|
Maruia River
The Maruia River is located in the northwestern South Island of New Zealand. It is a major tributary of the Buller River, flowing for 80 km before joining the larger river eight kilometres to the west of Murchison, New Zealand, Murchison. The Maruia River rises in the Spenser Mountains, travelling first to the southwest before turning north for the last 50 km of its length. In its upper reaches, the river's valley forms the western approach to the Lewis Pass, the northernmost of the three main mountain passes across the Southern Alps (New Zealand), Southern Alps. Hot springs are to be found close to the river in its upper reaches, and the spa of Maruia Springs is located five kilometres to the west of the Lewis Pass, 50 km southeast of Reefton, New Zealand, Reefton. 3 km east of Springs Junction, the Maruia River flows through the deep and narrow Sluice Box gorge. The river cuts through a band of marble amongst the otherwise predominant greywacke. The Sluice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (Layered intrusion, layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. The extraction of marble is performed by quarrying. Marble production is dominated by four countries: China, Italy, India and Spain, which account for almost half of world production of marble and decorative stone. Because of its high hardness and strong wear resistance, and because it will not be deformed by temperature, marble is often used in Marble sculpture, sculpture and construction. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of The West Coast Region
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buller District
Buller District is one of 53 districts of New Zealand, and is within the West Coast Region. It covers Westport, Karamea, Reefton and Inangahua Junction. Buller District's overall land area is . The district is administered by the Buller District Council with the seat in Westport, in which 45% of the district's population live. History It is understood by the carbon dating of umu (ovens) that the Māori people settled in this region some 700 years ago. The district takes its name from the Buller River, itself named for Charles Buller, a Member of Parliament in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (UK) and director of the New Zealand Company, a UK-based company established in the early 19th century with a royal charter supporting colonisation efforts of New Zealand. During the period 1853 to 1876, the current area of Buller District was administered as part of Nelson Province. With the Abolition of Provinces Act 1876, much of the current area of Buller Distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1929 Murchison Earthquake
The 1929 Murchison earthquake occurred at 10:17 am on 17 June. It struck the Murchison region of the South Island, with an estimated magnitude of 7.3, and was felt throughout New Zealand. There were 17 deaths, mostly as a result of landslides triggered by the earthquake. The rumbling sound of the earthquake was loud enough to be heard at New Plymouth, more than 250 km (155 mi) away. Tectonic setting New Zealand sits astride the boundary between the Indo-Australian plate and the Pacific plate. In the South Island most of the displacement is taken up on the Alpine Fault passing to the north onto a set of strike-slip faults, the Marlborough fault system. The sense of displacement across the plate boundary is oblique and most of the faults have a reverse component of slip. Some of the resulting deformation is accommodated within the plates themselves away from the boundary. The 1929 Murchison earthquake occurred on the White Creek Fault, located in the Buller Gor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maruia Falls 28
Maruia is a locality in the West Coast region of New Zealand. The Shenandoah Highway (State Highway 65) passes through it. Murchison is 65 km north, the Lewis Pass is 39 km to the south-east, and Reefton is 63 km west by road. The Maruia River flows past to the west. According to the 2013 New Zealand census The 2013 New Zealand census was the thirty-third national census. "The National Census Day" used for the census was on Tuesday, 5 March 2013. The population of New Zealand was counted as 4,242,048 – an increase of 214,101 or 5.3% over the 20 ..., Maruia and its surrounds have a population of 183, an increase of 9 people since the 2006 census. There were 96 males and 87 females. The principal activity is dairy farming. The community celebrated 100 years of settlement in the Maruia Valley in 2005. The Maruia Valley inspired the environmental lobby group, the Maruia Society (later changing its name to the Ecologic Foundation) and the Maruia Mail Order C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:Department Of Conservation (New Zealand)
The Department of Conservation (DOC; Māori: ''Te Papa Atawhai'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with the conservation of New Zealand's natural and historical heritage. An advisory body, the New Zealand Conservation Authority (NZCA) is provided to advise DOC and its ministers. In addition there are 15 conservation boards for different areas around the country that provide for interaction between DOC and the public. Functions and history Overview The department was formed on 1 April 1987, as one of several reforms of the public service, when the ''Conservation Act 1987'' was passed to integrate some functions of the Department of Lands and Survey, the Forest Service and the Wildlife Service. This act also set out the majority of the department's responsibilities and roles. As a consequence of Conservation Act all Crown land in New Zealand designated for conservation and protection became managed by the Department of Conservation. This is about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
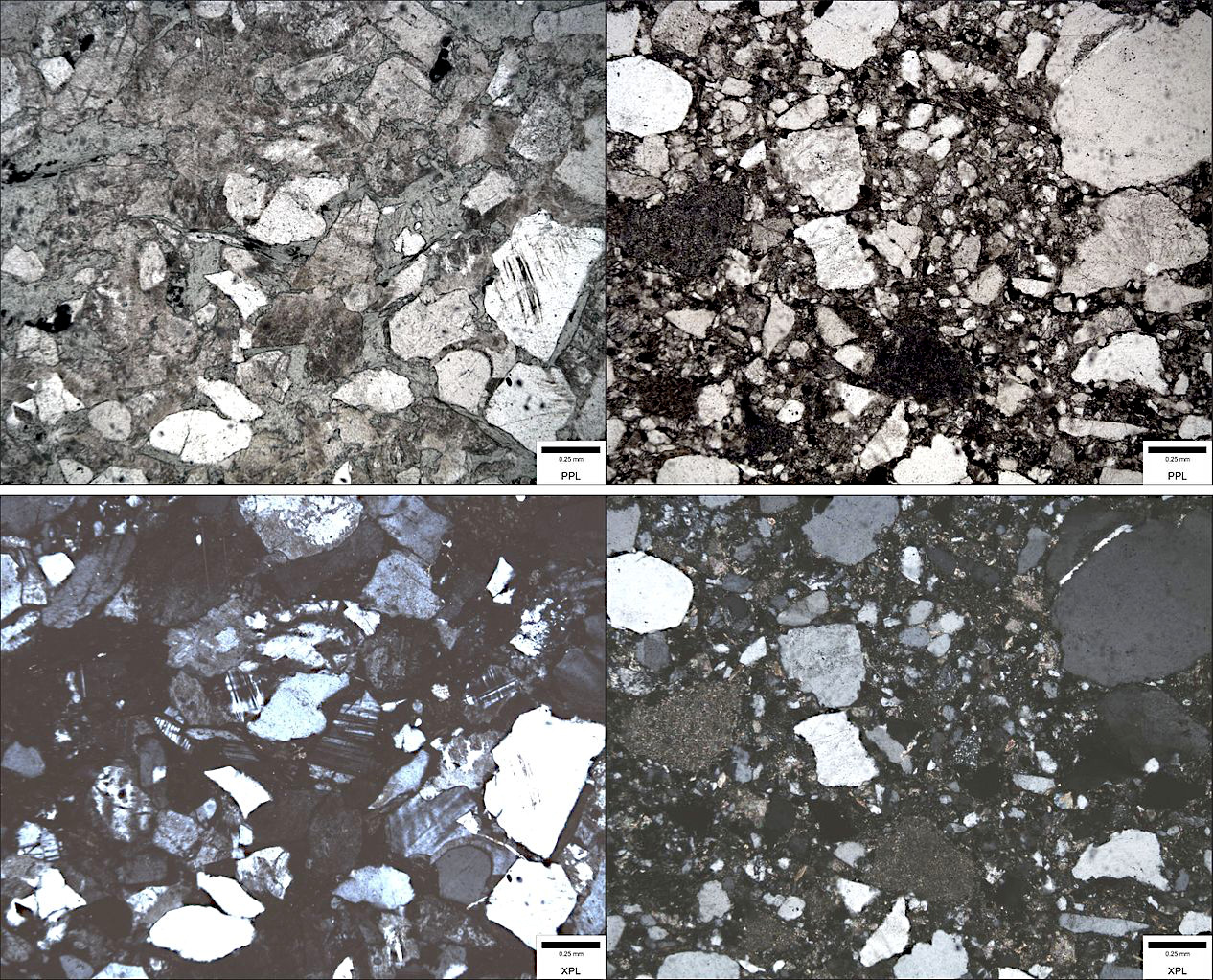
Greywacke
Greywacke or graywacke ( ) is a variety of sandstone generally characterized by its hardness (6–7 on Mohs scale), dark color, and Sorting (sediment), poorly sorted angular grains of quartz, feldspar, and small rock fragments or sand-size Lithic fragment (geology), lithic fragments set in a compact, clay-fine matrix. It is a texturally immature sedimentary rock generally found in Paleozoic Stratum, strata. The larger Particle size (grain size), grains can be sand- to gravel-sized, and Matrix (geology), matrix materials generally constitute more than 15% of the rock by volume. Formation The origin of greywacke was unknown until turbidity currents and turbidites were understood, since, according to the normal laws of sedimentation, gravel, sand and mud should not be laid down together. Geologists now attribute its formation to submarine avalanches or strong turbidity currents. These actions churn sediment and cause mixed-sediment slurries, in which the resulting deposits may ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reefton, New Zealand
Reefton is a small town in the West Coast region of New Zealand, approximately northeast of Greymouth, in the Inangahua River valley. Ahaura is south-west of Reefton, Inangahua Junction is to the north, Maruia is to the east, and the Lewis Pass is to the south-east. In 1888, it was the first town in New Zealand to be lit by electricity, generated by the Reefton Power Station. Reefton was a thriving gold mining town in the late 19th century, and gold mining lasted from the 1870s to the 1950s. Its economy is based on tourism, forestry, coal mining, and farming. Reefton is home to the Inangahua County Library. Name The rich veins of gold found in a quartz reef near the town led to its name, originally spelled "Reef Town". Two nicknames in use soon after it was founded were "Rest Town" and "Quartzopolis". The main street, Broadway, was named after West Coast magistrate Charles Broad. The nearby Wealth of Nations mine was named after Adam Smith's book because the gold been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the List of islands by area, world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The most populous cities are Christchurch, Dunedin, Nelson, New Zealand, Nelson and Invercargill. Prior to European settlement, Te Waipounamu was sparsely populated by three major iwi – Kāi Tahu, Kāti Māmoe, and the historical Waitaha (South Island iwi), Waitaha – with major settlements including in Kaiapoi Pā near modern-day Christchurch. During the Musket Wars expanding iwi colonised Te Tau Ihu Māori, Te Tau Ihu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maruia Springs
Maruia Springs is a settlement in the West Coast, New Zealand, West Coast Region of New Zealand's South Island. It is located on the south bank of the Maruia River on State Highway 7 (New Zealand), State Highway 7 to the west of the Lewis Pass. The settlement is named for the nearby hot springs. While not as commercially exploited as other southern hot water springs (such as those at Hanmer Springs) it is still a popular spot with visitors.Sabin, B.,Maruia Hot Springs: Inside New Zealand's hidden mountain hot springs" ''wwww.stuff.co.nz'', 1 March 2021. Retrieved 11 December 2021. Water at , or more, is pumped from springs and from a well to a hotel, Japanese bath house, six private spas and two rock pools. The hot spring is probably fed through the nearby Awatere Fault. The hot pools at Maruia have been known to Māori people for hundreds of years and used by jade traders as a place to rest and rejuvenate on their gruelling walk over to the West Coast. In the late 1800s, Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |