|
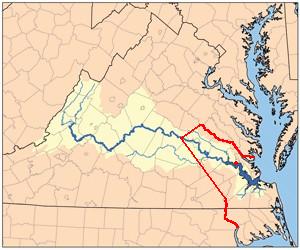
Mattaponi Indian Nation
The Mattaponi () tribe is one of only two Virginia Indian tribes in the Commonwealth of Virginia that owns reservation land, which it has held since the colonial era. The larger Mattaponi Indian Tribe lives in King William County on the reservation, which stretches along the borders of the Mattaponi River, near West Point, Virginia.Wood, Karenne, ed., ''The Virginia Indian Heritage Trail'', Charlottesville, VA: Virginia Foundation for the Humanities, 2007 The Mattaponi were one of six tribes inherited by in the late 16th century. The tribe spoke an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King William County
King William County is a county located in the U.S. state of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,810. Its county seat is King William. King William County is located in the Middle Peninsula and is included in the Greater Richmond Region. History For thousands of years before European contact, indigenous peoples of North America lived in the Tidewater area of present-day Virginia. At the time of the founding of Jamestown, 30 Virginia Native American tribes comprised the Powhatan paramountcy, numbering 14,000-21,000 people. The Algonquian-speaking Mattaponi Indian Tribe and Upper Mattaponi tribe, among the 11 tribes recognized by the state of Virginia, are located in the county. The Mattaponi are one of two Virginia Indian tribes who still occupy reservation land first allocated by the English under treaty in the 17th century. One prominent family during Colonial Virginia times was that of William Aylett. The Tobacco Inspection Act of 1730 establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiefdom
A chiefdom is a political organization of people representation (politics), represented or government, governed by a tribal chief, chief. Chiefdoms have been discussed, depending on their scope, as a stateless society, stateless, state (polity), state analogue or early state system or institution. Usually a chief's position is based on kinship, which is often monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites can form a political-ideological aristocracy relative to the general group. Chiefdoms and chiefs are sometimes identified as the same as kingdoms and kings, and therefore understood as monarchy, monarchies, particularly when they are understood as not necessarily states, but having monarchic representation or government. Concept In anthropology, anthropological theory, one model of human social development rooted in ideas of cultural evolution describes a chiefdom as a form of social organization more complex than a tribe or a band s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribal Chief
A tribal chief, chieftain, or headman is a leader of a tribe, tribal society or chiefdom. Tribal societies There is no definition for "tribe". The concept of tribe is a broadly applied concept, based on tribal concepts of societies of western Afroeurasia. Tribal societies are sometimes categorized as an intermediate stage between the band society of the Paleolithic stage and civilization with centralized, super-regional government based in Cities of the Ancient Near East, cities. Anthropologist Elman Service distinguishes two stages of tribal societies: simple societies organized by limited instances of social rank and prestige, and more stratified society, stratified societies led by chieftains or tribal kings (chiefdoms). Stratified tribal societies led by tribal kings are thought to have flourished from the Neolithic stage into the Iron Age, albeit in competition with Urban area, urban civilisations and empires beginning in the Bronze Age. In the case of tribal societies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscataway Creek
Piscataway Creek is an U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed August 15, 2011 tributary of the Potomac River in Prince George's County, Maryland. The creek is a tidal arm of the Potomac for its final , entering the Potomac at Fort Washington Park. Tinkers Creek is a tributary to Piscataway Creek, converging from the north upstream of the mouth of the Piscataway. The United States Geological Survey The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on Mar ... records two variant names for Piscataway Creek: Pascattawaye Creek and Puscattuway Creeke. The Fort Washington Light was built to provide guidance for mariners entering Piscataway Creek from the Potomac River. See also * List of Maryland rivers References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Powhatan War
The AngloPowhatan Wars were three wars fought between settlers of the Colony of Virginia and the Powhatan People of Tsenacommacah in the early 17th century. The first war started in 1609 and ended in a peace settlement in 1614. The second war lasted from 1622 to 1632. The third war lasted from 1644 until 1646 and ended when Opechancanough was captured and killed. That war resulted in a defined boundary between the Native Americans and colonial lands that could only be crossed for official business with a special pass. This situation lasted until 1677 and the Treaty of Middle Plantation which established Indian reservations following Bacon's Rebellion. Early conflict The settlement at Jamestown, Virginia, was established in May 1607 within the territory of the Powhatan, who were led by Chief Wahunsunacawh, known to the colonists as Chief Powhatan. The area was quite swampy and ill-suited to farming, and Powhatan wanted Captain John Smith and the colonists to forsake the swamp a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Strachey
William Strachey (4 April 1572 – buried 16 August 1621) was an English writer whose works are among the primary sources for the early history of the English colonisation of North America. He is best remembered today as the eye-witness reporter of the 1609 shipwreck on the uninhabited island of Bermuda of the colonial ship ''Sea Venture'', which was caught in a hurricane while sailing to Virginia. The survivors eventually reached Virginia after building two small ships during the ten months they spent on the island. His account of the incident and of the Colony of Virginia, Virginia colony is thought by most William Shakespeare, Shakespearean scholars to have been a source for Shakespeare's play ''The Tempest''. Family William Strachey, born 4 April 1572 in Saffron Walden, Essex, was the grandson of William Strachey (died 1587), and the eldest son of William Strachey (died 1598) and Mary Cooke (died 1587),. the daughter of Henry Cooke, Worshipful Company of Merchant Taylors, Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (explorer)
John Smith ( – 21 June 1631) was an English soldier, explorer, colonial governor, admiral of New England, and author. He was knighted for his services to Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, and his friend Mózes Székely. Following his return to England from a life as a soldier of fortune and as a slave, he played an important role in the establishment of the colony at Jamestown, Virginia, the first permanent English colonial empire, English settlement in North America, in the early 17th century. He was a leader of the Virginia Colony between September 1608 and August 1609, and he led an exploration along the rivers of Virginia and the Chesapeake Bay, during which he became the first English explorer to map the Chesapeake Bay area. Later, he explored and mapped the coast of New England. Jamestown was established on May 14, 1607. Smith trained the first settlers to work at farming and fishing, thus saving the colony from early devastation. He publicly stated, "He who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages () are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking. As of 2020, almost all surviving Iroquoian languages are severely or critically endangered, with some languages having only a few elderly speakers remaining. The two languages with the most speakers, Mohawk (Kenien'kéha) in New York and Canada, and Cherokee in Oklahoma and North Carolina, are spoken by less than 10% of the populations of their nations. Family division *Iroquoian **Northern Iroquoian ***(Lake Iroquoian) ****Iroquois Proper (Five Nations) ***** Seneca (severely endangered) ***** Cayuga (severely endangered) ***** Onondaga (severely endangered) *****Susquehannock or Conestoga *****Mohawk–Oneida ****** Oneida (severely endangered) ****** Mohawk ****Huronian ***** Huron-Wyandot ***** Petun (Tobacco) ***Tuscarora–Nottoway **** Tuscarora **** Meherri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siouan
Siouan ( ), also known as Siouan–Catawban ( ), is a language family of North America located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east. Name Authors who call the entire family ''Siouan'' distinguish the two branches as Western Siouan and Eastern Siouan or as "Siouan-proper" and "Catawban". Others restrict the name "Siouan" to the western branch and use the name ''Siouan–Catawban'' for the entire family. Generally, however, the name "Siouan" is used without distinction. Family division The Siouan family consists of some 20 languages and various dialects: * Siouan ** Western Siouan *** Mandan **** Nuptare **** Nuetare *** Missouri River Siouan (a.k.a. Crow–Hidatsa) **** Crow (a.k.a. Absaroka, Apsaroka, Apsaalooke, Upsaroka) – 3,500 speakers **** Hidatsa (a.k.a. Minitari, Minnetaree) – 200 speakers *** Mississippi Valley Siouan (a.k.a. Central Siouan) **** Mitchigamea? **** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territory, and an experience of subjugation and discrimination under a dominant cultural model. Estimates of the population of Indigenous peoples range from 250 million to 600 million. There are some 5,000 distinct Indigenous peoples spread across every inhabited climate zone and inhabited continent of the world. Most Indigenous peoples are in a minority in the state or traditional territory they inhabit and have experienced domination by other groups, especially non-Indigenous peoples. Although many Indigenous peoples have experienced colonization by settlers from European nations, Indigenous identity is not determined by Western colonization. The rights of Indigenous peoples are outlined in national legislation, treaties and international law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomasina Jordan
Thomasina Elizabeth Jordan (Red Hawk Woman) (? – 1999) was an American Indian (Wampanoag) activist who became the first American Indian to serve in the United States Electoral College in 1988. Jordan received bachelor's and master's degrees in fine arts at Bishop Lee College in Boston. She studied at Harvard University, received an educational doctorate from The Catholic University of America, and attended the American Academy of Fine Arts in New York City. She later resided in Alexandria, Virginia, where she was a member of the Alexandria Republican Democratic City Committee. Jordan was appointed Chairperson of the Virginia Council on Indians by Governors George Allen and Jim Gilmore. She also founded the American Indian Cultural Exchange, served on the Board of Directors of Save the Children and the National Rehabilitation Hospital, was president of Chapter I of the Capital Speakers Club, and was a recipient of the Medal of Honor of the National Society of the Daughter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |