|
Mathcamp
Canada/USA Mathcamp is a five-week academic summer program for middle and high school students in mathematics. Mathcamp was founded in 1993 by Dr. George Thomas, who believed that students interested in mathematics frequently lacked the resources and camaraderie to pursue their interest. Mira Bernstein became the director when Thomas left in 2002 to found MathPath, a program for younger students. Mathcamp is held each year at a college campus in the United States or Canada. Past locations have included the University of Toronto, the University of Washington, Colorado College, Reed College, University of Puget Sound, Colby College, the University of British Columbia, Mount Holyoke College, and the Colorado School of Mines. Mathcamp enrolls about 120 students yearly, 45-55 returning and 65-75 new. The application process for new students includes an entrance exam (the "Qualifying Quiz"), personal essay, and two letters of recommendation, but no grade reports. The process is int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summer Camp
A summer camp or sleepaway camp is a supervised program for children conducted during the summer summer vacation, months in some countries. Children and adolescents who attend summer camp are known as ''campers''. Summer school is usually a part of the academic curriculum for a student to make up work not accomplished during the academic year (summer camps can include academic work, but is not a requirement for graduation). The traditional view of a summer camp as a woody place with hiking, canoeing, and campfires is changing, with greater acceptance of newer types of summer camps that offer a wide variety of specialized activities. For example, there are camps for the performing arts, music, magic (illusion), magic, computer programming, language learning, mathematics, children with disability, special needs, and Dieting, weight loss. In 2006, the American Camp Association reported that 75 percent of camps added new programs. This is largely to counter a trend in decreasing enro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathPath
MathPath is a mathematics enrichment summer program for students ages 11–14 (middle school age in the US). It is four weeks long, and moves to a different location each year. MathPath is visited by mathematicians such as John H. Conway and Francis Su. It was probably the original, and is still one of the few, international residential high-end summer camps exclusively for mathematics and exclusively for students of middle school age. History MathPath was founded in 2002 by George Rubin Thomas, who had previously founded Mathcamp for high school students and has since founded Epsiloncamp for children age 7–11 (in 2011, originally aged 8-11) and Delta Camp for children 6 and 7 (in 2014 and 2015, now merged with Epsilon Camp). His goal was to inspire and advance the most mathematically gifted middle school age students, through a summer camp. Subjects At MathPath, students learn about many math topics that are rarely taught in American schools, or taught in much depth, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a ''topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. Basic examples of topological properties are: the dimension, which allows distinguishing between a line and a surface; compactness, which allows distinguishing between a line and a circle; connectedne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Aaronson
Scott Joel Aaronson (born May 21, 1981) is an American theoretical computer scientist and David J. Bruton Jr. Centennial Professor of Computer Science at the University of Texas at Austin. His primary areas of research are quantum computing and computational complexity theory. Early life and education Aaronson grew up in the United States, though he spent a year in Asia when his father—a science writer turned public-relations executive—was posted to Hong Kong. He enrolled in a school there that permitted him to skip ahead several years in math, but upon returning to the US, he found his education restrictive, getting bad grades and having run-ins with teachers. He enrolled in The Clarkson School, a gifted education program run by Clarkson University, which enabled Aaronson to apply for colleges while only in his freshman year of high school. He was accepted into Cornell University, where he obtained his BSc in computer science in 2000, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
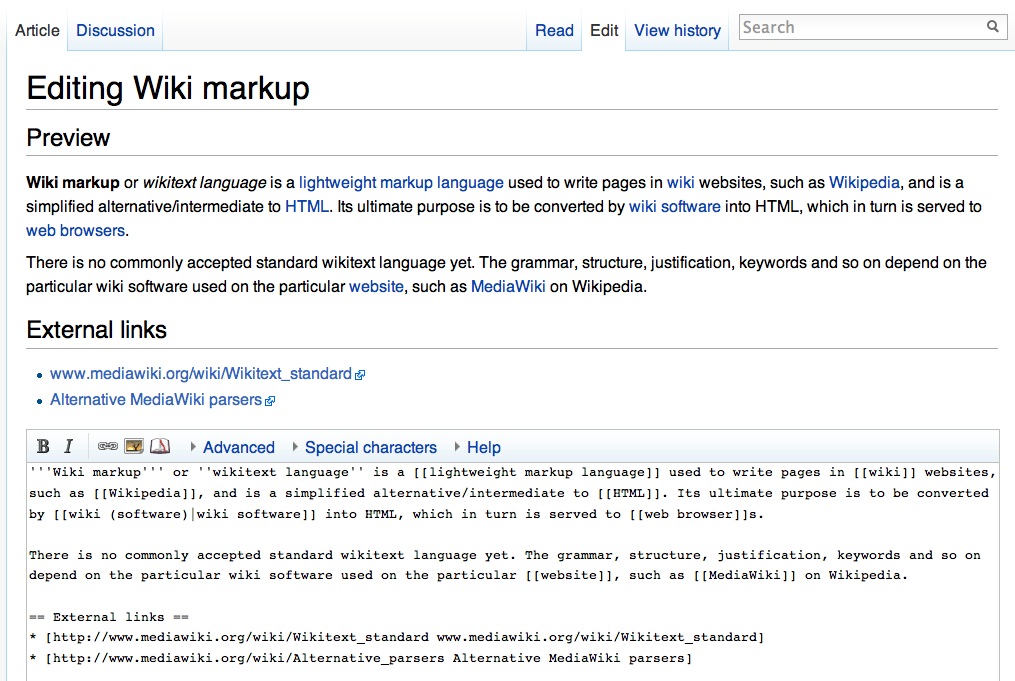
Wiki
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic ( Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells to provide energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth. Different species of animals have different feeding behaviours that satisfy the needs of their unique metabolisms, often evolved to fill a specific ecological niche within specific geographical contexts. Omnivorous humans are highly adaptable and have adapted to obtain food in many different ecosystems. The majority of the food energy required is supplied by the industrial food industry, which produces food with intensive agriculture and distributes it through complex food processing and food distribution systems. This system of conventional agriculture relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the food an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructed Language
A constructed language (sometimes called a conlang) is a language whose phonology, grammar, and vocabulary, instead of having developed naturally, are consciously devised for some purpose, which may include being devised for a work of fiction. A constructed language may also be referred to as an artificial, planned or invented language, or (in some cases) a fictional language. ''Planned languages'' (or engineered languages/engelangs) are languages that have been purposefully designed; they are the result of deliberate, controlling intervention and are thus of a form of ''language planning''. There are many possible reasons to create a constructed language, such as to ease human communication (see international auxiliary language and code); to give fiction or an associated constructed setting an added layer of realism; for experimentation in the fields of linguistics, cognitive science, and machine learning; for artistic creation; and for language games. Some people may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serge Lang
Serge Lang (; May 19, 1927 – September 12, 2005) was a French-American mathematician and activist who taught at Yale University for most of his career. He is known for his work in number theory and for his mathematics textbooks, including the influential ''Algebra''. He received the Frank Nelson Cole Prize in 1960 and was a member of the Bourbaki group. As an activist, Lang campaigned against the Vietnam War, and also successfully fought against the nomination of the political scientist Samuel P. Huntington to the National Academies of Science. Later in his life, Lang was an HIV/AIDS denialist. He claimed that HIV had not been proven to cause AIDS and protested Yale's research into HIV/AIDS. Biography and mathematical work Lang was born in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, close to Paris, in 1927. He had a twin brother who became a basketball coach and a sister who became an actress. Lang moved with his family to California as a teenager, where he graduated in 1943 from Beverly Hills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avi Wigderson
Avi Wigderson ( he, אבי ויגדרזון; born 9 September 1956) is an Israeli mathematician and computer scientist. He is the Herbert H. Maass Professor in the school of mathematics at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, United States of America. His research interests include complexity theory, parallel algorithms, graph theory, cryptography, distributed computing, and neural networks. Wigderson received the Abel Prize in 2021 for his work in theoretical computer science. Biography Avi Wigderson was born in Haifa, Israel, to Holocaust survivors. Wigderson is a graduate of the Hebrew Reali School in Haifa, and did his undergraduate studies at the Technion in Haifa, Israel, graduating in 1980, and went on to graduate study at Princeton University. He received his PhD in computer science in 1983 after completing a doctoral dissertation, titled "Studies in computational complexity", under the supervision of Richard Lipton. After short-term positions at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Horton Conway
John Horton Conway (26 December 1937 – 11 April 2020) was an English mathematician active in the theory of finite groups, knot theory, number theory, combinatorial game theory and coding theory. He also made contributions to many branches of recreational mathematics, most notably the invention of the cellular automaton called the Game of Life. Born and raised in Liverpool, Conway spent the first half of his career at the University of Cambridge before moving to the United States, where he held the John von Neumann Professorship at Princeton University for the rest of his career. On 11 April 2020, at age 82, he died of complications from COVID-19. Early life and education Conway was born on 26 December 1937 in Liverpool, the son of Cyril Horton Conway and Agnes Boyce. He became interested in mathematics at a very early age. By the time he was 11, his ambition was to become a mathematician. After leaving sixth form, he studied mathematics at Gonville and Caius College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, in the United States, an entry-level university student is known as an ''undergraduate'', while students of higher degrees are known as '' graduate students''. Upon completion of a number of required and elective courses as part of an undergraduate program, the student would earn the corresponding degree. (In some regions, individual "courses" and the "program" collection are given other terms, such as "units" and "course", respectively.) In some other educational systems, undergraduate education is postsecondary education up to the level of a master's degree; this is the case for some science courses in Britain and some medicine courses in Europe. Programs Africa Nigerian system In Nigeria, undergraduate degrees (excluding Medicine, Medical Laboratory Science, Nursing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |