|
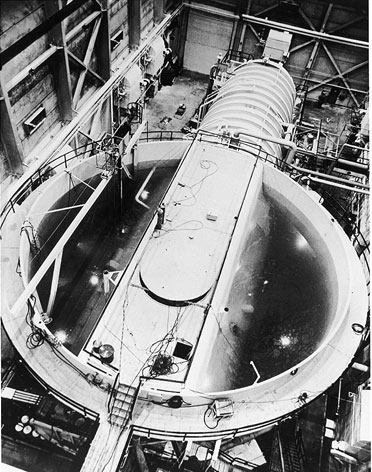
Matched Index Of Refraction Flow Facility
Matched Index of Refraction (or MIR) is a facility located at the Idaho National Laboratory built in the 1990s. The purpose of the fluid dynamics experiments in the MIR flow system at Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is to develop benchmark databases for the assessment of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) solutions of the momentum equations, scalar mixing, and turbulence models for the flow ratios between coolant channels and bypass gaps in the interstitial regions of typical prismatic standard fuel element or upper reflector block geometries of typical Very High Temperature Reactors (VHTR) in the limiting case of negligible buoyancy and constant fluid properties. How It Works MIR uses Doppler Velocimetry to produce a three-dimensional image of a model inside the loop. To do this, the loop circulates about 3500 gallons of semi-transparent mineral oil similar to baby oil. Special quartz models, built to scale, are inserted into the loop near the observation equipment. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idaho National Laboratory
Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is one of the national laboratories of the United States Department of Energy and is managed by the Battelle Energy Alliance. While the laboratory does other research, historically it has been involved with nuclear research. Much of current knowledge about how nuclear reactors behave and misbehave was discovered at what is now Idaho National Laboratory. John Grossenbacher, former INL director, said, "The history of nuclear energy for peaceful application has principally been written in Idaho". Various organizations have built more than 50 reactors at what is commonly called "the Site", including the ones that gave the world its first usable amount of electricity from nuclear power and the power plant for the world's first nuclear submarine. Although many are now decommissioned, these facilities are the largest concentration of reactors in the world. It is on a complex in the high desert of eastern Idaho, between Arco to the west and Idaho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Reactor Core
A nuclear reactor core is the portion of a nuclear reactor containing the nuclear fuel components where the nuclear reactions take place and the heat is generated. Typically, the fuel will be low-enriched uranium contained in thousands of individual fuel pins. The core also contains structural components, the means to both moderate the neutrons and control the reaction, and the means to transfer the heat from the fuel to where it is required, outside the core. Water-moderated reactors Inside the core of a typical pressurized water reactor or boiling water reactor are fuel rods with a diameter of a large gel-type ink pen, each about 4 m long, which are grouped by the hundreds in bundles called "fuel assemblies". Inside each fuel rod, pellets of uranium, or more commonly uranium oxide, are stacked end to end. Also inside the core are control rods, filled with pellets of substances like boron or hafnium or cadmium that readily capture neutrons. When the control rods are low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a '' geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers, so-called as they convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers however convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be categorized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index-matching Material
In optics, an index-matching material is a substance, usually a liquid, cement (adhesive), or gel, which has an index of refraction that closely approximates that of another object (such as a lens, material, fiber-optic, etc.). When two substances with the same index are in contact, light passes from one to the other with neither reflection nor refraction. As such, they are used for various purposes in science, engineering, and art. For example, in a popular home experiment, a glass rod is made almost invisible by immersing it in an index-matched transparent fluid such as mineral spirits. In microscopy In light microscopy, oil immersion is a technique used to increase the resolution of a microscope. This is achieved by immersing both the objective lens and the specimen in a transparent oil of high refractive index, thereby increasing the numerical aperture of the objective lens. Immersion oils are transparent oils that have specific optical and viscosity characteristics necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Tunnel
Wind tunnels are large tubes with air blowing through them which are used to replicate the interaction between air and an object flying through the air or moving along the ground. Researchers use wind tunnels to learn more about how an aircraft will fly. NASA uses wind tunnels to test scale models of aircraft and spacecraft. Some wind tunnels are large enough to contain full-size versions of vehicles. The wind tunnel moves air around an object, making it seem as if the object is flying. Most of the time, large powerful fans suck air through the tube. The object being tested is held securely inside the tunnel so that it remains stationary. The object can be an aerodynamic test object such as a cylinder or an airfoil, an individual component, a small model of the vehicle, or a full-sized vehicle. The air moving around the stationary object shows what would happen if the object was moving through the air. The motion of the air can be studied in different ways; smoke or dye can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere Of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention ( greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation). By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere. Air composition, temperature, and atmospheric pressure vary with altitude. Within the atmosphere, air suitable for use in photosynthesis by terrestrial plants and breathing of terrestrial animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baby Oil
Baby oil is, in general terms, an inert oil for the purpose of keeping skin soft and supple. It is often used on babies for the purpose of maintaining "baby-soft" skin, but it is also often used by adults for skincare and massage. The skin of an infant, especially a premature one, is sensitive, thin and fragile. The skin's neutral pH on the surface significantly reduces the protection against excessive bacterial growth. The epidermis and dermis are thinner than those of adults and the epidermal barrier is not yet fully developed. Consequences can for example be dry skin, infections, peeling, blister formation and poor thermoregulation. The application of different oils to the skin of the newborn is routinely practiced in many countries. In general, these oils are used for cleansing, to maintain the skin's moisture and to protect its surface. Additionally, baby oil is used for the massage of newborns and as additive in lotions and creams. Ingredients Baby oils can be cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids—liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including '' aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)