|
Marsupialization
400px, Marsupialization Marsupialization is the surgical technique of cutting a slit into an abscess or cyst and suturing the edges of the slit to form a continuous surface from the exterior surface to the interior surface of the cyst or abscess. Sutured in this fashion, the site remains open and can drain freely. This technique is used to treat a cyst or abscess when a single draining would not be effective and complete removal of the surrounding structure would not be desirable. The technique is often applied to Gartner's duct cysts, pancreatic cysts, pilonidal cysts, and Bartholin's cysts. In the case of a dentigerous cyst A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in ..., marsupialization may be performed to allow the growing tooth associated with the cyst to continue e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bartholin's Cyst
A Bartholin's cyst occurs when a Bartholin's gland within the labia becomes blocked. Small cysts may result in minimal or no symptoms. Larger cysts may result in swelling on one side of the vaginal opening, as well as pain during sex or walking. If the cyst becomes infected, an abscess can occur, which is typically red and very painful. If there are no symptoms, no treatment is needed. Bartholin's cysts affect about 2% of women at some point in their life. They most commonly occur during childbearing years. When the cyst becomes uncomfortable or painful, drainage is recommended. The preferred method is the insertion of a Word catheter for four weeks, as recurrence following simple incision and drainage is common. A surgical procedure known as marsupialization may be used or, if the problems persist, the entire gland may be removed. Removal is sometimes recommended in those older than 40 to ensure cancer is not present. Antibiotics are not generally needed to treat a Bartholin's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupialization التوخيف تقنية جراحية لقطع شق في خراج أو كيس وخياطة حوافه
400px, Marsupialization Marsupialization is the surgical technique of cutting a slit into an abscess or cyst and suturing the edges of the slit to form a continuous surface from the exterior surface to the interior surface of the cyst or abscess. Sutured in this fashion, the site remains open and can drain freely. This technique is used to treat a cyst or abscess when a single draining would not be effective and complete removal of the surrounding structure would not be desirable. The technique is often applied to Gartner's duct cysts, pancreatic cysts, pilonidal cysts, and Bartholin's cysts. In the case of a dentigerous cyst A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in ..., marsupialization may be performed to allow the growing tooth associated with the cyst to continue er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
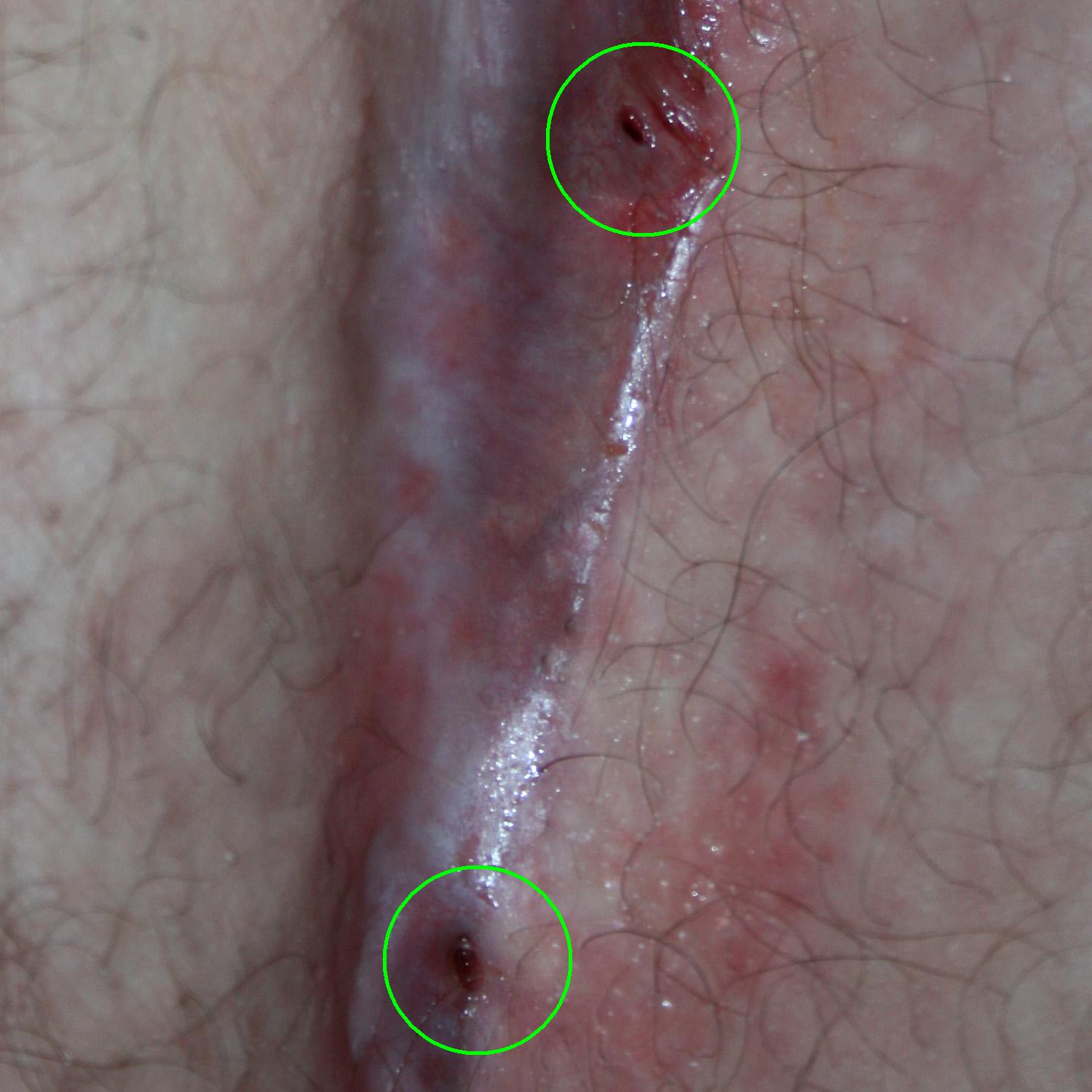
Pilonidal Cyst
Pilonidal disease is a type of skin infection that typically occurs as a cyst between the cheeks of the buttocks and often at the upper end. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and redness. There may also be drainage of fluid, but rarely a fever. Risk factors include obesity, family history, prolonged sitting, greater amounts of hair, and not enough exercise. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve a mechanical process where hair and skin debris get sucked into the subcutaneous tissues through skin openings called pits. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. If there is an infection, treatment is generally by incision and drainage just off the midline. Shaving the area and laser hair removal may prevent recurrence. More extensive surgery may be required if the disease recurs. Antibiotics are usually not needed. Without treatment, the condition may remain long-term. About 3 per 10,000 people per year are affected, and it occurs more often in males than fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. A cyst is related to an abscess, but it contains a material other than pus, and a cyst has a clearly defined wall. Abscesses can also form internally on internal organs and after surgery. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is ''methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartner's Duct Cyst
A Gartner's duct cyst (sometimes incorrectly referred to as ''vaginal inclusion cyst'') is a benign vaginal cyst that originates from the Gartner's duct, which is a vestigial remnant of the mesonephric duct (Wolffian duct) in females. They are typically small asymptomatic cysts that occur along the lateral walls of the vagina, following the course of the duct. They can present in adolescence with painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea) or difficulty inserting a tampon. They can also enlarge to substantial proportions and be mistaken for urethral diverticulum or cystocele. In some rare instances, they can be congenital. There is a small association between Gartner's duct cysts and metanephric urinary anomalies, such as ectopic ureter and ipsilateral renal hypoplasia. Symptoms of a Gartner's duct cyst include: infections, bladder dysfunction, abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, and urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontroll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. Ninety-nine percent of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentigerous Cyst
A dentigerous cyst, also known as a follicular cyst, is an epithelial-lined developmental cyst formed by accumulation of fluid between the reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. It is formed when there is an alteration in the reduced enamel epithelium and encloses the crown of an unerupted tooth at the cemento-enamel junction. Fluid is accumulated between reduced enamel epithelium and the crown of an unerupted tooth. Dentigerous cysts are the second most prevalent type of odontogenic cysts after radicular cyst. Seventy percent of the cases occur in the mandible. Dentigerous cysts are usually painless. The patient usually comes with a concern of delayed tooth eruption or facial swelling. A dentigerous cyst can go unnoticed and may be discovered coincidentally on a regular radiographic examination. Pathogenesis Odontogenesis happens by means of a complex interaction between oral epithelium and surrounding mesenchymal tissue. Abnormal tissue interaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |