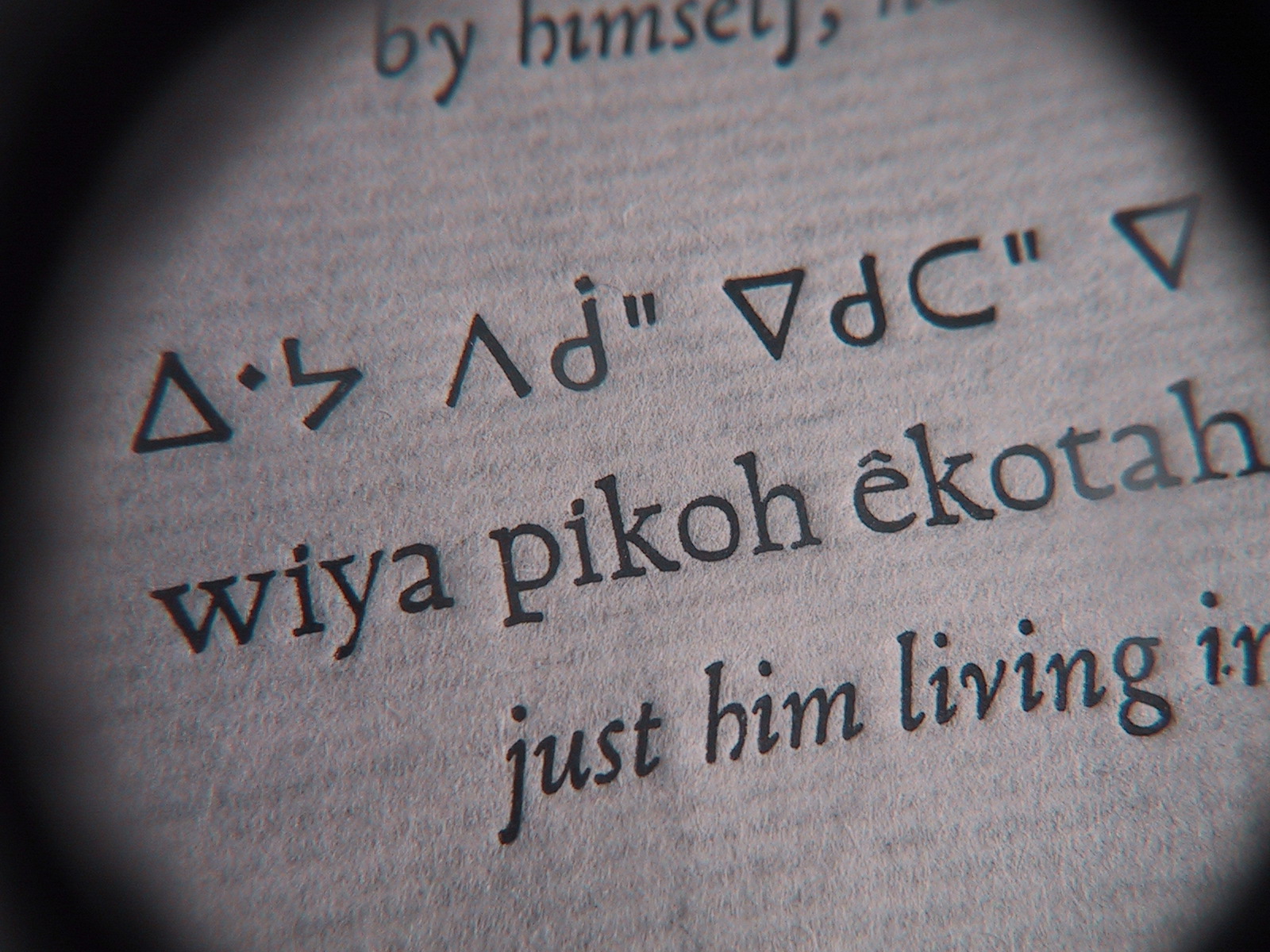|
Marmaduke Johnson
Marmaduke Johnson (1628 – December 25, 1674) was a London printer who was commissioned and sailed from England to Massachusetts Bay Colony in 1660 to assist Samuel Green in the printing of '' The Indian Bible'', which had been laboriously translated by John Eliot into the Massachusett Indian language, Franklin V., 1980, p. 303 which became the first Bible printed in America. Byington, 1899, p. 251 Adams, 1847, p. 241 Johnson is considered the first master printer to emerge in America. When he attempted to operate his own privately owned printing house in Boston, without an official license from the Crown, the Massachusetts General Court interceded and censured his operation, which in turn started one of the first 'Freedom of the Press' issues in colonial America. Littlefield, 1900, p. 89 After several appeals the Court conceded, where Johnson moved to Boston, set up and outfitted his printing shop, and ultimately became the first printer in America allowed to operate his own pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothwell, West Yorkshire
Rothwell is a town in the south-east of the City of Leeds metropolitan borough in West Yorkshire, England. It is situated between Leeds and Wakefield. It is in the Rothwell ward of Leeds City Council and Elmet and Rothwell parliamentary constituency. Rothwell is part of the West Yorkshire Urban Area. Rothwell had a population of 21,010 in the 2001 census, and the Rothwell ward has an estimated population of 32,365. At the 2011 census the ward had a population of 20,354. The town is close to the A1/ M1 link road and the Stourton park and ride. The nearest railway station is Woodlesford. History Rothwell was mentioned in the Domesday Book as ''"Rodewelle"''. One of the royal lodge's documented owners was John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, who is supposed to have killed the last wild boar in England while hunting nearby; hence a boar's head formed part of the arms of the former Rothwell Urban District Council. The parish church (Church Street) is dedicated to Holy Trini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
, mottoeng = Literal: From here, light and sacred draughts. Non literal: From this place, we gain enlightenment and precious knowledge. , established = , other_name = The Chancellor, Masters and Scholars of the University of Cambridge , type = Public research university , endowment = £7.121 billion (including colleges) , budget = £2.308 billion (excluding colleges) , chancellor = The Lord Sainsbury of Turville , vice_chancellor = Anthony Freeling , students = 24,450 (2020) , undergrad = 12,850 (2020) , postgrad = 11,600 (2020) , city = Cambridge , country = England , campus_type = , sporting_affiliations = The Sporting Blue , colours = Cambridge Blue , website = , logo = University of Cambridge log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa2007
Costa may refer to: Biology * Rib (Latin: ''costa''), in vertebrate anatomy * Costa (botany), the central strand of a plant leaf or thallus * Costa (coral), a stony rib, part of the skeleton of a coral * Costa (entomology), the leading edge of the forewing of winged insects, as well as a part of the male clasper Organisations * Costa Coffee, a British coffee shop chain, sponsor of the book award * Costa Cruises, a leading cruise company in Europe * Costa Del Mar, an American manufacturer of polarized sunglasses * Costa Group, Australian food supplier Places * Costa, Haute-Corse, a commune on the island of Corsica *Costa Head, prominent headland on the Orkney Islands * Costa Rica, a country in Central America * Costa Mesa, California, a city in Orange County * Costa, Lajas, Puerto Rico, a barrio Other uses * Costa (surname), including origin of the name and people sharing the surname * ''Costa!'', a 2001 Dutch film from BNN * Costa Book Awards, formerly the Whitbread Book Aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algic Languages
The Algic languages (also Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok or Algonquian–Ritwan) are an indigenous language family of North America. Most Algic languages belong to the Algonquian subfamily, dispersed over a broad area from the Rocky Mountains to Atlantic Canada. The other Algic languages are the Yurok and Wiyot of northwestern California, which, despite their geographic proximity, are not closely related. All these languages descend from Proto-Algic, a second-order proto-language estimated to have been spoken about 7,000 years ago and reconstructed using the reconstructed Proto-Algonquian language and the Wiyot and Yurok languages. History The term ''Algic'' was first coined by Henry Schoolcraft in his ''Algic Researches'', published in 1839. Schoolcraft defined the term as "derived from the words Allegheny and Atlantic, in reference to the indigenous people anciently located in this geographical area." Schoolcraft's terminology was not retained. The peoples he calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipmuc
The Nipmuc or Nipmuck people are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who historically spoke an Eastern Algonquian language. Their historic territory Nippenet, "the freshwater pond place," is in central Massachusetts and nearby parts of Connecticut and Rhode Island. The Nipmuc had sporadic contact with traders and fishermen from Europe prior to the colonization of the Americas. The first recorded contact with Europeans was in 1630, when John Acquittamaug (Nipmuc) took maize to sell to the starving colonists of Boston, Massachusetts. The colonists carried diseases, such as smallpox, to which the Native Americans had no immunity, and tribes in New England suffered high mortality rates to these infectious diseases. After the colonists encroached on their land, negotiated fraudulent land sales and introduced legislation designed to encourage further European settlement, many Nipmuc joined Metacomet's war against colonial expansion- known as King Philip's War- in 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Printer
James Printer, also known as Wowaus, (1640–1709) was a Native American from the Nipmuc tribe who studied and worked as a printer in Cambridge, Massachusetts. He was one of the most famous early Nipmuc writers. Printer was the first Native American printer's devil in America as well as one of John Eliot's most accomplished interpreters who assisted in the creation of the Eliot Indian Bible. Early life Little is known of Printer's early years. Printer was born in the Indian Praying town of Hassanamesit near what is now Grafton, Massachusetts. He was the son of Naoas. Naoas was a convert of John Eliot and a leading member of the Christian Native church in Hassanamesit. Education Printer attended Harvard's Indian College beginning in 1659. He worked as an apprentice to Samuel Green at his printing press. Through his apprenticeship he became an accomplished typesetter and he pursued a printing career for most of his life. He lived and worked among the English for nearly his entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquian Languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically similar Algonquin dialect of the Indigenous Ojibwe language (Chippewa), which is a senior member of the Algonquian language family. The term ''Algonquin'' has been suggested to derive from the Maliseet word (), "they are our relatives/allies". A number of Algonquian languages are considered extinct languages by the modern linguistic definition. Speakers of Algonquian languages stretch from the east coast of North America to the Rocky Mountains. The proto-language from which all of the languages of the family descend, Proto-Algonquian, was spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago. There is no scholarly consensus about where this language was spoken. Family division This subfamily of around 30 languages is divided into three groups acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |