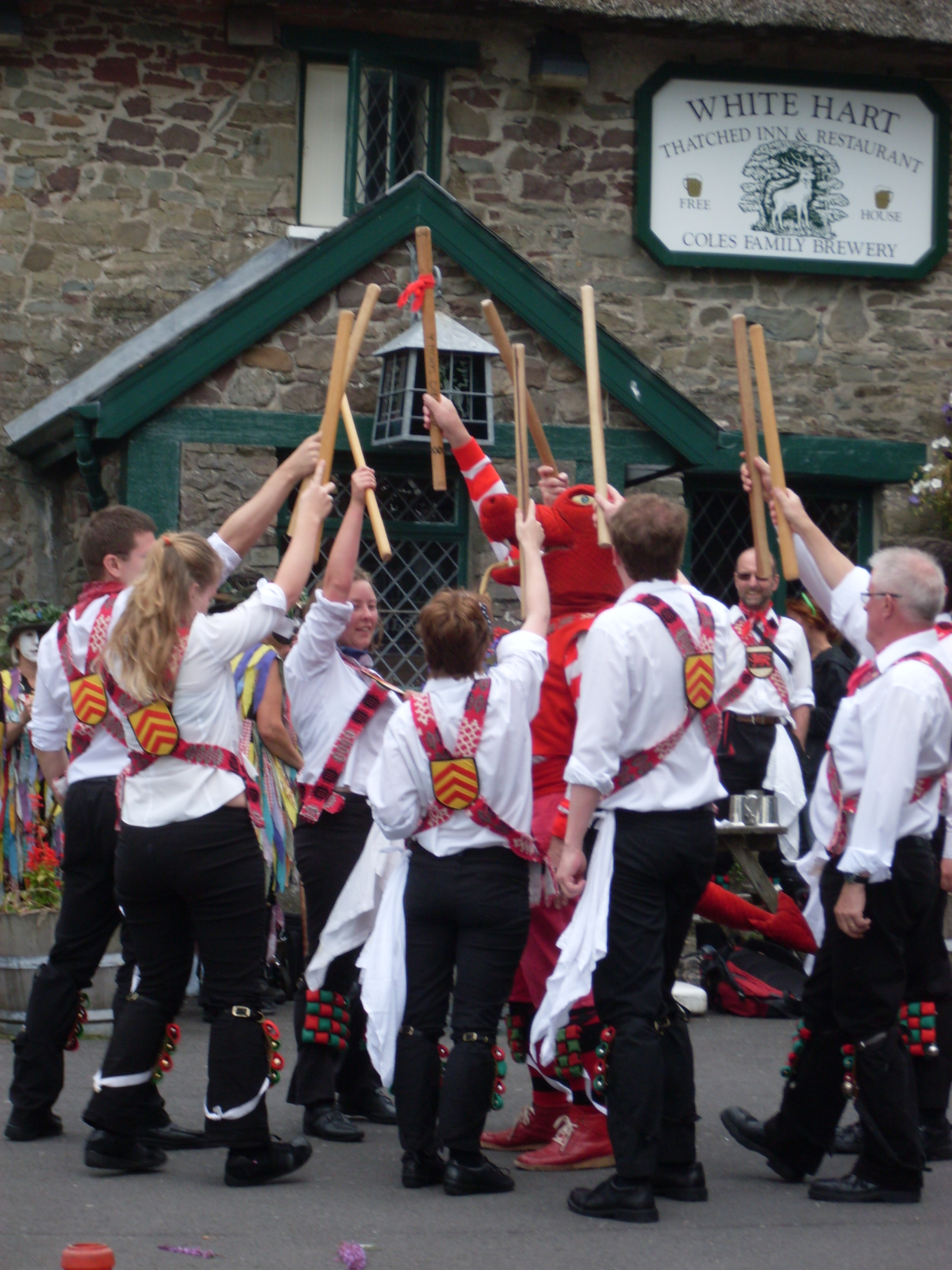
Morris Dance
Morris dancing is a form of English folklore, English folk dance. It is based on rhythmic stepping and the execution of choreographed figures by a group of dancers in costume, usually wearing bell pads on their shins, their shoes or both. A band or single musician, also costumed, will accompany them. Sticks, swords, handkerchiefs, and a variety of other implements may be wielded by the dancers. Morris dancing first appeared in England in the Middle Ages, England in the 15th century. Its earliest surviving mention dates to 1448 and records the payment of seven shillings to Morris dancers by the Goldsmiths' Company in London. The term ''Morris'' derives from the Spanish language, Spanish term , although Morris dancing has no known historical connection to the Moors. Three prominent groups organise and support Morris in England: Morris Ring, Morris Federation and Open Morris; all three organisations have members from other countries as well. There are around 150 Morris sides (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espérance Club
The Espérance Club, and the Maison Espérance dressmaking cooperative, were founded in the mid-1890s by Emmeline Pethick-Lawrence and Mary Neal in response to distressing conditions for girls in the London dress trade. The club was based at 50 Cumberland Market, in the St Pancras area of London. Mary Neal had become fascinated by the folk songs and dances being collected by Cecil Sharp, and invited William Kimber, a musician and dancer from Headington Quarry in Oxfordshire, to teach morris dancing to the young women of the Espérance Club. Thus was born the Espérance Morris, which inspired a modern London women's side, New Esperance Morris. After donating a £1,000 legacy to the club and meeting Emmeline Pethick-Lawrence, Lady Constance Lytton was enthused by the women's movement and thus became a leading suffragette A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Neal
Mary Neal (born Clara Sophia Neal; 5 June 1860 – 22 June 1944) was an English social worker, suffragette and collector of English folk dances. Neal was born in Edgbaston, Birmingham, to a prosperous family. Her father was David Neal, a button manufacturer. In 1888, she began voluntary social work with the West London Methodist Mission of Hugh Price Hughes, helping the poor of Soho, Fitzrovia, and Marylebone in London, taking the name "Sister Mary". Neal set up and ran a "Club for Working Girls" at the mission's Cleveland Hall, and also wrote for the Mission Magazine. According to Emmeline Pethick, who worked with her in the Girls' Club, Neal had "a strong sense of humour and a profound aversion from unreality; she had also a sharp tongue". Neal said of the Girls' Club, The Girls' Club was a great success, but in the autumn of 1895, Neal and Pethick left the mission to set up their own Espérance Club for girls in Cumberland Market, as they wanted to escape from the mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Sharp
Cecil James Sharp (22 November 1859 – 23 June 1924) was an English collector of folk songs, folk dances and instrumental music, as well as a lecturer, teacher, composer and musician. He was a key figure in the folk-song revival in England during the Edwardian period. According to Roud's ''Folk Song in England'', Sharp was the country's "single most important figure in the study of folk song and music". Sharp collected over four thousand folk songs, both in South-West England and the Southern Appalachian region of the United States. He published an extensive series of songbooks based on his fieldwork, often with piano arrangements, and wrote an influential theoretical work, ''English Folk Song: Some Conclusions''. He notated examples of English Morris dancing, and played an important role in the revival both of the Morris and English country dance. In 1911, he co-founded the English Folk Dance Society, which was later merged with the Folk-Song Society to form the English Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratford-upon-Avon
Stratford-upon-Avon ( ), commonly known as Stratford, is a market town and civil parish in the Stratford-on-Avon (district), Stratford-on-Avon district, in the county of Warwickshire, in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England. It is situated on the River Avon, Warwickshire, River Avon, north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and south-west of Warwick. The town is the southernmost point of the Arden, Warwickshire, Arden area at the northern extremity of the The Cotswolds, Cotswolds. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 British census Stratford had a population of 30,495. Stratford was inhabited originally by Celtic Britons, Britons before Anglo-Saxons and remained a village before the lord of the manor, John of Coutances, set out plans to develop it into a town in 1196. In that same year, Stratford was granted a charter from King Richard I to hold a weekly Marketplace, market in the town, giving it its status as a market town. As a result, Strat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |