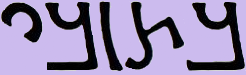|
Maronite Patriarch
This is a list of the Maronite patriarchs of Antioch and all the East, the primate of the Maronite Church, one of the Eastern Catholic Churches. Starting with Paul Peter Massad in 1854, after becoming patriarch of the Maronite Catholic Patriarchate of Antioch, they assume the name "Peter" (Boutros in Arabic, بطرس), after the traditional first Bishop of Antioch, St. Peter, who was also the head of the Apostles. The official title that the Maronite Patriarch assumes is "Patriarch of Antioch and All the East". To this date 15 patriarchs have been canonized by the Catholic Church, with an extra two being beatified but not yet canonized. For the Patriarchs of Antioch before John Maron, see List of Patriarchs of Antioch. List of Patriarchs of Antioch and all the Levant of the Maronite Church A famous list of Maronite Patriarchs of Antioch was written and published by Giuseppe Simone Assemani,J.S.Assemani ''Serie chronologica Patriarchorum Antionchiae'', edited and integrated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate (bishop)
Primate () is a title or rank bestowed on some important archbishops in certain Christian churches. Depending on the particular tradition, it can denote either jurisdictional authority ( title of authority) or (usually) ceremonial precedence ( title of honour). Catholic Church In the Latin Church, a primate is an archbishop—or, rarely, a suffragan or exempt bishop—of a specific (mostly metropolitan) episcopal see (called a ''primatial see'') who has precedence over the bishoprics of one or more ecclesiastical provinces of a particular historical, political or cultural area. Historically, primates of particular sees were granted privileges including the authority to call and preside at national synods, jurisdiction to hear appeals from metropolitan tribunals, the right to crown the sovereign of the nation, and presiding at the investiture (installation) of archbishops in their sees. The office is generally found only in older Catholic countries, and is now purel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodion Of Antioch
Herodion of Antioch or ''Heron'' (died 136 AD) was a 2nd-century Christian martyr and Bishop of Antioch, successor of Ignatius Ignatius is a male given name and a surname. Notable people with the name include: Given name Religious * Ignatius of Antioch (35–108), saint and martyr, Apostolic Father, early Christian bishop * Patriarch Ignatius of Constantinople, Ignati ... at Antioch, a title he held for two decades. Notes and references 136 deaths Saints from Roman Syria 2nd-century Christian martyrs Year of birth unknown {{Saint-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucian Of Antioch
Lucian of Antioch (Greek: Λουκιανός Αντιοχείας c. 240 – January 7, 312), known as Lucian the Martyr, was a Christian presbyter, theologian and martyr. He was noted for both his scholarship and ascetic piety. History According to Suidas, Lucian was born at Samosata, Kommagene, Syria, to Christian parents, and was educated in the neighbouring city of Edessa, Mesopotamia, at the school of Macarius. However, this tradition might be due to a conflation with his famous namesake, Lucian of Samosata, the pagan satirist of the second century. At Antioch, Lucian was ordained presbyter. Eusebius of Caesarea notes his theological learning and Lucian's vita (composed after 327) reports that he founded a ''Didaskaleion'', a school. Scholars following Adolf von Harnack see him as the first head of the School of Antioch, with links to later theologians Diodorus of Tarsus and Theodore of Mopsuestia, but that contention is unrecorded in the extant sources. After the depos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
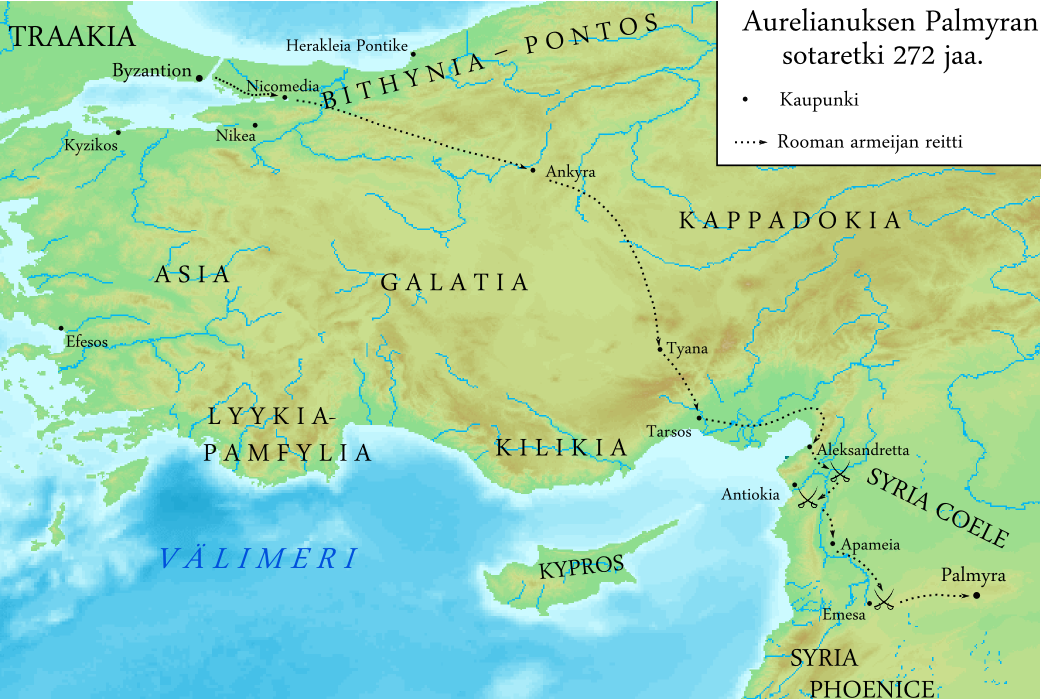
Aurelian
Aurelian (; ; 9 September ) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 270 to 275 AD during the Crisis of the Third Century. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited the Roman Empire after it had nearly disintegrated under the pressure of barbarian invasions and internal revolts. Born in modest circumstances, most likely in Moesia, Moesia Superior, he entered the Roman army in 235 and climbed up the ranks. He went on to lead the cavalry of the emperor Gallienus, until Gallienus' Gallienus#Assassination, assassination in 268. Following that, Claudius Gothicus became emperor until his own death in 270. Claudius' brother Quintillus then ruled for three months, before Aurelian took the empire for himself. Aurelian was chosen Roman emperor by the Illyrians, Illyriciani as one of themselves. During his reign, he defeated the Alamanni after a devastating war. He also defeated the Goths, Vandals, Juthungi, Sarmatians, and Carpi (people), Carpi. Aurelian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zenobia
Septimia Zenobia (Greek: Ζηνοβία, Palmyrene Aramaic: , ; 240 – c. 274) was a third-century queen of the Palmyrene Empire in Syria. Many legends surround her ancestry; she was probably not a commoner, and she married the ruler of the city, Odaenathus. Her husband became king in 260, elevating Palmyra to supreme power in the Near East by defeating the Sasanian Empire of Persia and stabilizing the Roman East. After Odaenathus' assassination, Zenobia became the regent of her son Vaballathus and held de facto power throughout his reign. In 270, Zenobia launched an invasion that brought most of the Roman East under her sway and culminated with the annexation of Egypt. By mid-271 her realm extended from Ancyra, central Anatolia, to Upper Egypt, although she remained nominally subordinate to Rome. However, in reaction to the campaign of the Roman emperor Aurelian in 272, Zenobia declared her son emperor and assumed the title of empress, thus declaring Palmyra's secession f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Of Samosata
Paul of Samosata (, lived from 200 to 275) was patriarch of Antioch from 260 to 268 and the originator of the Paulianist heresy named after him. He was a believer in monarchianism, a nontrinitarian doctrine; his teachings reflect adoptionism. Life Paul was born at Samosata into a family of humble origin. He was elected patriarch of Antioch in 260. He held the civil office of Procurator ducenarius. His Monarchianist teachings aroused strong opposition in the church. He was also accused of corruption on a grand scale. Edward Gibbon describes him as follows: The wealth of that prelate was a sufficient evidence of his guilt since it was neither derived from the inheritance of his fathers nor acquired by the arts of honest industry. But Paul considered the service of the church as a very lucrative profession. His ecclesiastical jurisdiction was venal and rapacious; he extorted frequent contributions from the most opulent of the faithful and converted to his own use a considera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shapur I
Shapur I (also spelled Shabuhr I; ) was the second Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nusaybin, Nisibis and Harran, Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III (), the following year he was able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab () to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty". Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrius Of Antioch
Demetrius of Antioch was patriarch of Antioch in the 3rd century AD. In 253 he was taken to Persia as a captive by Shapur I, where he became the first bishop of Gundeshapur. Despite being far from his original see, Demetrius was not replaced as patriarch of Antioch until Paul of Samosata became Patriarch in 260.Gillman, Ian and Hans-Joachim Klimkeit; ''Christians in Asia before 1500'', (Ann Arbor, University of Michigan Press The University of Michigan Press is a university press that is a part of Michigan Publishing at the University of Michigan Library. It publishes 170 new titles each year in the humanities and social sciences. Titles from the press have earn ..., 1999), p. 30 Notes and references Bibliography * Christians in the Sasanian Empire Ancient Roman prisoners of war People of ancient Roman descent Christians in the Roman Empire 3rd-century bishops in Roman Anatolia {{Bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decius
Gaius Messius Quintus Trajanus Decius ( 201June 251), known as Trajan Decius or simply Decius (), was Roman emperor from 249 to 251. A distinguished politician during the reign of Philip the Arab, Decius was proclaimed emperor by his troops after putting down a rebellion in Moesia. In 249, he defeated and killed Philip Battle of Verona (249), near Verona and was recognized as emperor by the Roman Senate, Senate afterwards. During his reign, he attempted to strengthen the Roman state and its religion, leading to the Decian persecution, where a number of prominent Christians (including Pope Fabian) were put to death. In the last year of his reign, Decius co-ruled with his son Herennius Etruscus, until they were both killed by the Goths in the Battle of Abritus. Early life and rise to power Trajanus Decius was born Gaius Messius Quintus Decius Valerinus at Budalia, Illyricum (Roman province), Illyricum, near Sirmium in Pannonia Inferior.Lesley Adkins, Rot A. Adkins (2004). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Babylas
Babylas of Antioch (, from ; ; died 253) was a Syrian patriarch of Antioch (237–253), who died in prison during the Decian persecution. In the Eastern Orthodox Church and Eastern Catholic Churches of the Byzantine rite his feast day is 4 September, in the Roman Rite, 24 January. He has the distinction of being the first saint recorded as having had his remains moved or " translated" for religious purposes; a practice that was to become extremely common in later centuries. Life Babylas was the successor of Zebinnus as Bishop of Antioch in the reign of the Emperor Gordian III (238–244), being the twelfth bishop of the see. During the Decian persecution (250) he made an unwavering confession of faith and was thrown into prison where he died from his sufferings. He was, therefore, venerated as a martyr.Kirsch, Johann Peter"St. Babylas" Catholic Encyclopedia, Vol. 2, New York, Robert Appleton Company, 1907, 12 February 2014. John Chrysostom's homily upon Babylas and the '' Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
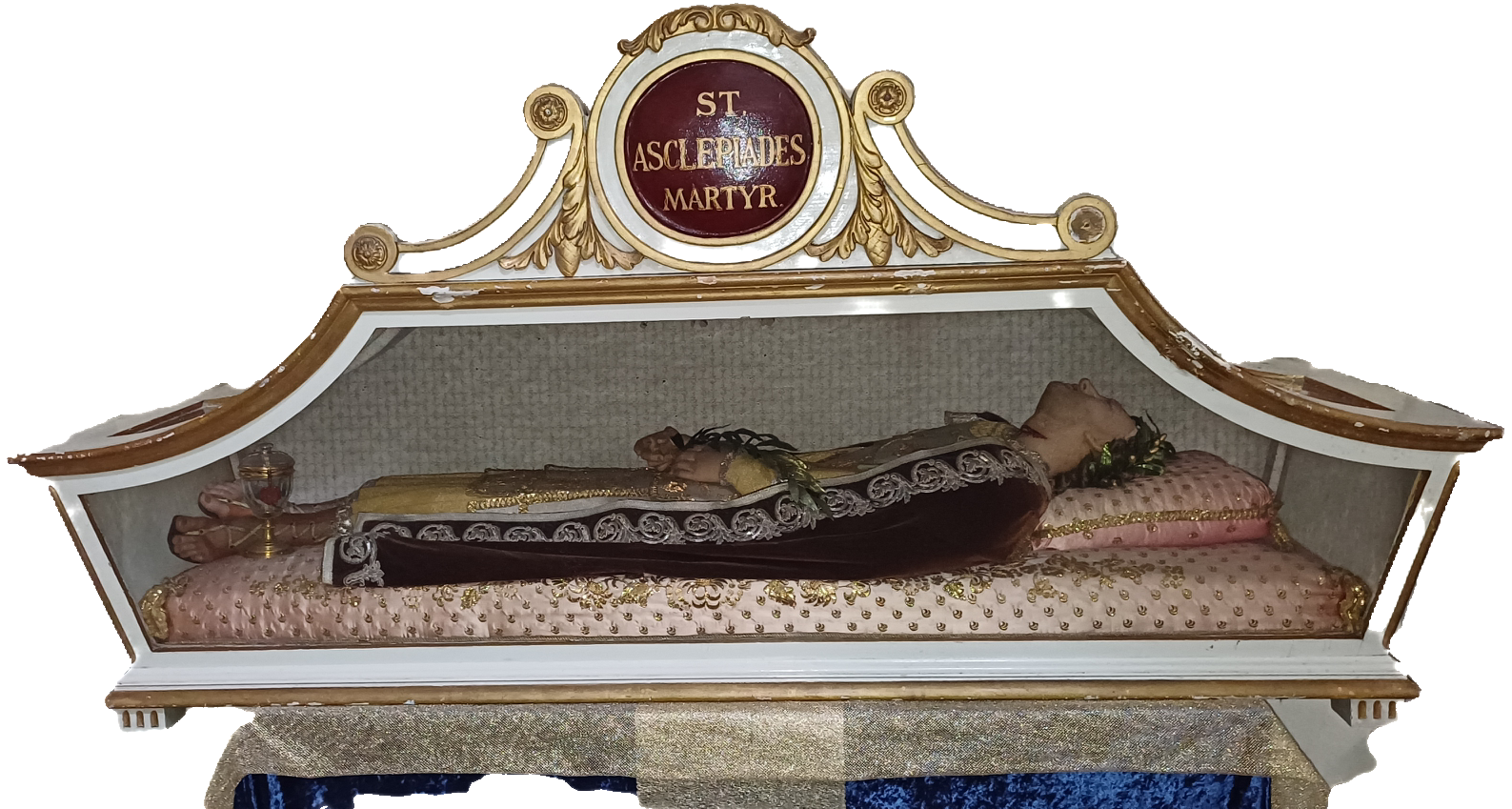
Asclepiades Of Antioch
Asclepiades of Antioch (, also: ''Aslipiades'' or ''Askelpiades'' - † ) called the Confessor, was Patriarch of Antioch from 211 until his death. He succeeded Serapion as Patriarch of Antioch in 211. He was given the title of martyr, due to the trials he endured during Roman persecution. Catholic Online states that his term of office began in the first year of Roman emperor 's reign so that 212 is usually given as the year in which Asclepiades took office. Harnack, referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serapion Of Antioch
Serapion of Antioch was a Patriarch of Antioch ( Greek: Σεραπίων; 191–211). He is known primarily through his theological writings, although all but a few fragments of his works have perished. His feast day is celebrated on 30 October. Serapion was considered one of the chief theologians of his era. Eusebius refers to three works of Serapion in his history, but admits that others probably existed: first is a private letter addressed to Caricus and Pontius against Montanism, from which Eusebius quotes an extract ('' Historia ecclesiastica'' V, 19), as well as ascriptions showing that it was circulated amongst bishops in Asia and Thrace; next is a work addressed to a certain Domninus, who in time of persecution abandoned Christianity for the error of "Jewish will-worship" (''Hist. Eccles'', VI, 12). Lastly, Eusebius quotes (vi.12.2) from a pamphlet Serapion wrote concerning the Docetic '' Gospel of Peter'', in which Serapion presents an argument to the Christian commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |