|
Matter Parity
R-parity is a concept in particle physics. In the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model, baryon number and lepton number are no longer conserved by all of the renormalizable couplings in the theory. Since baryon number and lepton number conservation have been tested very precisely, these couplings need to be very small in order not to be in conflict with experimental data. R-parity is a \mathbb_2 symmetry acting on the Minimal Supersymmetric Standard Model (MSSM) fields that forbids these couplings and can be defined as :P_\mathrm = (-1)^, or, equivalently, as :P_\mathrm = (-1)^, where is spin, is baryon number, and is lepton number. All Standard Model particles have R-parity of +1 while supersymmetric particles have R-parity of −1. Note that there are different forms of parity with different effects and principles, one should not confuse this parity with any other parity. Dark matter candidate With R-parity being preserved, the lightest supersymmetric particle ( LSP) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antineutron
The antineutron is the antiparticle of the neutron with symbol . It differs from the neutron only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. It has the same mass as the neutron, and no net electric charge, but has opposite baryon number (+1 for neutron, −1 for the antineutron). This is because the antineutron is composed of antiquarks, while neutrons are composed of quarks. The antineutron consists of one up antiquark and two down antiquarks. Background The antineutron was discovered in proton–antiproton collisions at the Bevatron (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory) by the team of Bruce Cork, Glen Lambertson, Oreste Piccioni, and William Wenzel in 1956, one year after the antiproton was discovered. Since the antineutron is electrically neutral, it cannot easily be observed directly. Instead, the products of its annihilation with ordinary matter are observed. In theory, a free antineutron should decay into an antiproton, a positron, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
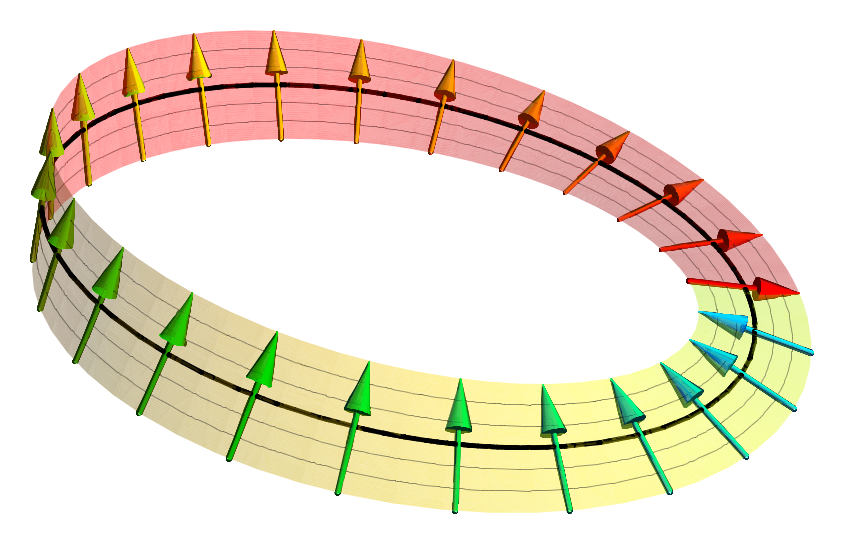
Spinor Representation
In geometry and physics, spinors (pronounced "spinner" IPA ) are elements of a complex vector space that can be associated with Euclidean space. A spinor transforms linearly when the Euclidean space is subjected to a slight (infinitesimal) rotation, but unlike geometric vectors and tensors, a spinor transforms to its negative when the space rotates through 360° (see picture). It takes a rotation of 720° for a spinor to go back to its original state. This property characterizes spinors: spinors can be viewed as the "square roots" of vectors (although this is inaccurate and may be misleading; they are better viewed as "square roots" of sections of vector bundles – in the case of the exterior algebra bundle of the cotangent bundle, they thus become "square roots" of differential forms). It is also possible to associate a substantially similar notion of spinor to Minkowski space, in which case the Lorentz transformations of special relativity play the role of rotations. Spinors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Unified Theory
A Grand Unified Theory (GUT) is any Mathematical model, model in particle physics that merges the electromagnetism, electromagnetic, weak interaction, weak, and strong interaction, strong fundamental interaction, forces (the three gauge theory, gauge interactions of the Standard Model) into a single force at high energy, energies. Although this Unification (physics), unified force has not been directly observed, many GUT models theorize its existence. If the unification of these three interactions is possible, it raises the possibility that there was a grand unification epoch in the Chronology of the universe#Very early universe, very early universe in which these three fundamental interactions were not yet distinct. Experiments have confirmed that at high energy, the electromagnetic interaction and weak interaction unify into a single combined electroweak interaction. GUT models predict that at even grand unification energy, higher energy, the strong and electroweak interaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SO(10)
In particle physics, SO(10) refers to a grand unified theory (GUT) based on the spin group Spin(10). The shortened name SO(10) is conventional among physicists, and derives from the Lie algebra or less precisely the Lie group of SO(10), which is a special orthogonal group that is Double covering group, double covered by Spin(10). SO(10) subsumes the Georgi–Glashow model, Georgi–Glashow and Pati–Salam models, and unifies all fermions in a Generation (particle physics), generation into a single field. This requires 12 new gauge bosons, in addition to the 12 of Georgi–Glashow model, SU(5) and 9 of Pati–Salam model, SU(4)×SU(2)×SU(2). History Before the SU(5) theory behind the Georgi–Glashow model, Harald Fritzsch and Peter Minkowski, and independently Howard Georgi, found that all the matter contents are incorporated into a single representation, spinorial 16 of SO(10). However, Georgi found the SO(10) theory just a few hours before finding SU(5) at the end of 1973 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seesaw Mechanism
In the theory of grand unification of particle physics, and, in particular, in theories of neutrino masses and neutrino oscillation, the seesaw mechanism is a generic model used to understand the relative sizes of observed neutrino masses, of the order of eV, compared to those of quarks and charged leptons, which are millions of times heavier. The name of the seesaw mechanism was given by Tsutomu Yanagida in a Tokyo conference in 1981. There are several types of models, each extending the Standard Model. The simplest version, "Type 1", extends the Standard Model by assuming two or more additional right-handed neutrino fields inert under the electroweak interaction, and the existence of a very large mass scale. This allows the mass scale to be identifiable with the postulated scale of grand unification. Type 1 seesaw This model produces a light neutrino, for each of the three known neutrino flavors, and a corresponding very heavy neutrino for each flavor, which has yet to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroweak
In particle physics, the electroweak interaction or electroweak force is the unified description of two of the fundamental interactions of nature: electromagnetism (electromagnetic interaction) and the weak interaction. Although these two forces appear very different at everyday low energies, the theory models them as two different aspects of the same force. Above the unification energy, on the order of 246 GeV,The particular number 246 GeV is taken to be the vacuum expectation value v = (G_\text \sqrt)^ of the Higgs field (where G_\text is the Fermi coupling constant). they would merge into a single force. Thus, if the temperature is high enough – approximately 1015 K – then the electromagnetic force and weak force merge into a combined electroweak force. During the quark epoch (shortly after the Big Bang), the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak force. It is thought that the required temperature of 1015 K has not been see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics B
Nuclear may refer to: Physics Relating to the nucleus of the atom: *Nuclear engineering *Nuclear physics *Nuclear power *Nuclear reactor *Nuclear weapon *Nuclear medicine *Radiation therapy *Nuclear warfare Mathematics *Nuclear space *Nuclear operator * Nuclear congruence *Nuclear C*-algebra Biology Relating to the nucleus of the cell: * Nuclear DNA Society *Nuclear family, a family consisting of a pair of adults and their children Music * "Nuclear" (band), chilean thrash metal band * "Nuclear" (Ryan Adams song), 2002 *"Nuclear", a song by Mike Oldfield from his ''Man on the Rocks'' album * ''Nu.Clear'' (EP) by South Korean girl group CLC Films * ''Nuclear'' (film), a 2022 documentary by Oliver Stone. See also *Nucleus (other) *Nucleolus *Nucleation *Nucleic acid Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Letters B
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of the human intellect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review D
Physical may refer to: *Physical examination In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ..., a regular overall check-up with a doctor * ''Physical'' (Olivia Newton-John album), 1981 ** "Physical" (Olivia Newton-John song) * ''Physical'' (Gabe Gurnsey album) * "Physical" (Alcazar song) (2004) * "Physical" (Enrique Iglesias song) (2014) * "Physical" (Dua Lipa song) (2020) *"Physical (You're So)", a 1980 song by Adam & the Ants, the B side to " Dog Eat Dog" * ''Physical'' (TV series), an American television series *'' Physical: 100'', a Korean reality show on Netflix See also {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Flavor Violation
Minimal may refer to: * Minimal (music genre), art music that employs limited or minimal musical materials * "Minimal" (song), 2006 song by Pet Shop Boys * Minimal (supermarket) or miniMAL, a former supermarket chain in Germany and Poland * Minimal (''Dungeons & Dragons''), a creature of magically reduced size in the game ''Dungeons & Dragons'' * Minimal (chocolate), a bean to bar chocolate store in Japan, featured in '' Kantaro: The Sweet Tooth Salaryman'' * Minimal (clothing), an Indonesia clothing-retail company that worked with fashion model Ayu Gani * MINIMAL (restaurant), high end restaurant in Taichung, Taiwan See also * *Minimalism (other) * Maximal (other) *Minimisation (other) Minimisation or minimization may refer to: * Minimisation (psychology), downplaying the significance of an event or emotion * Minimisation (clinical trials) * Minimisation (code) or Minification, removing unnecessary characters from source code * ... * Minimal prime ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big O Notation
Big ''O'' notation is a mathematical notation that describes the asymptotic analysis, limiting behavior of a function (mathematics), function when the Argument of a function, argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. Big O is a member of a #Related asymptotic notations, family of notations invented by German mathematicians Paul Gustav Heinrich Bachmann, Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau, and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation. The letter O was chosen by Bachmann to stand for '':wikt:Ordnung#German, Ordnung'', meaning the order of approximation. In computer science, big O notation is used to Computational complexity theory, classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. In analytic number theory, big O notation is often used to express a bound on the difference between an arithmetic function, arithmetical function and a better understood approximation; one well-known exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |